Makindo Medical Notes"One small step for man, one large step for Makindo" |
|
|---|---|
| Download all this content in the Apps now Android App and Apple iPhone/Pad App | |
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: The contents are under continuing development and improvements and despite all efforts may contain errors of omission or fact. This is not to be used for the assessment, diagnosis, or management of patients. It should not be regarded as medical advice by healthcare workers or laypeople. It is for educational purposes only. Please adhere to your local protocols. Use the BNF for drug information. If you are unwell please seek urgent healthcare advice. If you do not accept this then please do not use the website. Makindo Ltd. |
Acute Heart Failure and Pulmonary Oedema
-
| About | Anaesthetics and Critical Care | Anatomy | Biochemistry | Cardiology | Clinical Cases | CompSci | Crib | Dermatology | Differentials | Drugs | ENT | Electrocardiogram | Embryology | Emergency Medicine | Endocrinology | Ethics | Foundation Doctors | Gastroenterology | General Information | General Practice | Genetics | Geriatric Medicine | Guidelines | Haematology | Hepatology | Immunology | Infectious Diseases | Infographic | Investigations | Lists | Microbiology | Miscellaneous | Nephrology | Neuroanatomy | Neurology | Nutrition | OSCE | Obstetrics Gynaecology | Oncology | Ophthalmology | Oral Medicine and Dentistry | Paediatrics | Palliative | Pathology | Pharmacology | Physiology | Procedures | Psychiatry | Radiology | Respiratory | Resuscitation | Rheumatology | Statistics and Research | Stroke | Surgery | Toxicology | Trauma and Orthopaedics | Twitter | Urology
Related Subjects: Chronic Heart Failure | Acute Heart Failure and Pulmonary Oedema | Loop Diuretics | Entresto Sacubitril with Valsartan | Ivabradine | Furosemide | Angiotensin Converting Enzyme Inhibitors | Cardiac Resynchronisation Therapy (CRT) Pacemaker |
💔 Cardiogenic Pulmonary Oedema (CPO) is a medical emergency. Often triggered by STEMI, arrhythmia, or mechanical failure. Always exclude these early. A simple bedside echo is invaluable.
| 💔 Emergency Management: Cardiogenic Pulmonary Oedema (CPO) |
|---|
|
🪑 Position → Sit upright, legs dependent
🫁 Oxygen → Maintain sats >92% (88–92% if COPD); CPAP if hypoxic 💧 Diuretics → Furosemide 40–80 mg IV bolus 💉 Opiates → Morphine 2.5–5 mg IV slow + antiemetic 💊 Nitrates → GTN spray; IV infusion if SBP >110 mmHg 🫀 Arrhythmias/STEMI → Treat AF/VT; urgent PCI if STEMI 🔌 Advanced Support → CPAP/NIV, balloon pump, dialysis if needed 💡 Mnemonic: LMNOP → Lasix (furosemide), Morphine, Nitrates, Oxygen, Position |
| 📋 Initial Management (Detailed) |
|---|
Position & Oxygen
Diuretics
Opiates
Nitrates
Non-Invasive Ventilation
Arrhythmias
STEMI / Mechanical Causes
Renal Support
|
💡 Mnemonic: LMNOP = Lasix (Furosemide), Morphine, Nitrates, Oxygen, Position upright.
📖 About
- CPO = acute left ventricular dysfunction → pulmonary venous hypertension → alveolar flooding.
- Rapidly leads to respiratory failure ± cardiogenic shock.
- 30-day mortality ~15% if NT-proBNP >5000 ng/L.
- LV systolic function strongly influences prognosis.
⚖️ Pathophysiology
- Normally: Plasma oncotic pressure (~25 mmHg) holds water in; Pulmonary capillary pressure (~7–12 mmHg) pushes fluid out.
- If PCP > POP → alveolar oedema → hypoxia, ↑ work of breathing.
🔎 Aetiology
- Poor systolic function (e.g. MI).
- Poor diastolic function (HFpEF).
- Valve lesions (MR, AR, AS).
- Arrhythmias (AF, VT, bradycardia).
- Hypertension, myocarditis, cardiomyopathy.
- Fluid overload (transfusion, renal failure).
