| Download the amazing global Makindo app: Android | Apple | |
|---|---|
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: Educational use only. Not for diagnosis or management. See below for full disclaimer. |
Hepatorenal syndromes
Related Subjects: |Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) / Acute Renal Failure |Chronic liver disease |Cirrhosis |Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) |Liver Function Tests |Ascites Assessment and Management |Budd-Chiari syndrome |Autoimmune Hepatitis |Primary Biliary Cirrhosis |Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis |Wilson disease | |Hereditary Haemochromatosis |Alpha-1 Antitrypsin (AAT) deficiency |Non alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) |Spontaneous Bacterial Peritonitis |Alcoholism and Alcoholic Liver Disease
ℹ️ About
- Hepatorenal Syndrome (HRS): A severe form of acute kidney failure occurring in patients with advanced liver disease and ascites. It is a life-threatening complication commonly associated with cirrhosis, alcoholic hepatitis, or fulminant liver failure.
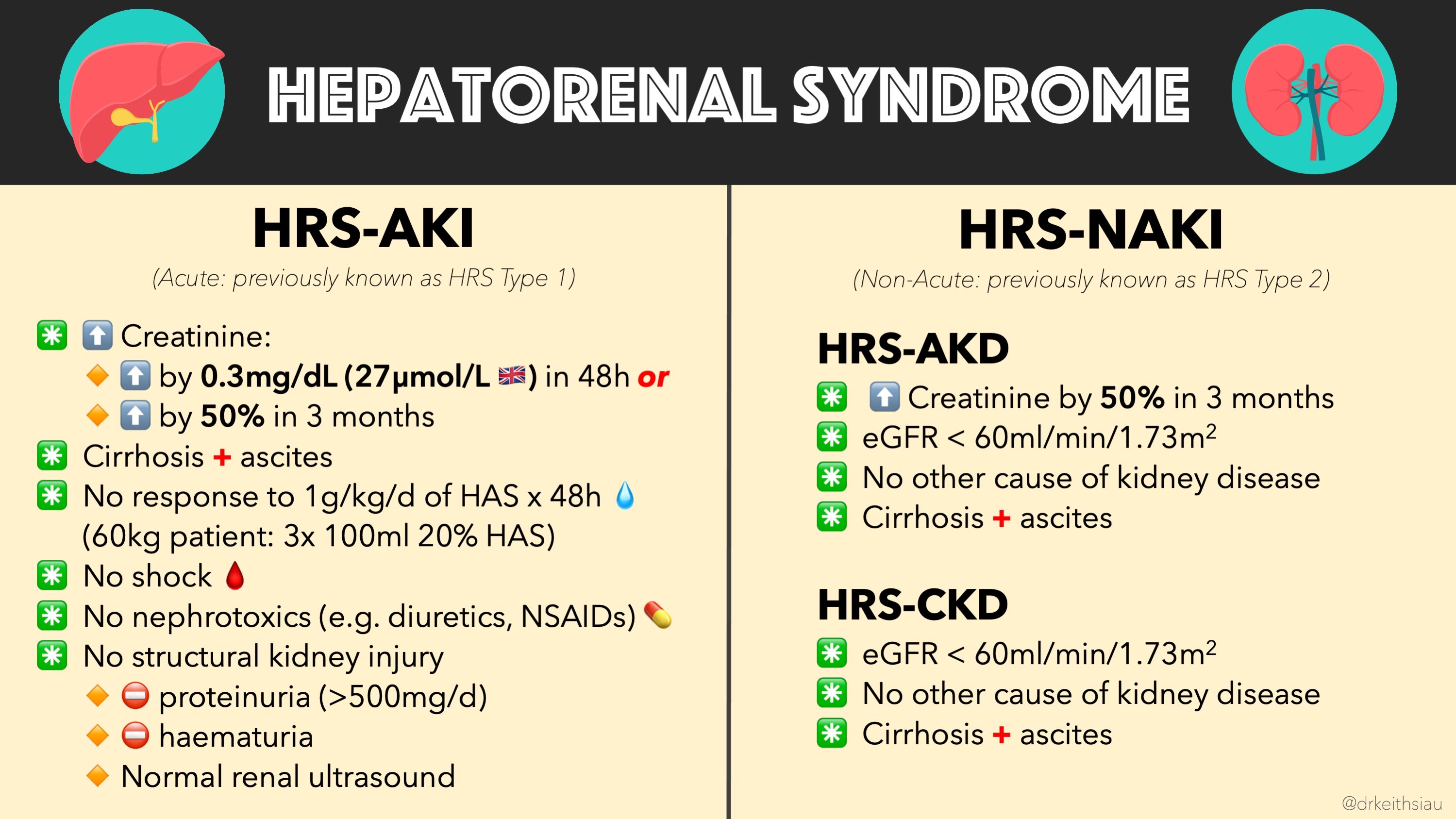
- HRS is now classified using the International Club of Ascites (ICA) system, aligning with the Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) framework for a more nuanced understanding of renal dysfunction in liver disease.
