| Download the amazing global Makindo app: Android | Apple | |
|---|---|
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: Educational use only. Not for diagnosis or management. See below for full disclaimer. |
Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy (PML)
Related Subjects: |Neurological History taking |Motor Neuron Disease (MND-ALS) |Miller-Fisher syndrome |Guillain Barre Syndrome |Multifocal Motor Neuropathy with Conduction block |Multiple Sclerosis (MS) Demyelination |Transverse myelitis |Acute Disseminated Encephalomyelitis |Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy (PML) |Inclusion Body Myositis |Cervical spondylosis |Anterior Spinal Cord syndrome |Central Spinal Cord syndrome |Brown-Sequard Spinal Cord syndrome |Spinal Cord Compression |Spinal Cord Haematoma |Spinal Cord Infarction
🧠 Progressive Multifocal Leukoencephalopathy (PML) is a rare, often severe JC virus (JCV) CNS infection causing progressive demyelination in immunocompromised patients. ⚠️ Think PML in any patient with new, progressive focal neurology who is immunosuppressed or on high-risk drugs (especially natalizumab, rituximab/anti-CD20, S1P modulators, fumarates).
🔎 What it is (and why it happens)
- JCV reactivates when cell-mediated immunity is impaired → infects oligodendrocytes → multifocal demyelination.
