| Download the amazing global Makindo app: Android | Apple | |
|---|---|
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: Educational use only. Not for diagnosis or management. See below for full disclaimer. |
Skin Pathology and Description and Examination
Related Subjects: |Anatomy of Skin |Skin and soft tissue and bone infections | Skin or subcutaneous lump |Skin Pathology and Description and Examination
🧪 Pathology
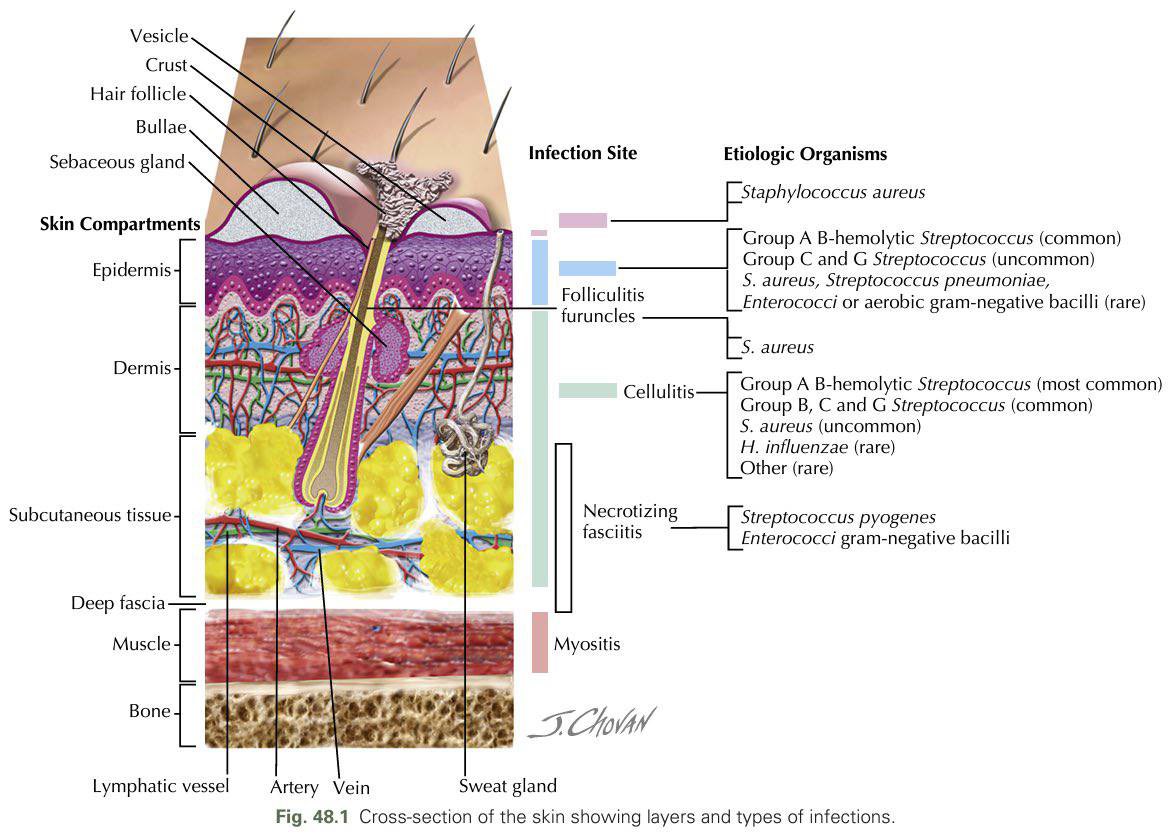
📍 By Location
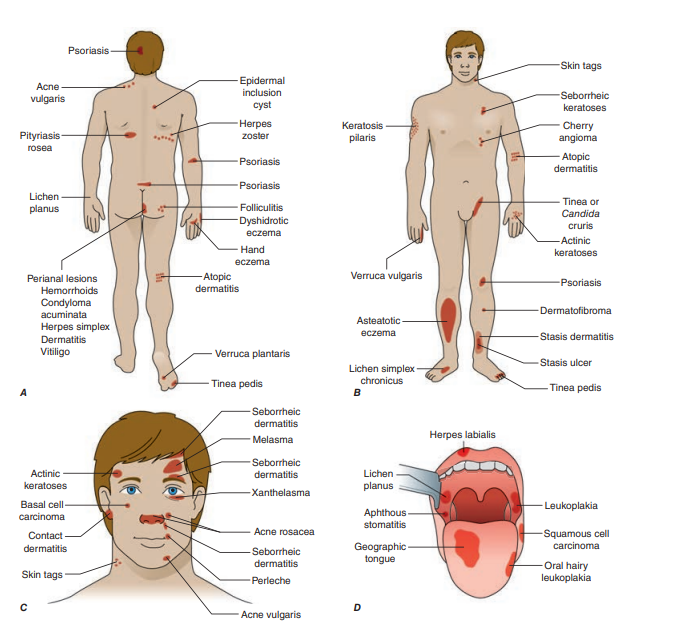
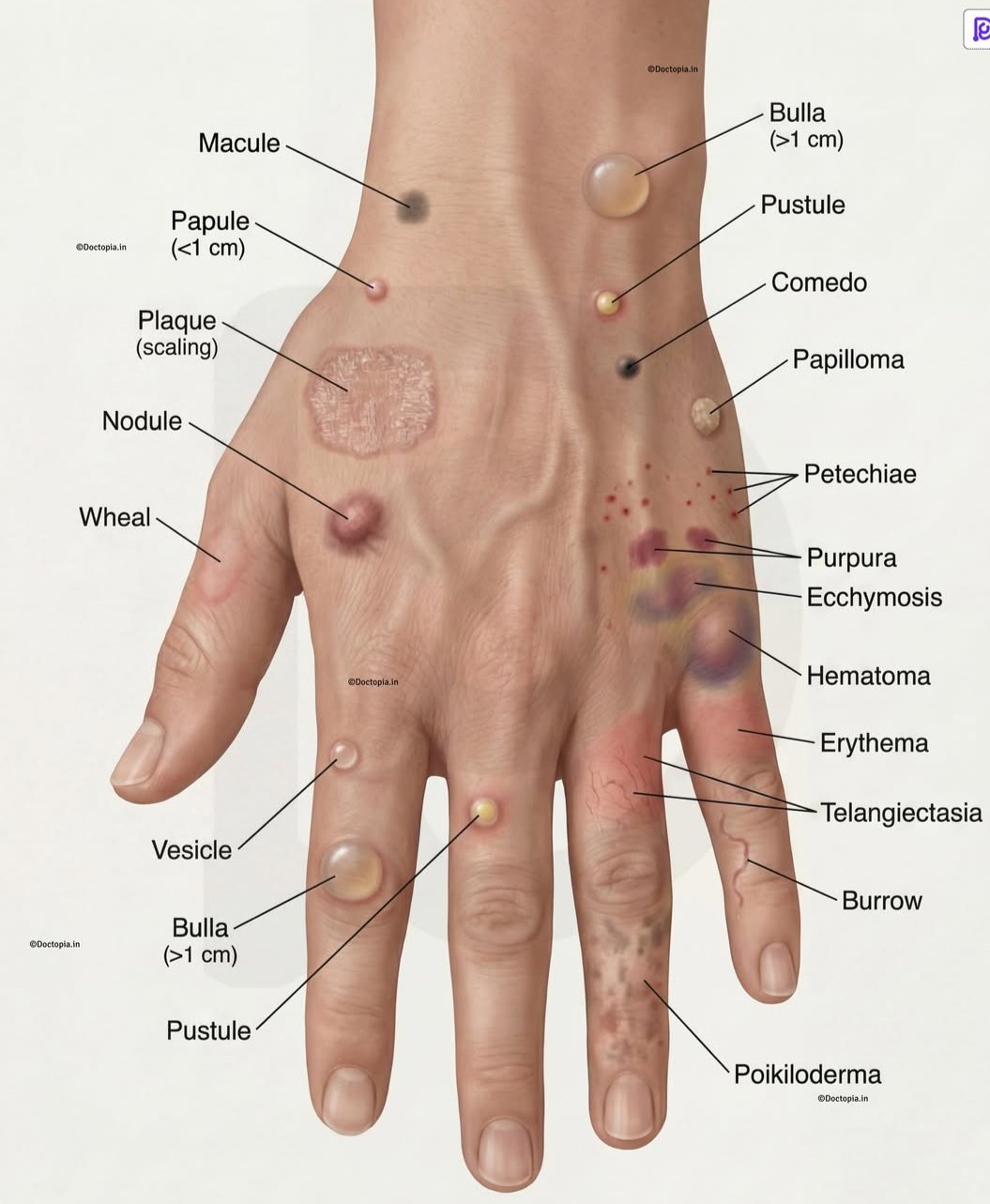
🔍 Examination – Types of Lesions
- 🔴 Macule: Flat lesion < 1 cm
- 🟠 Patch: Flat lesion > 1 cm
- 🔵 Papule: Elevated, palpable lesion < 1 cm
- 🟣 Plaque: Elevated, palpable lesion > 1 cm
- ⚪ Nodule: Deep, palpable lesion < 1 cm (dermal or subcutaneous)
- ⚫ Tumour: Deep, palpable lesion > 1 cm
- 💧 Vesicle: Fluid-filled lesion < 1 cm
- 💦 Bulla: Fluid-filled lesion > 1 cm
- 🟡 Cyst: Nodule with semi-solid or fluid material
- 🤢 Pustule: Elevated lesion with pus (white, grey, yellow, green)
- 🩹 Erosion: Epidermal disruption, heals without scarring
- 🩸 Ulcer: Extends into dermis, heals with scarring
- 🟤 Crust: Dried serum/blood/pus (e.g., impetigo)
- ⚖️ Scale: Excess keratin (e.g., seborrheic dermatitis)
- 🪵 Lichenification: Thickened skin with exaggerated markings (e.g., chronic eczema)
- ✂️ Fissure: Linear skin slit
- 🪶 Excoriation: Scratch mark
- 🌵 Xerosis: Pathological dryness of skin, mucosa, or conjunctiva
- ⬇️ Atrophy: Thinning/depression from reduced cell/tissue mass
- ⚫ Comedones: Sebum + keratin plugs in acne (blackheads/whiteheads)
- 🟣 Purpura: Non-blanchable dermal bleeding
- 🔴 Petechiae: Small pinpoint purpura
- 🟢 Ecchymosis: Larger flat purpura ("bruise")
- 🔍 Telangiectasia: Dilated superficial blood vessels, blanchable