Classification
The new ICA classification integrates traditional Type 1 and Type 2 HRS into a more detailed system based on the severity and progression of kidney dysfunction, facilitating earlier detection and tailored management.
- HRS-AKI (Hepatorenal Syndrome - Acute Kidney Injury):
- Characterized by a rapid increase in serum creatinine, following AKI criteria.
- Subdivided into:
- Stage 1: Increase in serum creatinine ≥0.3 mg/dL within 48 hours or ≥1.5 times baseline within 7 days.
- Stage 2: Further elevation of serum creatinine by ≥2 times baseline.
- Stage 3: Serum creatinine >4.0 mg/dL or initiation of renal replacement therapy.
- HRS-CKD (Hepatorenal Syndrome - Chronic Kidney Disease):
- Represents stable, long-term impairment of renal function.
- Associated with diuretic-resistant ascites and persistent renal dysfunction.
🧬 Aetiology
- Nitric Oxide (NO): Excessive production leads to splanchnic vasodilation, reducing systemic vascular resistance and effective arterial blood volume.
- Splanchnic Vasodilation: Decreases effective blood volume, triggering compensatory renal vasoconstriction to maintain blood pressure.
- Renal Vasoconstriction: Reduces renal blood flow, causing oliguria and acute kidney injury without structural kidney damage.
- Systemic Inflammation: Elevated inflammatory cytokines contribute to vasodilation and renal dysfunction.
🩺 Clinical Features
- Oliguria: Significant reduction in urine output, often less than 500 mL per day.
- Hypotension: Persistently low blood pressure due to decreased systemic vascular resistance.
- Signs of Chronic Liver Disease: Jaundice, ascites, hepatic encephalopathy, and other manifestations alongside renal symptoms.
- Electrolyte Imbalances: Hyponatremia and hyperkalemia may be present.
Comparing Classifications
The table below contrasts the traditional classification (Type 1 and Type 2) with the new ICA classification (HRS-AKI and HRS-CKD).
| Feature | Traditional Classification | New ICA Classification |
|---|---|---|
| Classification Basis | Type 1 and Type 2 based on onset and severity. | HRS-AKI and HRS-CKD based on AKI framework and chronicity. |
| Onset | Type 1: Rapid onset.
Type 2: Gradual onset. |
HRS-AKI: Rapid increase in serum creatinine.
HRS-CKD: Chronic, stable renal dysfunction. |
| Serum Creatinine | Type 1: Doubles to >2.5 mg/dL in <2 weeks.
Type 2: Slowly rising. |
HRS-AKI: Staged per AKI criteria.
HRS-CKD: Elevated and stable over months. |
| Urinary Output | Type 1: Marked oliguria.
Type 2: Moderate reduction. |
HRS-AKI: Varies with stage.
HRS-CKD: Persistent reduction. |
| Associated Features | Type 1: Precipitated by events like GI bleeding.
Type 2: Diuretic-resistant ascites. |
HRS-AKI: Similar precipitating events under AKI framework.
HRS-CKD: Diuretic-resistant ascites. |
| Prognosis | Type 1: Poor without transplant.
Type 2: Better but still poor. |
HRS-AKI: Varies with AKI stage; high mortality in advanced stages.
HRS-CKD: Better than HRS-AKI but still guarded. |
| Survival without Liver Transplant | Type 1: Median <2 weeks.
Type 2: Median ~6 months. |
HRS-AKI: Dependent on AKI stage; lower survival in higher stages.
HRS-CKD: Median survival better than HRS-AKI. |
| Key Characteristic | Type 1: Acute renal failure.
Type 2: Chronic renal dysfunction. |
HRS-AKI: Acute changes per AKI.
HRS-CKD: Chronic impairment. |
🔎 Investigations
- Laboratory Tests:
- Rising Urea and Creatinine: Indicative of renal failure without significant structural kidney damage.
- No Proteinuria: Helps differentiate HRS from intrinsic renal diseases.
- Low Urinary Sodium: Typically <10 mmol/L, reflecting sodium conservation by the kidneys.
- Urine/Plasma Osmolarity: Ratio usually >1.5, indicating concentrated urine despite impaired function.
- Imaging Studies:
- Ultrasonography: To rule out other causes of renal dysfunction such as obstruction.
