Makindo Medical Notes"One small step for man, one large step for Makindo" |
|
|---|---|
| Download all this content in the Apps now Android App and Apple iPhone/Pad App | |
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: The contents are under continuing development and improvements and despite all efforts may contain errors of omission or fact. This is not to be used for the assessment, diagnosis, or management of patients. It should not be regarded as medical advice by healthcare workers or laypeople. It is for educational purposes only. Please adhere to your local protocols. Use the BNF for drug information. If you are unwell please seek urgent healthcare advice. If you do not accept this then please do not use the website. Makindo Ltd. |
ECG - Sinoatrial block
-
| About | Anaesthetics and Critical Care | Anatomy | Biochemistry | Cardiology | Clinical Cases | CompSci | Crib | Dermatology | Differentials | Drugs | ENT | Electrocardiogram | Embryology | Emergency Medicine | Endocrinology | Ethics | Foundation Doctors | Gastroenterology | General Information | General Practice | Genetics | Geriatric Medicine | Guidelines | Haematology | Hepatology | Immunology | Infectious Diseases | Infographic | Investigations | Lists | Microbiology | Miscellaneous | Nephrology | Neuroanatomy | Neurology | Nutrition | OSCE | Obstetrics Gynaecology | Oncology | Ophthalmology | Oral Medicine and Dentistry | Paediatrics | Palliative | Pathology | Pharmacology | Physiology | Procedures | Psychiatry | Radiology | Respiratory | Resuscitation | Rheumatology | Statistics and Research | Stroke | Surgery | Toxicology | Trauma and Orthopaedics | Twitter | Urology
Related Subjects: |ECG Basics |ECG Axis |ECG Analysis |ECG LAD |ECG RAD |ECG Low voltage |ECG Pathological Q waves |ECG ST/T wave changes |ECG LBBB |ECG RBBB |ECG short PR |ECG Heart Block |ECG Asystole and P wave asystole |ECG QRS complex |ECG ST segment |ECG: QT interval |ECG: LVH |ECG RVH |ECG: Bundle branch blocks |ECG Dominant R wave in V1 |ECG Acute Coronary Syndrome |ECG Sino atrial block
