| Download the amazing global Makindo app: Android | Apple | |
|---|---|
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: Educational use only. Not for diagnosis or management. See below for full disclaimer. |
Hirschsprung disease (congenital megacolon)
🧠 Hirschsprung's disease is a congenital absence of enteric ganglion cells in the distal bowel → tonic contraction and functional obstruction. Early recognition and surgery prevent life-threatening enterocolitis and support normal growth. 👶
📖 About
- Hirschsprung's disease = aganglionosis of the distal bowel (myenteric + submucosal plexuses) → failure of relaxation 🚫.
- Also called congenital megacolon; incidence ≈ 1:5,000 live births.
🤝 Associations
- Family history 👪
- Genetic: Down syndrome (Trisomy 21), Waardenburg, MEN2 (RET), neurofibromatosis 🧬
- Other anomalies: VSD, renal anomalies 🫀🟦
🧪 Pathology
- Failed neural crest migration → absent parasympathetic ganglion cells distally.
- Aganglionic segment remains narrowed; proximal bowel becomes dilated and hypertrophic → megacolon 📈.
📍 Extent (Aetiology)
- ~70% rectosigmoid (short-segment) ✅
- ~20% entire colon (long-segment) ⚠️
- ~10% may extend into small intestine (total colonic/ileal) ⚠️
🩺 Clinical Features
- 🍼 Neonate: Delayed meconium >48 h, abdominal distension, bilious vomiting, poor feeding.
- 👶 Infant/child: Chronic constipation, abdominal bloating, FTT; explosive stool after DRE (“squirt sign”).
- 🔥 Hirschsprung-associated enterocolitis (HAEC): Fever, severe distension, foul diarrhoea, lethargy → emergency.
🔍 Differential Diagnoses
- Functional constipation
- Meconium ileus (CF) 🧪
- Imperforate anus / anorectal malformation
- Neonatal sepsis, intestinal atresia
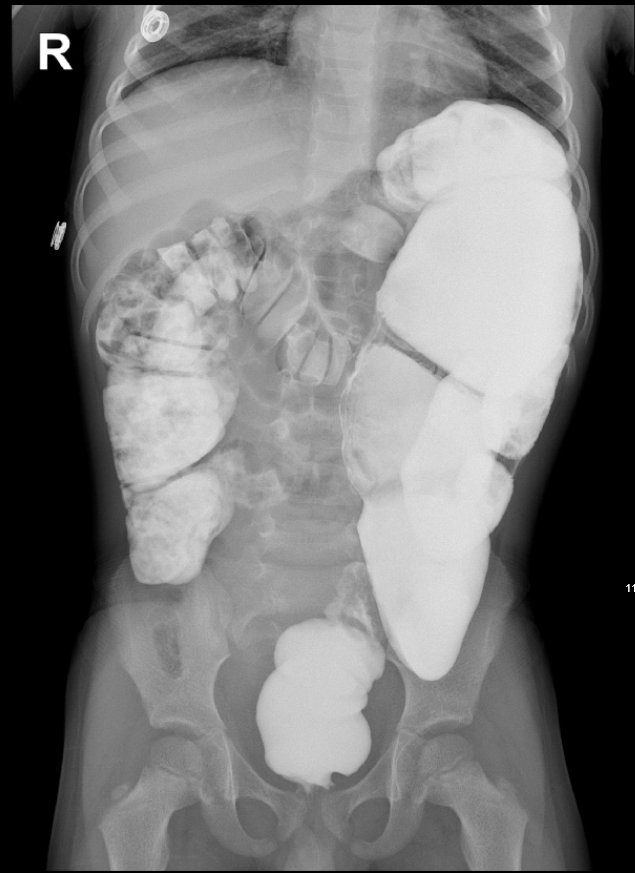
🧪 Investigations (corrected)
- 🩻 Abdominal X-ray: Distended bowel loops; paucity of rectal gas.
- 🧪 Contrast enema: Transition zone (narrow distal aganglionic segment with proximal dilatation); avoid rectal exam just before study.
- 🎯 Anorectal manometry (infants): Absent recto-anal inhibitory reflex (RAIR) ➖.
- 🔬 Suction rectal biopsy (gold standard): Absent ganglion cells + hypertrophic nerve trunks; do ≥1.5 cm above dentate line.
- 🧬 Consider genetic testing (RET) and screen for associated anomalies; newborn CF screen if meconium ileus suspected.
🛠️ Management
- ⛑️ Stabilise: IV fluids, NG decompression, broad-spectrum antibiotics if HAEC, rectal saline washouts 💧.
- 🔪 Definitive surgery (pull-through):
- Swenson: Resection of aganglionic rectum with coloanal anastomosis.
- Soave: Endorectal mucosectomy; pull-through within muscular cuff.
- Duhamel: Side-to-side retrorectal anastomosis forming a neorectum.
- 🧷 Stoma: Considered in enterocolitis, severe dilatation, or staged procedures.
- 🏥 Post-op: Monitor for HAEC, anastomotic leak/stricture; bowel regimen, pelvic floor support.
📚 Case Example
👶 Case: Term male, day-3 of life, has not passed meconium. Marked distension, bilious vomiting, and a gush of foul stool after DRE (“squirt sign”). 🩻 AXR: Dilated bowel loops, paucity of rectal gas. 🧪 Contrast enema: Rectosigmoid transition zone. 🔬 Suction rectal biopsy: Absent ganglion cells with hypertrophic nerves → Hirschsprung’s confirmed. 🛠️ Management: IV fluids, rectal washouts, then laparoscopic-assisted Soave pull-through. ✅ Outcome: Good weight gain; stooling programme and surveillance for HAEC/stricture.
🔭 Prognosis
- 👍 Generally favourable after pull-through.
- ♻️ Some children have persistent constipation, soiling, or enterocolitis episodes—needs long-term follow-up.
🔗 References
Categories
- A Level
- About
- Acute Medicine
- Anaesthetics and Critical Care
- Anatomy
- Anatomy and Physiology
- Biochemistry
- Book
- Cardiology
- Collections
- CompSci
- Crib Sheets
- Crib sheets
- Dental
- Dermatology
- Differentials
- Drugs
- ENT
- Education
- Electrocardiogram
- Embryology
- Emergency Medicine
- Endocrinology
- Ethics
- Foundation Doctors
- GCSE
- Gastroenterology
- General Practice
- Genetics
- Geriatric Medicine
- Guidelines
- Gynaecology
- Haematology
- Hepatology
- Immunology
- Infectious Diseases
- Infographic
- Investigations
- Lists
- Mandatory Training
- Medical Students
- Microbiology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Nutrition
- OSCE
- OSCEs
- Obstetrics
- Obstetrics Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Medicine and Dentistry
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatrics
- Palliative
- Pathology
- Pharmacology
- Physiology
- Procedures
- Psychiatry
- Public Health
- Radiology
- Renal
- Respiratory
- Resuscitation
- Revision
- Rheumatology
- Statistics and Research
- Stroke
- Surgery
- Toxicology
- Trauma and Orthopaedics
- USMLE
- Urology
- Vascular Surgery