❓ Precipitating Causes
| Cause | Clues | Diagnostics |
|---|---|---|
| MI | Chest pain, diaphoresis | ECG, troponin, echo |
| AF | Palpitations, irregular pulse | ECG, echo |
| HTN | Headache, chest pain | BP, LVH on echo |
| Valvular disease | Murmur, dyspnoea | Echo, Doppler |
| PE | Pleuritic pain, haemoptysis | CTPA, D-dimer |
| Sepsis | Fever, hypotension | Blood cultures, lactate |
| Drug/alcohol | Recent change | Medication review |
📊 Clinical: Left vs Right HF
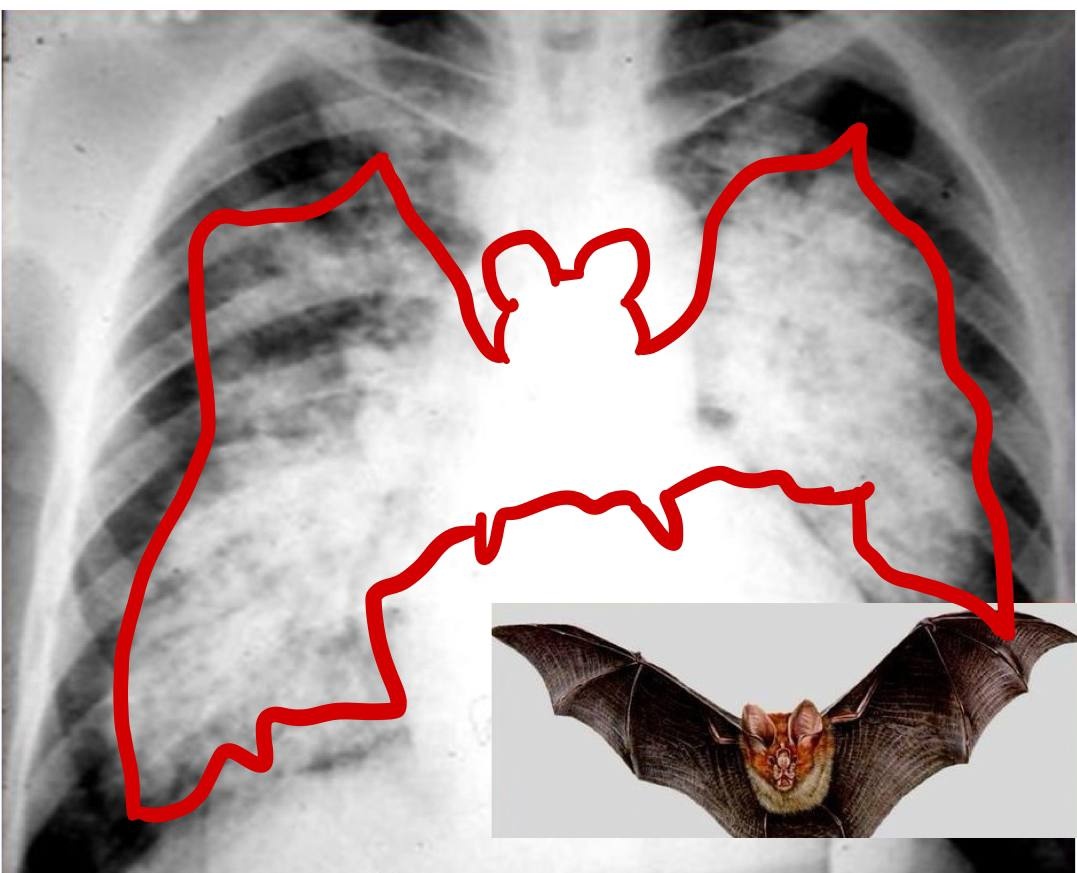
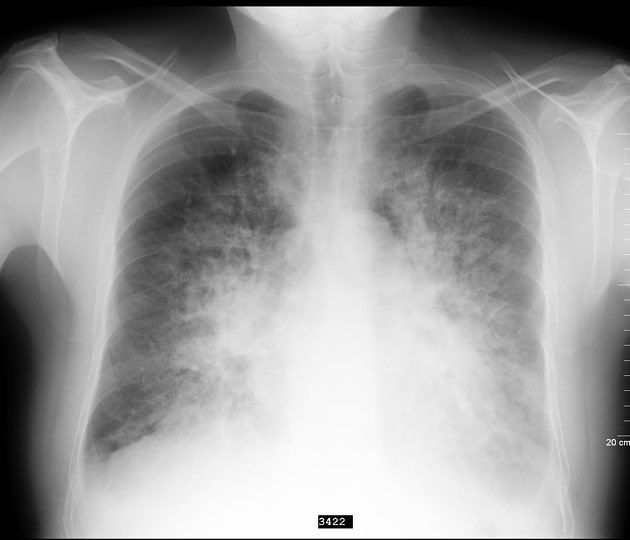
- Left-sided: Orthopnoea, PND, bibasal creps, “bat-wing” CXR.
