| Download the amazing global Makindo app: Android | Apple | |
|---|---|
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: Educational use only. Not for diagnosis or management. See below for full disclaimer. |
Dermoid cysts
Dermoid Cyst 🧬: A benign, slow-growing cystic tumour (sometimes considered a form of teratoma) containing tissues such as hair, skin, sebaceous glands, and occasionally teeth 🦷. Most are congenital (present at birth) and enlarge slowly, but complications can occur depending on location.
About ℹ️
- Derived from ectodermal tissue: dermis, hair follicles, sebaceous glands.
- May contain hair, keratinous fluid, fat, skin glands, or teeth.
- Can arise in skin, ovaries, or intracranial spaces.
- Generally benign, but rare risk of malignant transformation ⚠️ (e.g., squamous cell carcinoma).
Aetiology 🧬
- Embryonic tissue trapped during development → ectodermal remnants persist.
- Can develop in:
- Face/head/neck → congenital dermoid sinus or midline cysts.
- Ovary → “mature cystic teratoma.”
- Intracranial regions → skull base or brain cysts.
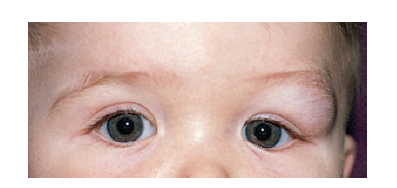
Clinical Presentation 👀
- Facial dermoid cysts: Firm, painless mass (often periorbital or nasal bridge).
- Ovarian dermoid cysts (teratomas): Abdominal/pelvic pain, torsion ⚠️, rupture, or mass effect.
- Intracranial dermoid cysts: Headaches, seizures, or raised ICP due to pressure effects.
- Most are slow-growing and discovered incidentally unless complicated.
Differential Diagnoses 🔍
- Epidermoid cyst.
- Other teratomas.
- Sebaceous cyst / pilonidal cyst.
- Sinus mucoceles or other cystic tumours.
Investigations 🧪
- Ultrasound 🖤: First line for superficial or ovarian dermoid cysts.
- CT scan: Useful for abdominal/pelvic cysts; detects calcification/teeth 🦷.
- MRI: Best for intracranial or deep-seated lesions; delineates fat signal intensity.
Management 💊🔪
- Surgical excision: Curative in most cases, low recurrence if complete.
- Skin/face dermoids: Simple excision.
- Ovarian dermoids: Laparoscopy/laparotomy (especially if torsion/rupture suspected).
- Intracranial dermoids: Craniectomy if mass effect/neurological symptoms.
- Monitoring: Selected asymptomatic ovarian dermoids (esp. <5 cm) can be followed with imaging.
References 📚
- Smith, J. R., & Miller, A. L. (2021). *Dermoid Cysts: Diagnosis and Management*. J Surg Oncol.
- Jones, T. D. (2020). *Ovarian Teratomas and Dermoid Cysts: A Clinical Review*. Obstet & Gynecol J.
- American Academy of Dermatology – Dermoid Cysts
💡 Clinical Pearls
- Ovarian dermoid cyst = mature cystic teratoma 🥚 → most common ovarian tumour in young women.
- Intracranial dermoid: may rupture → chemical meningitis (rare but dangerous).
- Always consider dermoid in a midline childhood facial mass — may connect to intracranial space.
Categories
- A Level
- About
- Acute Medicine
- Anaesthetics and Critical Care
- Anatomy
- Biochemistry
- Book
- Cardiology
- Collections
- CompSci
- Crib Sheets
- Dental
- Dermatology
- Differentials
- Drugs
- ENT
- Education
- Electrocardiogram
- Embryology
- Emergency Medicine
- Endocrinology
- Ethics
- Foundation Doctors
- GCSE
- Gastroenterology
- General Practice
- Genetics
- Geriatric Medicine
- Guidelines
- Gynaecology
- Haematology
- Hepatology
- Immunology
- Infectious Diseases
- Infographic
- Investigations
- Lists
- Mandatory Training
- Medical Students
- Microbiology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Nutrition
- OSCE
- Obstetrics
- Obstetrics Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Medicine and Dentistry
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatrics
- Palliative
- Pathology
- Pharmacology
- Physiology
- Procedures
- Psychiatry
- Public Health
- Radiology
- Renal
- Respiratory
- Resuscitation
- Revision
- Rheumatology
- Statistics and Research
- Stroke
- Surgery
- Toxicology
- Trauma and Orthopaedics
- USMLE
- Urology
- Vascular Surgery