- Clinical pattern is usually subacute and progressive over days–weeks (not “maximal at onset” like stroke).
- Often mistaken for “MS relapse” or tumour—especially in patients on MS disease-modifying therapy.
⏱️ Timing: drug exposure ↔ PML (high-yield)
- Natalizumab: risk rises with longer treatment, particularly beyond 2 years.
- Natalizumab carry-over: PML can present after stopping—patient safety information warns it can occur up to 6 months post-cessation.
- Rituximab: reported median time from last dose → PML diagnosis ~5.5 months; from first dose → diagnosis ~16 months.
- Dimethyl fumarate: PML risk relates strongly to lymphopenia; UK MHRA highlights that even mild lymphopenia is a risk factor.
🩺 Clinical features (what you actually see)
- Progressive focal deficits: weakness/sensory loss, aphasia, hemianopia, ataxia, cognitive/behaviour change.
- Seizures can occur (especially with cortical/juxtacortical involvement).
- Key clue: symptoms typically worsen stepwise or steadily rather than improving spontaneously.
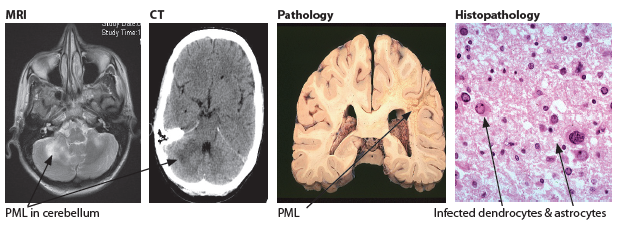
🖼️ Imaging pattern (classic clues)
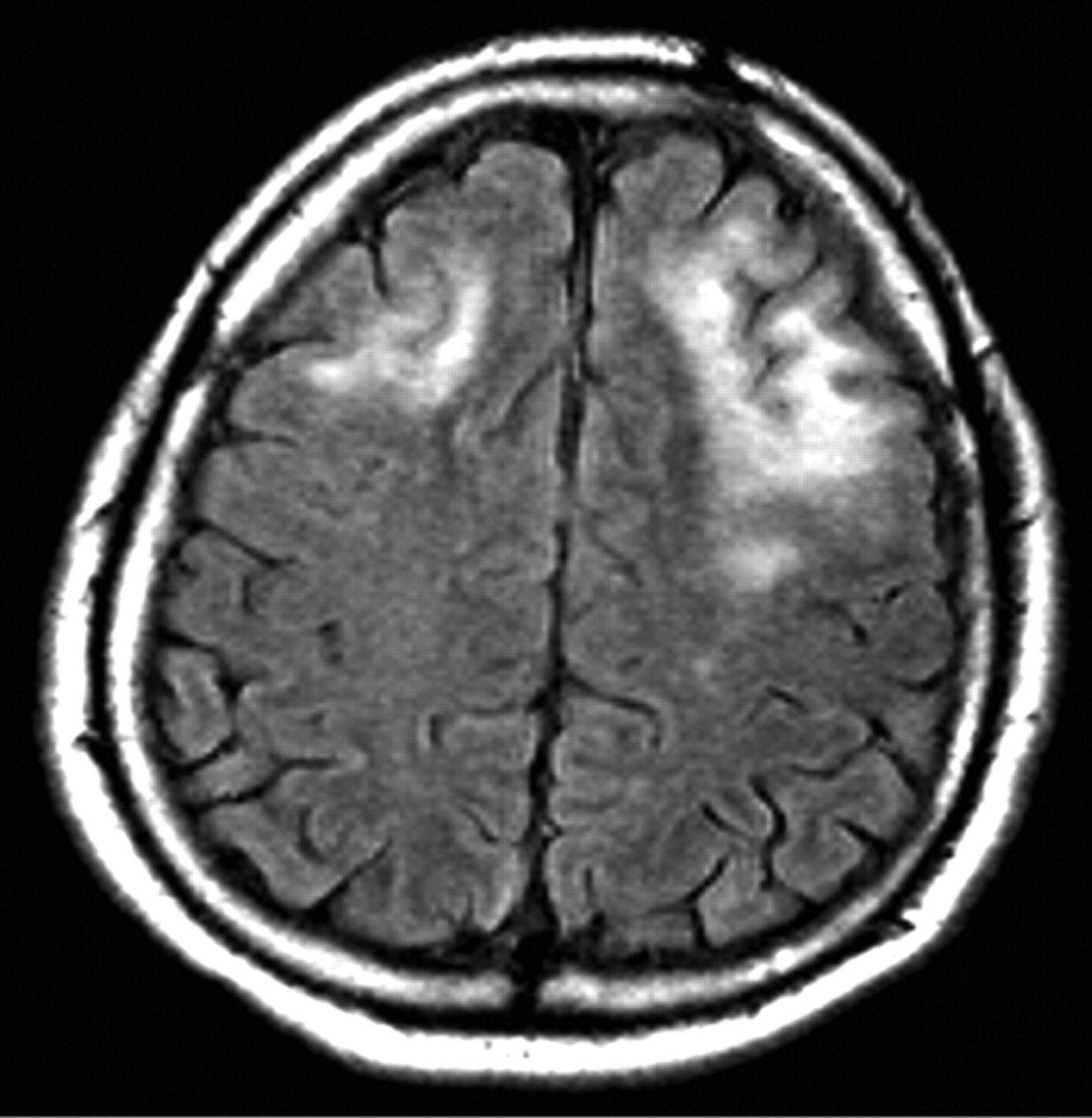
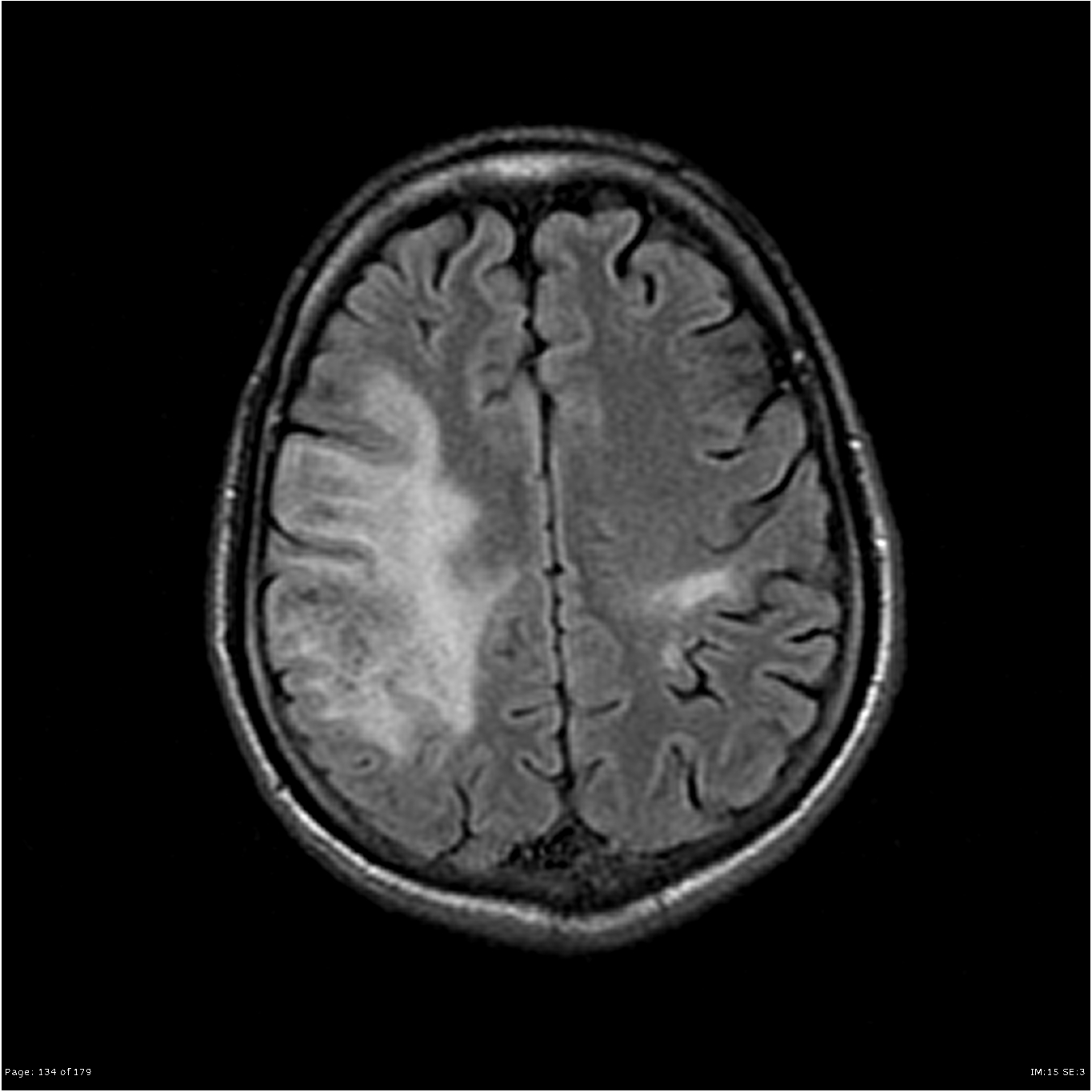
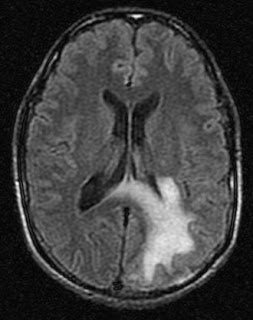
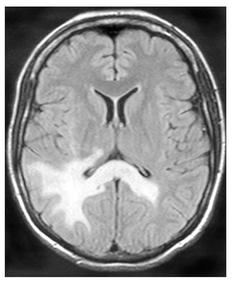
- MRI: asymmetric T2/FLAIR hyperintense white matter lesions, often involving subcortical U-fibres, usually with little mass effect.
