| Download the amazing global Makindo app: Android | Apple | |
|---|---|
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: Educational use only. Not for diagnosis or management. See below for full disclaimer. |
Genetic Diseases
Related Subjects: |DNA replication |DNA structure in Nucleus |Cell Cycle |Mitosis and Meiosis |Ribosomes |Microtubules |Mitochondria |Smooth and Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
🧬 Genetic Definitions
- Gene: 🧾 A region of DNA that encodes a protein.
- Genome: 🌍 The complete set of genes of an organism, including coding and non-coding DNA sequences.
- Locus: 📍 The specific location of a gene on a chromosome.
- Chromosome: 📦 Self-replicating structures containing DNA. Humans have 23 pairs (22 autosomes + 1 sex pair).
- Alleles: 🔀 Alternative forms of a gene at the same locus; one allele inherited from each parent.
- Haploid: 🎯 A single set of 23 chromosomes (e.g., egg or sperm).
- Codon: 🧩 A 3-base sequence of nucleotides encoding a specific amino acid.
- Karyotype: 🔬 The number and appearance of chromosomes in a nucleus (46 in humans = 44 autosomes + 2 sex chromosomes).
- Autosome: 🚹🚺 Any chromosome other than the sex chromosomes (22 pairs in humans).
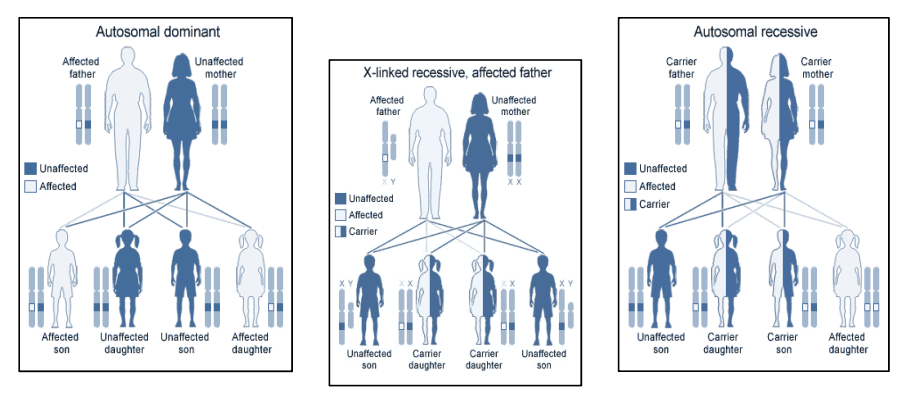
Inheritance Pearl: 🟢 Autosomal recessive → usually metabolic disorders (exceptions: inherited ataxias). 🔵 Autosomal dominant → usually structural disorders (exceptions: hyperlipidaemia type II, hypokalaemia periodic paralysis).
🟢 Autosomal Recessive Conditions (Metabolic)
Usually enzymatic or metabolic defects; both alleles must be faulty:
- ⚪ Albinism
- ⚪ Ataxia telangiectasia
- ⚪ Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 4
- ⚪ Hemochromatosis
- ⚪ Cystic fibrosis
- ⚪ Cystinosis
- ⚪ Fanconi anaemia
- ⚪ Familial Mediterranean fever
- ⚪ Homocystinuria
- ⚪ Sickle cell disease
- ⚪ Thalassemia
- ⚪ Phenylketonuria
- ⚪ Refsum’s disease
- ⚪ Lipid storage diseases (Tay-Sachs, Gaucher’s, Niemann-Pick)
- ⚪ Mucopolysaccharidoses (Hurler’s syndrome, etc.)
- ⚪ Retinitis pigmentosa (AR form)
- ⚪ Wilson’s disease
🔵 Autosomal Dominant Conditions (Structural)
Often affect connective tissue, receptors, or structural proteins:
- 🔹 Achondroplasia
- 🔹 Aniridia
- 🔹 Tuberous sclerosis
- 🔹 Charcot-Marie-Tooth types 1 & 2
- 🔹 Myotonic dystrophy
- 🔹 Gilbert’s syndrome
- 🔹 Hyperlipidemia type II
- 🔹 Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
- 🔹 Facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy
- 🔹 Familial hypercholesterolemia
- 🔹 Marfan syndrome
- 🔹 Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia (MEN)
- 🔹 Neurofibromatosis 1 & 2
- 🔹 Polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD)
- 🔹 Retinitis pigmentosa (AD form)
- 🔹 Retinoblastoma
- 🔹 Von Willebrand’s disease
🧑🍼 X-Linked Recessive Conditions
Affect males (only one X chromosome). Females usually carriers unless they have Turner syndrome (XO).
- ❌ G6PD deficiency
- ❌ Hunter syndrome
- ❌ Hemophilia A & B
- ❌ Fabry disease
- ❌ Duchenne & Becker muscular dystrophy
- ❌ Androgen insensitivity syndrome
- ❌ Color blindness
- ❌ Lesch-Nyhan syndrome
- ❌ Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus
- ❌ Ocular albinism
- ❌ Retinitis pigmentosa (X-linked)
- ❌ Severe combined immunodeficiency
- ❌ Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome
🧬 X-Linked Dominant Conditions
- ⭐ Vitamin D-resistant rickets (more severe in males)
- ⭐ Alport syndrome (85% X-linked dominant)
- ⭐ Rett syndrome
Categories
- A Level
- About
- Acute Medicine
- Anaesthetics and Critical Care
- Anatomy
- Anatomy and Physiology
- Biochemistry
- Book
- Cardiology
- Collections
- CompSci
- Crib Sheets
- Crib sheets
- Dental
- Dermatology
- Differentials
- Drugs
- ENT
- Education
- Electrocardiogram
- Embryology
- Emergency Medicine
- Endocrinology
- Ethics
- Foundation Doctors
- GCSE
- Gastroenterology
- General Practice
- Genetics
- Geriatric Medicine
- Guidelines
- Gynaecology
- Haematology
- Hepatology
- Immunology
- Infectious Diseases
- Infographic
- Investigations
- Lists
- Mandatory Training
- Medical Students
- Microbiology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Nutrition
- OSCE
- OSCEs
- Obstetrics
- Obstetrics Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Medicine and Dentistry
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatrics
- Palliative
- Pathology
- Pharmacology
- Physiology
- Procedures
- Psychiatry
- Public Health
- Radiology
- Renal
- Respiratory
- Resuscitation
- Revision
- Rheumatology
- Statistics and Research
- Stroke
- Surgery
- Toxicology
- Trauma and Orthopaedics
- USMLE
- Urology
- Vascular Surgery