- ⭐ Scar: Fibrosis replacing dermis/subcutis
- 💨 Wheal: Transient, blanchable dermal edema (e.g., urticaria)
📖 Descriptive Terms
- ✋ Acral: Hands & feet (e.g., hand-foot-mouth)
- ⭕ Annular: Ring-shaped (e.g., granuloma annulare)
- 🧵 Follicular: Hair follicle lesions (e.g., folliculitis)
- 💧 Guttate: Drop-like pattern (e.g., guttate psoriasis)
- ⚡ Koebner Phenomenon: Lesions appear at trauma sites (psoriasis, warts)
- 🌡️ Morbilliform: Measles-like maculopapular rash
- 🕸️ Reticular: Net-like (e.g., livedo reticularis)
- 🎯 Target/Iris: Concentric rings (e.g., erythema multiforme)
- 🌱 Satellite: Smaller lesions around a main one (e.g., candida)
- 🐍 Serpiginous: Snake-like (e.g., cutaneous larva migrans)
- ✨ Other: Discrete, clustered, linear, confluent, indurated
🦠 Infectious Causes
- 🟡 Impetigo: Honey-crust lesions (children). ➡️ Topical mupirocin; oral antibiotics if extensive.
- 🔴 Cellulitis: Red, hot, tender swelling (often leg). ➡️ Oral/IV antibiotics, limb elevation.
- ⭕ Tinea (Ringworm): Annular scaly plaques. ➡️ Topical antifungals (clotrimazole); oral terbinafine if severe.
🔥 Inflammatory Causes
- 🪨 Psoriasis: Silvery, well-demarcated plaques on extensors. ➡️ Topical steroids, phototherapy, methotrexate.
- 🌾 Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis): Itchy, erythematous, scaly patches (flexural). ➡️ Emollients, topical steroids, antihistamines.
- ☣️ Contact Dermatitis: Red, blistered rash after irritant/allergen. ➡️ Avoid trigger, topical steroids.
🦠 Viral Causes
- 🌋 Herpes Zoster (Shingles): Painful vesicular rash along dermatome. ➡️ Acyclovir, analgesia, gabapentin for pain.
- 🧩 Warts (Verrucae): Rough, raised lesions (hands/feet/genitals). ➡️ Salicylic acid, cryotherapy, excision.
🧬 Malignant Causes
