| Download the amazing global Makindo app: Android | Apple | |
|---|---|
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: Educational use only. Not for diagnosis or management. See below for full disclaimer. |
Acne Vulgaris
Related Subjects: | Nikolsky's sign | Koebner phenomenon | Erythema Multiforme | Pyoderma gangrenosum | Erythema Nodosum | Dermatitis Herpetiformis | Lichen Planus | Acanthosis Nigricans | Acne Rosacea | Acne Vulgaris | Alopecia | Vitiligo | Urticaria | Basal Cell Carcinoma | Malignant Melanoma | Squamous Cell Carcinoma | Mycosis Fungoides (Sezary Syndrome) | Xeroderma pigmentosum | Bullous Pemphigoid | Pemphigus Vulgaris | Seborrheic Dermatitis | Pityriasis/Tinea versicolor infections | Pityriasis rosea | Scabies | Dermatomyositis | Toxic Epidermal Necrolysis | Stevens-Johnson Syndrome | Atopic Eczema/Atopic Dermatitis | Psoriasis
Acne Vulgaris is the most common chronic skin condition of adolescence, affecting up to 80–90% of teenagers worldwide 🌍. It is a disease of the pilosebaceous unit, characterised by comedones, inflammatory papules/pustules, and in severe cases, nodules and cysts. Although often dismissed as “cosmetic,” acne can cause significant scarring and psychological morbidity. 💡 Remember: acne is not caused by poor hygiene.
📊 Epidemiology
- Peak onset: 12–18 years; often persists into the mid-20s, occasionally beyond.
- More severe in males (androgen-driven), but more persistent in females.
- Common across all ethnic groups; post-inflammatory pigmentation more problematic in darker skin tones.
- Strong genetic influence – family history is a risk factor.
🧬 Pathophysiology
Acne arises from a combination of 4 interlinked processes within the pilosebaceous unit:
- Sebum overproduction due to androgen stimulation of sebaceous glands.
- Follicular hyperkeratinisation → formation of keratin plugs (comedones).
- Colonisation with Cutibacterium acnes (formerly Propionibacterium acnes) → promotes inflammation.
- Inflammatory cascade → papules, pustules, nodules, scarring.
Additional factors: diet (high glycaemic index foods, dairy 🥛), drugs (steroids, lithium, antiepileptics), and endocrine disorders (e.g. PCOS).
🔎 Clinical Features
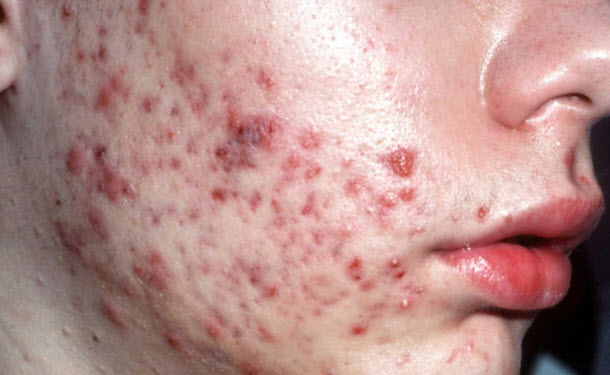
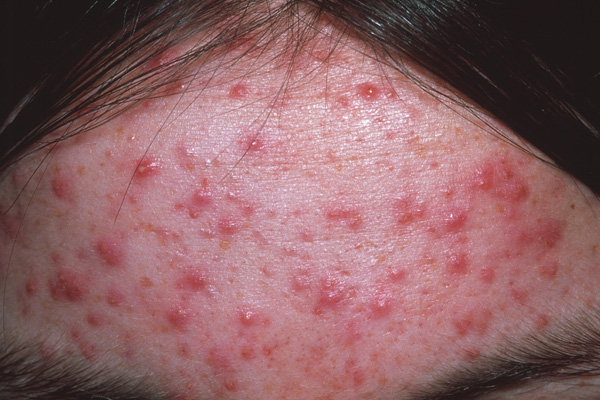
- Lesions: open comedones (blackheads), closed comedones (whiteheads), papules, pustules, nodules, cysts.
- Distribution: face, chest, shoulders, and back.
- Symptoms: may be itchy or painful; often psychological distress is prominent.