- Renal Doppler Studies: May show reduced renal blood flow.
- Exclusion of Other Causes: Essential to confirm HRS by ruling out intrinsic renal diseases.
💊 Management
- Albumin Infusions: Expand plasma volume and improve renal perfusion. Typical dosing: 1 g/kg on the first day, followed by 20-40 g/day as needed.
- Terlipressin: A vasopressor counteracting splanchnic vasodilation to improve renal blood flow. Standard dosing: 2 mg every 4-6 hours, titrated based on response.
- Nitric Oxide Inhibitors: Agents like midodrine may be combined with other vasoconstrictors to enhance efficacy.
- Diuretics: Often discontinued to prevent further intravascular volume depletion.
- Haemodialysis: Generally not indicated unless severe electrolyte imbalances or volume overload are present.
- Liver Transplantation: The definitive treatment offering the best chance for renal recovery and overall survival.
- Vasoconstrictor Therapy: Combination of vasopressors (e.g., terlipressin) and albumin is first-line therapy for HRS-AKI.
- Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt (TIPS): May be considered in select cases to reduce portal hypertension, though its role in HRS is limited.
Type II Hepatorenal Syndrome (HRS)
- Characterized by less severe but more chronic renal dysfunction compared to Type I.
- Primary features include diuretic-resistant ascites, where standard diuretic therapy fails, leading to persistent fluid accumulation.
- Renal dysfunction progresses more slowly, allowing for potential stabilization with appropriate medical management.
- Despite a gradual course, Type II HRS carries significant morbidity and a poor prognosis without liver transplantation.
- Treatment strategies include vasoconstrictors, albumin infusions, and consideration of liver transplantation for eligible patients.
References
Cases — Hepatorenal Syndrome (HRS)
- Case 1 — Type 1 (rapid onset) ⚡: A 58-year-old man with decompensated alcoholic cirrhosis is admitted with tense ascites and spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Within 2 weeks, his creatinine rises from 95 → 340 µmol/L despite fluid resuscitation. Diagnosis: HRS type 1 (acute, rapidly progressive). Managed with IV albumin, terlipressin, and evaluation for liver transplant.
- Case 2 — Type 2 (chronic/insidious) 🐢: A 62-year-old woman with hepatitis C cirrhosis presents with gradually worsening ascites resistant to diuretics. Renal function is impaired (creatinine 160 µmol/L) but stable over months. No response to fluid challenge. Diagnosis: HRS type 2 (slowly progressive, linked to refractory ascites). Managed with diuretic withdrawal, albumin infusions, vasoconstrictors, and transplant referral.
- Case 3 — Precipitated by variceal bleed 💉: A 55-year-old man with Child-Pugh C cirrhosis is admitted with massive variceal haemorrhage. Despite haemostasis, his renal function deteriorates rapidly with oliguria and rising urea/creatinine. No evidence of shock or nephrotoxins. Diagnosis: HRS triggered by GI bleed. Managed with vasoconstrictors (terlipressin), albumin, and critical care support.
Teaching Point 🩺: Hepatorenal Syndrome is a functional renal failure in advanced cirrhosis, due to intense renal vasoconstriction and splanchnic vasodilatation. Key clues: cirrhosis, ascites, renal impairment, no structural kidney disease. Two main patterns: Type 1 (rapid, severe, often after infection/bleed) and Type 2 (slower, with refractory ascites). Definitive treatment is liver transplantation.
Categories
- A Level
- About
- Acute Medicine
- Anaesthetics and Critical Care
- Anatomy
- Anatomy and Physiology
- Biochemistry
- Book
- Cardiology
- Collections
- CompSci
- Crib Sheets
- Crib sheets
- Dental
- Dermatology
- Differentials
- Drugs
- ENT
- Education
- Electrocardiogram
- Embryology
- Emergency Medicine
- Endocrinology
- Ethics
- Foundation Doctors
- GCSE
- Gastroenterology
- General Practice
- Genetics
- Geriatric Medicine
- Guidelines
- Gynaecology
- Haematology
- Hepatology
- Immunology
- Infectious Diseases
- Infographic
- Investigations
- Lists
- Mandatory Training
- Medical Students
- Microbiology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Nutrition
- OSCE
- OSCEs
- Obstetrics
- Obstetrics Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Medicine and Dentistry
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatrics
- Palliative
- Pathology
- Pharmacology
- Physiology
- Procedures
- Psychiatry
- Public Health
- Radiology
- Renal
- Respiratory
- Resuscitation
- Revision
- Rheumatology
- Statistics and Research
- Stroke
- Surgery
- Toxicology
- Trauma and Orthopaedics
- USMLE
- Urology
- Vascular Surgery
