| Download the app: Android | Apple | |
|---|---|
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: Educational use only. Not for diagnosis or management. |
Metabolic alkalosis
Related Subjects: |Metabolic acidosis |Metabolic alkalosis |Arterial Blood gas analysis
🌡️ Analysis of Blood Gas (Metabolic Alkalosis)
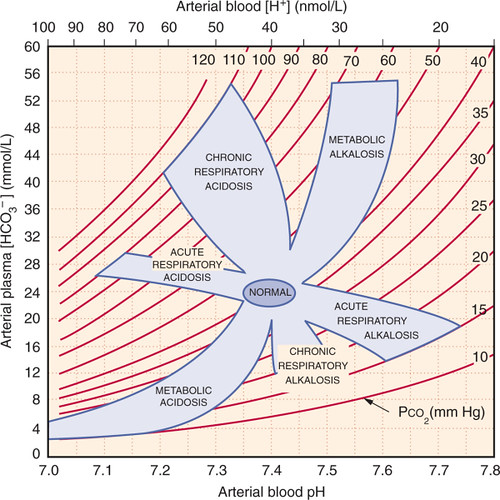
- 📉 pH > 7.45 (alkalosis)
- ⬆️ HCO₃⁻ increased (primary cause)
- PaCO₂ usually normal (unless compensated with hypoventilation)
- PaO₂ usually normal
- ⚡ Often associated with hypokalaemia
🔎 Aetiology
- Caused by either acid loss (vomiting, NG suction) or alkali gain (bicarbonate, milk-alkali syndrome).
📋 Causes and Management
| 🩺 Cause | 🤒 Clinical Features | 🔬 Diagnostic Tests | 💊 Management |
|---|---|---|---|
| 🤮 Vomiting / NG Suction | Loss of HCl → dehydration, postural hypotension | ABG: ↑pH, ↑HCO₃⁻
U&E: ↓Cl⁻, ↓K⁺ |
IV 0.9% NaCl + K⁺ replacement
Stop suction / treat vomiting |
| 💊 Diuretics (Loop / Thiazide) | Weakness, dizziness, dehydration | ABG: ↑pH, ↑HCO₃⁻
Electrolytes: ↓K⁺, ↓Cl⁻ |
Stop / adjust diuretic
IV saline + KCl supplements |
| 🧬 Hyperaldosteronism | HTN, muscle weakness, thirst, polyuria | ABG: ↑pH, ↑HCO₃⁻
Electrolytes: ↓K⁺, ↑Na⁺ Renin: ↓, Aldosterone: ↑ |
Treat cause (e.g., adrenal adenoma)
Spironolactone / eplerenone |
| 💉 Excess Bicarbonate | Confusion, paraesthesia, cramps, fluid overload | ABG: ↑pH, ↑HCO₃⁻
Electrolytes: ↑Na⁺, ↓K⁺ |
Stop bicarbonate
Treat underlying acidosis cause |
| ⚡ Hypokalaemia | Weakness, palpitations, arrhythmias (PVCs) | ECG: U waves, flat T waves
Serum: ↓K⁺ |
Potassium replacement (oral / IV)
Treat underlying cause |
| 💧 Contraction Alkalosis | Dehydration (dry mouth, low BP) | ABG: ↑pH, ↑HCO₃⁻
U&E: ↓Cl⁻, ↓K⁺ Urine Cl⁻: low |
IV 0.9% NaCl + KCl
Correct volume loss |
| 🥛 Milk-Alkali Syndrome | Nausea, vomiting, confusion, kidney stones | ABG: ↑pH
Electrolytes: ↑Ca²⁺, ↑HCO₃⁻ Creatinine ↑ |
Stop Ca²⁺ / antacids
IV fluids Severe hypercalcaemia → bisphosphonates |
📝 Key Clinical Pearls
- 🔄 Compensation is usually by hypoventilation (↑PaCO₂).