- Right-sided: Raised JVP, hepatomegaly, ascites, oedema.
- Often coexist → congestive HF.
📌 NYHA Functional Classes
| Class | Symptoms |
|---|---|
| I | No limitation; ordinary activity tolerated. |
| II | Slight limitation; ordinary activity causes dyspnoea/fatigue. |
| III | Marked limitation; less than ordinary activity causes symptoms. |
| IV | Symptoms at rest; unable to tolerate activity. |
🧪 Investigations
- Bedside: ECG, SpO₂, ABG.
- Bloods: FBC, U&E, LFT, TFT, Troponin, NT-proBNP.
- Imaging: CXR (bat-wing, Kerley B lines), Echo (EF, valves).
- Advanced: MRI, SPECT/PET, Angio.
⚡ Complications
- Resp failure (Type 1 → Type 2).
- Arrhythmias (AF, VT, SCD).
- Renal failure, hepatic congestion.
- Electrolyte imbalance (Na⁺, K⁺).
- VTE, cachexia, frailty.
💊 Ongoing Management
- Diuretics: Loop (Furosemide, Bumetanide).
- ACEi/ARBs: Ramipril, Enalapril.
- Beta-blockers: Bisoprolol, Carvedilol.
- Aldosterone antagonists: Spironolactone, Eplerenone.
- Other: Digoxin, Ivabradine, Amiodarone.
- Advanced: CRT, LVAD, transplant.
📉 Prognosis
- HF prognosis worse than many cancers.
- EF <35% = poor marker.
- NT-proBNP correlates with survival.
- Consider palliative care in end-stage disease.
📚 References
Cases — Acute Heart Failure & Pulmonary Oedema
- Case 1 — Hypertensive Emergency 💥: A 72-year-old man with untreated hypertension presents acutely breathless at night, unable to lie flat. Exam: BP 210/110, tachypnoea, widespread crackles, S3 gallop. CXR: bilateral perihilar “bat-wing” shadowing. Diagnosis: Acute pulmonary oedema triggered by hypertensive crisis. Acute Management: Sit upright, oxygen, IV furosemide, IV GTN infusion, morphine if distressed, strict BP control. Monitor U&Es and fluid balance.
- Case 2 — Acute MI Complication ❤️: A 64-year-old man presents with acute chest pain followed by severe dyspnoea. Exam: hypotension, crackles to mid-zones, raised JVP, cool peripheries. ECG: anterior STEMI. Echo: severe LV systolic dysfunction. Diagnosis: Acute cardiogenic pulmonary oedema secondary to MI. Acute Management: Sit upright, O₂, IV diuretics, cautious opioids; urgent PCI for MI; inotropes or mechanical support (IABP) if shock persists.
- Case 3 — Acute Decompensation in Chronic HF 🌀: A 78-year-old woman with known HFrEF (EF 30%) presents with sudden worsening breathlessness after a chest infection. Exam: tachypnoeic, bibasal crackles, elevated JVP, peripheral oedema. BNP elevated, CXR: pulmonary congestion. Diagnosis: Acute decompensated heart failure with pulmonary oedema, triggered by infection. Acute Management: Sit upright, O₂, IV furosemide; treat infection (antibiotics); optimise chronic therapy (ACEi, beta-blocker, spironolactone) once stable.
Teaching Commentary 🧠
Acute heart failure with pulmonary oedema is a medical emergency. - Pathophysiology: raised LV end-diastolic pressure → pulmonary venous congestion → alveolar fluid → hypoxia. - Precipitants: MI, arrhythmias, hypertensive crisis, infection, fluid overload, non-compliance. - Clinical: severe breathlessness, orthopnoea, crackles, frothy pink sputum, gallop rhythm. - Acute management (“PODMAN”): Position upright, Oxygen, Diuretics (IV loop), Morphine, Afterload reduction (nitrates), Non-invasive ventilation if hypoxic. Long-term: optimise HF therapy (ACEi/ARNI, beta-blockers, MRA, SGLT2 inhibitors); lifestyle and fluid restriction; device therapy (CRT, ICD) in select patients.