- ⚪ Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC): Pearly, vascular nodule (face). ➡️ Excision, Mohs, topical therapy if small.
- 🔺 Squamous Cell Carcinoma (SCC): Red nodule/ulcer on sun-exposed skin. ➡️ Excision, cryo, radiotherapy if advanced.
- ⚫ Melanoma: Asymmetric, irregular, colour-varied lesion (ABCDE). ➡️ Wide excision, lymph node biopsy, immunotherapy if advanced.
🔶 Other Causes
- 🌞 Actinic Keratosis: Scaly patches on sun-exposed skin; precancerous. ➡️ 5-FU cream, cryo, photodynamic therapy.
- 💜 Lichen Planus: Purple, polygonal, pruritic papules (wrists, ankles, genitals). ➡️ Steroids, antihistamines, phototherapy if severe.
Categories
- A Level
- About
- Acute Medicine
- Anaesthetics and Critical Care
- Anatomy
- Anatomy and Physiology
- Biochemistry
- Book
- Cardiology
- Collections
- CompSci
- Crib Sheets
- Crib sheets
- Dental
- Dermatology
- Differentials
- Drugs
- ENT
- Education
- Electrocardiogram
- Embryology
- Emergency Medicine
- Endocrinology
- Ethics
- Foundation Doctors
- GCSE
- Gastroenterology
- General Practice
- Genetics
- Geriatric Medicine
- Guidelines
- Gynaecology
- Haematology
- Hepatology
- Immunology
- Infectious Diseases
- Infographic
- Investigations
- Lists
- Mandatory Training
- Medical Students
- Microbiology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Nutrition
- OSCE
- OSCEs
- Obstetrics
- Obstetrics Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Medicine and Dentistry
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatrics
- Palliative
- Pathology
- Pharmacology
- Physiology
- Procedures
- Psychiatry
- Public Health
- Radiology
- Renal
- Respiratory
- Resuscitation
- Revision
- Rheumatology
- Statistics and Research
- Stroke
- Surgery
- Toxicology
- Trauma and Orthopaedics
- USMLE
- Urology
- Vascular Surgery