- Contrast enhancement may be minimal in “classic” PML, but can appear in inflammatory PML/IRIS.

🧪 Investigations of PML
- Urgent MRI brain (preferred test): include T2/FLAIR, DWI/ADC and ideally post-contrast sequences. CT is often non-diagnostic early and can falsely reassure.
- Interpret MRI with suspicion in mind: look for asymmetric subcortical white matter lesions (often involving U-fibres), usually with little mass effect; enhancement may be absent in “classic” PML but can appear in inflammatory PML/IRIS.
- CSF JCV PCR supports diagnosis, but can be negative early (low viral load). If suspicion stays high, repeat lumbar puncture and ensure the lab uses a sensitive assay; re-review imaging with neuroradiology/neurology. (AAN consensus criteria)
- Baseline bloods to define the immune context: FBC (lymphocytes), U&E/LFTs, CRP; HIV test; consider lymphocyte subsets (CD4) and review drug exposure history (natalizumab/anti-CD20/S1P/fumarates).
- Apply recognised diagnostic criteria: diagnosis is based on a combination of clinical course + MRI + virology, with brain biopsy reserved for unresolved cases where CSF/MRI remain non-diagnostic and management hinges on certainty. (AAN consensus criteria)
💊 Management of PML (what to do first)
- Act immediately: treat as a neuro-emergency. Stop/hold the suspected causative drug and escalate same day to the relevant team (Neurology/MS, Haem/Onc, Rheum, Infectious Diseases).
- Secure diagnosis in parallel: arrange urgent MRI brain (with contrast if possible) and CSF JCV PCR. If CSF is negative but suspicion remains high, repeat CSF and re-review MRI with neuroradiology/neurology.
- Core principle = immune reconstitution:
- HIV: start/optimise ART promptly.
- Drug-associated PML: support immune recovery after withdrawal; consider strategies to speed clearance where appropriate (e.g. plasmapheresis/immunoadsorption has been used in natalizumab-associated PML under specialist protocols).
- Anticipate IRIS: after immune recovery, patients may worsen due to inflammatory rebound (new enhancement/oedema on MRI, clinical deterioration). Manage with senior input; corticosteroids may be used for severe IRIS with mass effect or marked decline, balancing infection control versus inflammation.
- Supportive care: seizure control, swallow assessment/aspiration prevention, VTE prophylaxis when safe, neurorehab early, and early goals-of-care discussions if extensive disease.
📚 References
- AAN consensus diagnostic criteria for PML (Neurology 2013). ([pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov]
- EMA Tysabri overview: risk rises with longer treatment (>2 years highlighted).
- Tysabri patient safety leaflet: PML can occur up to 6 months after stopping.
- Rituximab-associated PML latency (median ~5.5 months from last dose; ~16 months from first dose).
- MHRA: dimethyl fumarate—PML risk with mild lymphopenia.
Categories
- A Level
- About
- Acute Medicine
- Anaesthetics and Critical Care
- Anatomy
- Biochemistry
- Book
- Cardiology
- Collections
- CompSci
- Crib Sheets
- Dental
- Dermatology
- Differentials
- Drugs
- ENT
- Education
- Electrocardiogram
- Embryology
- Emergency Medicine
- Endocrinology
- Ethics
- Foundation Doctors
- GCSE
- Gastroenterology
- General Practice
- Genetics
- Geriatric Medicine
- Guidelines
- Gynaecology
- Haematology
- Hepatology
- Immunology
- Infectious Diseases
- Infographic
- Investigations
- Lists
- Mandatory Training
- Medical Students
- Microbiology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Nutrition
- OSCE
- OSCEs
- Obstetrics
- Obstetrics Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Medicine and Dentistry
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatrics
- Palliative
- Pathology
- Pharmacology
- Physiology
- Procedures
- Psychiatry
- Public Health
- Radiology
- Renal
- Respiratory
- Resuscitation
- Revision
- Rheumatology
- Statistics and Research
- Stroke
- Surgery
- Toxicology
- Trauma and Orthopaedics
- USMLE
- Urology
- Vascular Surgery