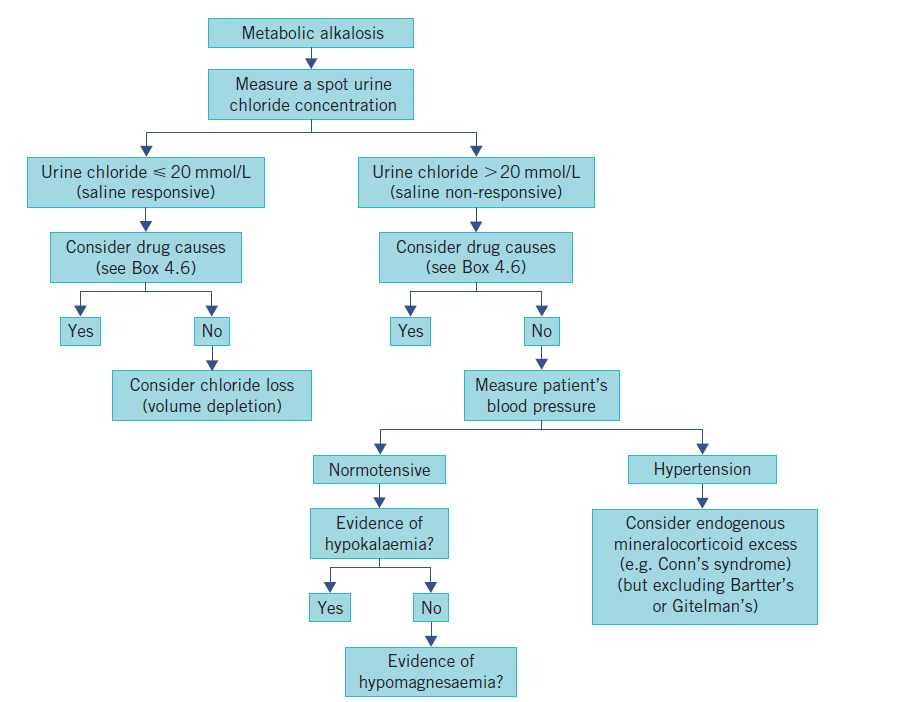
- 🧪 Urine chloride helps: low (<15 mmol/L) suggests vomiting/diuretics, high (>20 mmol/L) suggests mineralocorticoid excess.
- ⚠️ Hypokalaemia and hypochloraemia are hallmarks and must be corrected.
🩺 Case 1 — Vomiting-Induced Alkalosis
A 45-year-old woman presents with 5 days of persistent vomiting from severe gastritis. She is weak, dizzy, and hypotensive. Labs: pH 7.50, HCO₃⁻ 36 mmol/L, K⁺ 2.8 mmol/L, Cl⁻ low. Management: 💧 IV 0.9% saline and potassium replacement to correct volume and electrolyte deficits. Treat underlying cause of vomiting. Avoid: ❌ Continuing NG suction or antiemetics alone without fluid/electrolyte correction.
🩺 Case 2 — Diuretic-Induced Alkalosis
A 72-year-old man with chronic heart failure on furosemide presents with weakness and muscle cramps. Vitals stable. Labs: pH 7.48, HCO₃⁻ 34 mmol/L, K⁺ 3.0 mmol/L. Management: 💊 Review diuretic dose, replace potassium and magnesium, consider adding potassium-sparing diuretic (spironolactone, amiloride). Avoid: ❌ Escalating loop diuretic dose without electrolyte monitoring.
🩺 Case 3 — Post-Hypercapnic Alkalosis
A 65-year-old man with COPD on home oxygen is admitted with acute hypercapnic respiratory failure. After aggressive ventilation in ICU, his PaCO₂ normalises but labs now show pH 7.52, HCO₃⁻ 36 mmol/L, K⁺ 3.4 mmol/L. Management: 🏥 Careful weaning of ventilation, electrolyte correction (K⁺, Cl⁻), acetazolamide may be considered to promote renal bicarbonate excretion. Avoid: ❌ Over-ventilation leading to sudden CO₂ drop; avoid bicarbonate administration.
Categories
- A Level
- About
- Acute Medicine
- Anaesthetics and Critical Care
- Anatomy
- Biochemistry
- Book
- Cardiology
- Collections
- CompSci
- Crib Sheets
- Dental
- Dermatology
- Differentials
- Drugs
- ENT
- Education
- Electrocardiogram
- Embryology
- Emergency Medicine
- Endocrinology
- Ethics
- Foundation Doctors
- GCSE
- Gastroenterology
- General Practice
- Genetics
- Geriatric Medicine
- Guidelines
- Gynaecology
- Haematology
- Hepatology
- Immunology
- Infectious Disease
- Infectious Diseases
- Infographic
- Investigations
- Lists
- Mandatory Training
- Medical Students
- Microbiology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Nutrition
- OSCE
- Obstetrics
- Obstetrics Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Medicine and Dentistry
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatrics
- Palliative
- Pathology
- Pharmacology
- Physiology
- Procedures
- Psychiatry
- Public Health
- Radiology
- Renal
- Respiratory
- Resuscitation
- Revision
- Rheumatology
- Statistics and Research
- Stroke
- Surgery
- Toxicology
- Trauma and Orthopaedics
- USMLE
- Urology