- Variants:
- Acne conglobata – severe, nodulocystic, sinus tracts, scarring.
- Acne fulminans – sudden, ulcerative acne with systemic upset (fever, arthralgia, ↑ESR/CRP).
⚖️ Differential Diagnoses
- Rosacea 🌹 (no comedones, later age, flushing, telangiectasia).
- Perioral dermatitis (papules around mouth, spares vermillion border).
- Folliculitis (monomorphic pustules, bacterial/fungal causes).
- Drug-induced acneiform eruptions (steroids, lithium, anti-TB drugs).
- Keratosis pilaris (rough follicular papules on arms/thighs).
⚠️ Complications
- Physical: Atrophic scarring (ice-pick, boxcar), hypertrophic scars, keloids.
- Pigmentation: Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (esp. darker skin).
- Psychological: Depression, anxiety, social withdrawal, suicidal ideation.
- Systemic: Acne fulminans (rare, emergency).
🧪 Investigations
- Diagnosis is clinical ✅ – based on morphology and distribution.
- Consider investigations if:
- Sudden severe onset → exclude drug-induced acneiform rash.
- Signs of hyperandrogenism (oligomenorrhoea, hirsutism, obesity) → screen for PCOS (testosterone, LH, FSH, prolactin, pelvic US).
- Refractory acne → consider culture/swabs (to exclude Gram-negative folliculitis).
💊 Management (Stepwise)
Treatment depends on severity, duration, and impact. Always consider psychological burden.
| Severity | First-line Treatment | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Mild
(comedonal) |
Topical therapies:
|
Combine retinoid + benzoyl peroxide to ↓ resistance. Warn about skin irritation and photosensitivity 🌞. |
| Moderate
(papules/pustules) |
Add oral antibiotics:
|
Duration: 3–6 months. Avoid oral antibiotic monotherapy ❌. Reassess at 12 weeks. |
| Severe / Nodulocystic |
|
Specialist only. Monitor LFTs, fasting lipids. Pregnancy prevention programme essential 🚫🤰. |
| Females (hormonal) |
|
Useful in PCOS. Avoid oestrogen-containing OCP in smokers >35 or clot risk 🚭. |
🌍 Lifestyle & Self-care Advice
- 🧴 Use gentle cleansers; avoid excessive washing or scrubbing (can worsen irritation).
- 🚫 Avoid oily/cosmetic products that are “comedogenic.”
- 🍫 Diet: evidence is mixed, but high-GI foods & dairy may exacerbate acne in some patients.
- ⏳ Emphasise adherence: treatments take 6–8 weeks before improvement is seen.
🧠 Exam Pearls
– Comedones = diagnostic of acne vulgaris. Rosacea never has comedones. – Always combine oral/topical antibiotics with benzoyl peroxide to prevent resistance. – Isotretinoin is highly effective but carries risks: teratogenicity, mood disturbance, hepatotoxicity, ↑ triglycerides. – Psychological morbidity is common: always ask about mood & self-esteem. – Acne fulminans = sudden severe acne + systemic upset → dermatology emergency.
🖼️ Illustrations
Categories
- A Level
- About
- Acute Medicine
- Anaesthetics and Critical Care
- Anatomy
- Biochemistry
- Book
- Cardiology
- Collections
- CompSci
- Crib Sheets
- Dental
- Dermatology
- Differentials
- Drugs
- ENT
- Education
- Electrocardiogram
- Embryology
- Emergency Medicine
- Endocrinology
- Ethics
- Foundation Doctors
- GCSE
- Gastroenterology
- General Practice
- Genetics
- Geriatric Medicine
- Guidelines
- Gynaecology
- Haematology
- Hepatology
- Immunology
- Infectious Disease
- Infectious Diseases
- Infographic
- Investigations
- Lists
- Mandatory Training
- Medical Students
- Microbiology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Nutrition
- OSCE
- Obstetrics
- Obstetrics Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Medicine and Dentistry
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatrics
- Palliative
- Pathology
- Pharmacology
- Physiology
- Procedures
- Psychiatry
- Public Health
- Radiology
- Renal
- Respiratory
- Resuscitation
- Revision
- Rheumatology
- Statistics and Research
- Stroke
- Surgery
- Toxicology
- Trauma and Orthopaedics
- USMLE
- Urology
