| Download the amazing global Makindo app: Android | Apple | |
|---|---|
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: Educational use only. Not for diagnosis or management. See below for full disclaimer. |
Alkaptonuria
|Adult Onset Still's Disease |Alkaptonuria🧬 Alkaptonuria is a rare autosomal recessive metabolic disorder. It leads to accumulation of homogentisic acid → dark pigmentation of connective tissues (ochronosis) + early arthritis. Classically: urine that darkens on standing! ⚗️
ℹ️ About
- Autosomal recessive inherited cause of arthritis.
- Dark pigmentation of cartilage and connective tissues = Ochronosis.
⚙️ Aetiology
- Deficiency of homogentisic acid oxidase.
- Enzyme encoded on chromosome 3q.
- Accumulated homogentisic acid binds collagen → tissue fragility and degeneration.
👩⚕️ Clinical Features
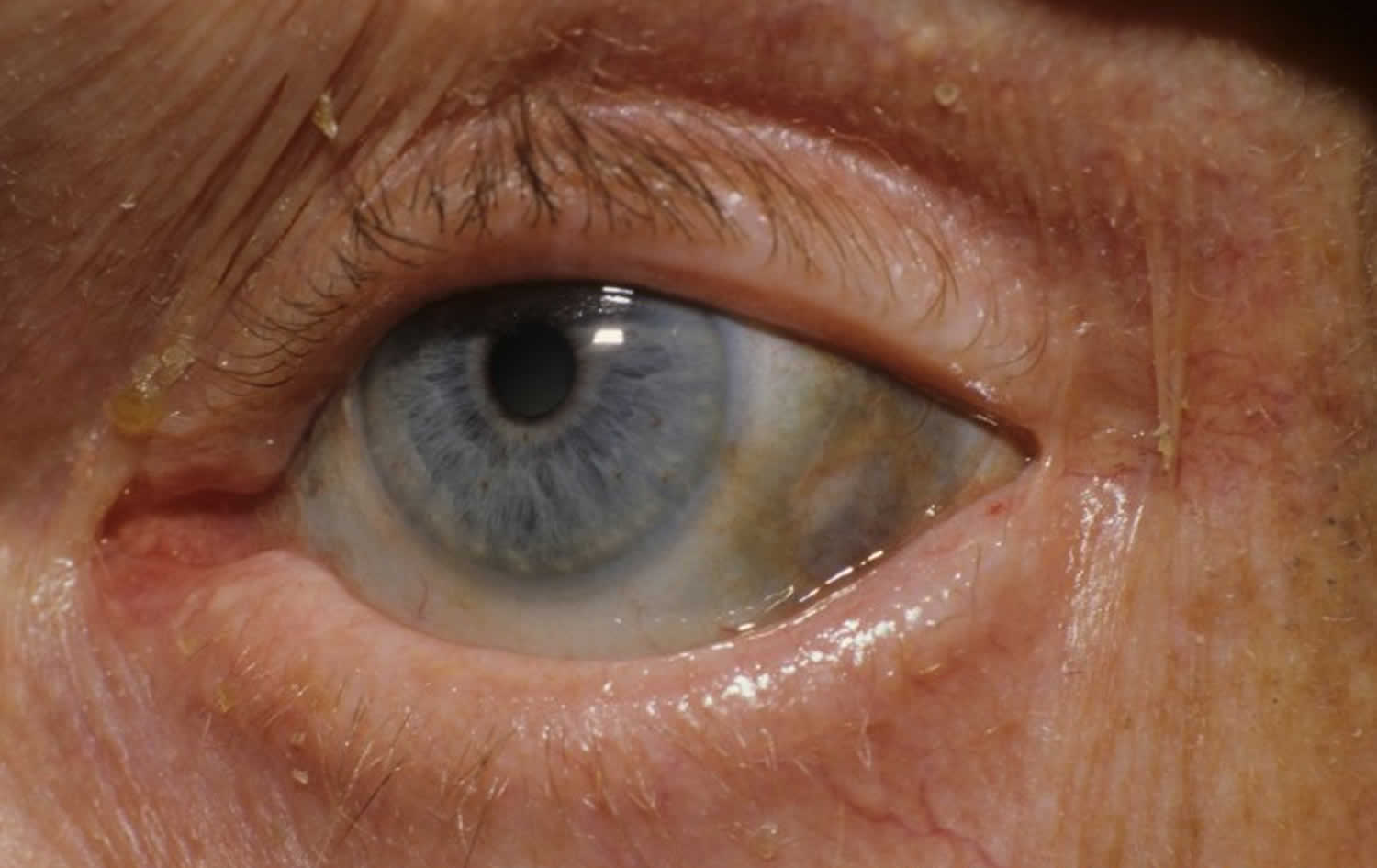
- 👁️ Blue-black pigmentation of sclerae and ear cartilage (first sign).
- 🦴 Crystal deposition in joints → destructive arthritis, especially spine, hips, knees.
- 🎧 Ochronosis: darkening of pinna and cartilage.
- 🧴 Sweat and connective tissues may be pigmented.
- ⚗️ Urine clear on voiding, but turns dark on standing or with alkali.
- Early-onset osteoarthritis due to brittle, pigmented cartilage.
🔬 Investigations
- Urine darkens on exposure to air or alkali (bedside clue!).
- Confirm with ↑ urinary homogentisic acid (GC-MS or HPLC).
- Genetic testing for HGD gene mutation if needed.
💊 Management
- Low protein diet (↓ phenylalanine & tyrosine intake).
- Vitamin C (ascorbic acid) → may ↑ renal clearance of homogentisic acid.
- Symptomatic management of arthritis (analgesia, physio, joint replacement if severe).
- Experimental: Nitisinone (tyrosine metabolism inhibitor) reduces homogentisic acid production.
Cases - Alkaptonuria
- Case 1 - Dark urine in childhood 🍼: A 6-year-old boy is brought by parents because his nappies consistently turn dark brown after a few hours. He is otherwise well. Urine test: homogentisic acid positive. Diagnosis: alkaptonuria, a rare autosomal recessive disorder of tyrosine metabolism due to deficiency of homogentisate oxidase. Parents are counselled on long-term monitoring.
- Case 2 - Ochronosis and joint disease 🤕: A 52-year-old man presents with progressive back stiffness, knee pain, and bluish-black discolouration of ear cartilage and sclerae. Past history reveals dark urine since youth but never investigated. X-rays: calcification of intervertebral discs and degenerative changes in large joints. Diagnosis: adult presentation of alkaptonuria with ochronosis. Managed with analgesia, joint replacement consideration, and metabolic specialist referral.
Teaching Point 🩺: Alkaptonuria is a rare metabolic disorder (1 in 250,000) that causes accumulation of homogentisic acid. Classic clues are dark urine in childhood and later ochronosis with early osteoarthritis. Treatment is supportive; nitisinone is under study.
Categories
- A Level
- About
- Acute Medicine
- Anaesthetics and Critical Care
- Anatomy
- Anatomy and Physiology
- Biochemistry
- Book
- Cardiology
- Collections
- CompSci
- Crib Sheets
- Crib sheets
- Dental
- Dermatology
- Differentials
- Drugs
- ENT
- Education
- Electrocardiogram
- Embryology
- Emergency Medicine
- Endocrinology
- Ethics
- Foundation Doctors
- GCSE
- Gastroenterology
- General Practice
- Genetics
- Geriatric Medicine
- Guidelines
- Gynaecology
- Haematology
- Hepatology
- Immunology
- Infectious Diseases
- Infographic
- Investigations
- Lists
- Mandatory Training
- Medical Students
- Microbiology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Nutrition
- OSCE
- OSCEs
- Obstetrics
- Obstetrics Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Medicine and Dentistry
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatrics
- Palliative
- Pathology
- Pharmacology
- Physiology
- Procedures
- Psychiatry
- Public Health
- Radiology
- Renal
- Respiratory
- Resuscitation
- Revision
- Rheumatology
- Statistics and Research
- Stroke
- Surgery
- Toxicology
- Trauma and Orthopaedics
- USMLE
- Urology
- Vascular Surgery