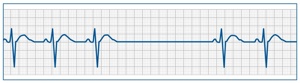
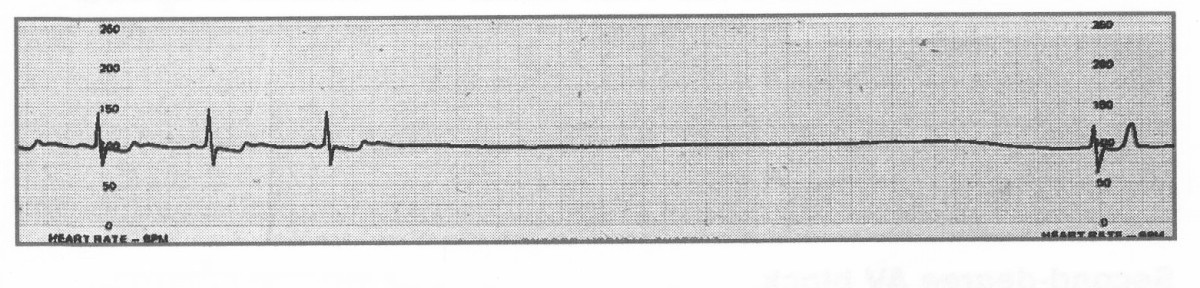
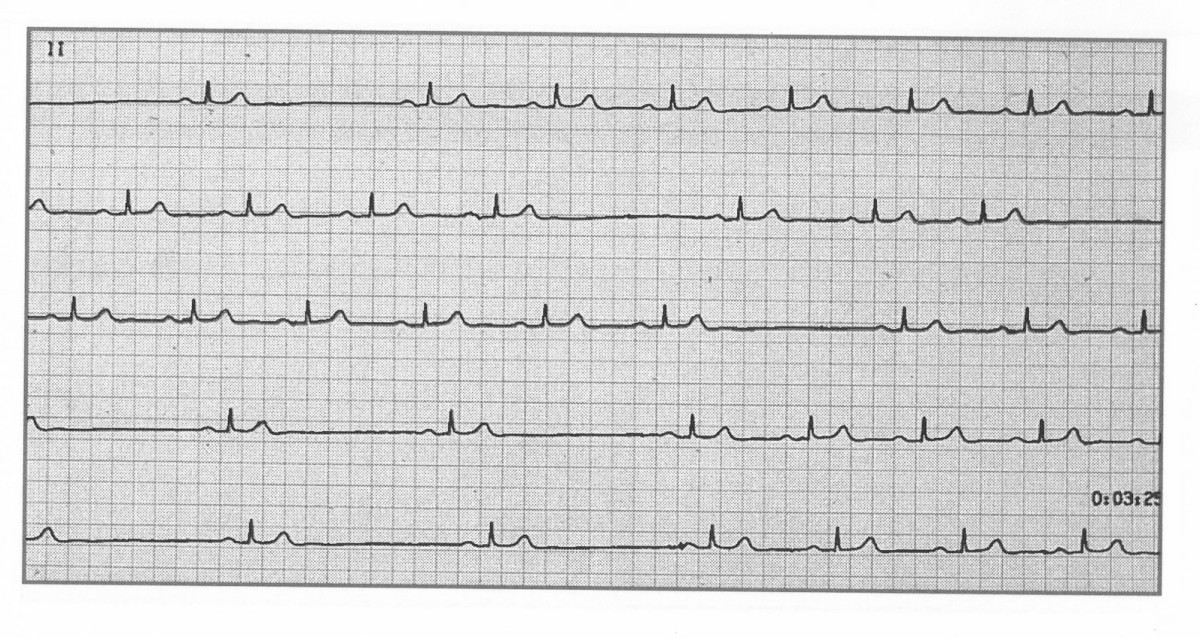
Sinoatrial (SA) block occurs when impulses from the SA node are delayed or fail to reach the atria. This leads to intermittent pauses in atrial and ventricular activity. Causes include high vagal tone (e.g., in athletes or during sleep), medications that depress conduction, or intrinsic SA node disease. Continuous monitoring (e.g., 24-hour Holter) may be needed for diagnosis, particularly in patients with infrequent symptoms. Pauses >3 seconds, especially if associated with syncope, dizziness, or fatigue, often prompt consideration for a pacemaker. ⚡
🫀 About Sinoatrial Block
- Definition: Failure or delay of impulse conduction from the SA node to atria.
- Mechanism:
- Failure of impulse initiation (intrinsic node dysfunction).
- Impulse generation occurs but is blocked before reaching the atria.
📌 Aetiology
- Increased Vagal Tone: Common in young athletes, during sleep, or in vasovagal episodes.
- Medications: Beta-blockers, calcium channel blockers, digoxin, amiodarone.
- Intrinsic SA Node Disease: Age-related fibrosis, sick sinus syndrome.
- Other Causes: Myocarditis, ischaemic heart disease, electrolyte imbalance (esp. hyperkalemia), thyroid dysfunction.
📊 Types of Sinoatrial Block
- First-Degree: Delay in conduction, invisible on ECG, asymptomatic.
- Second-Degree: Intermittent failure of conduction → dropped beats.
- Type I (Wenckebach): Progressive delay then dropped beat (rare, difficult to see).
- Type II: Random dropped beats without progressive delay → more serious, risk of progression.
- Third-Degree (Complete): No impulses conducted → complete pause, may require escape rhythm.
💡 Exam Tip: Differentiate SA block from sinus arrest – in SA block, the pause is an exact multiple of the normal P-P interval; in sinus arrest, it is not.
🩺 Clinical Features
- Symptoms: Dizziness, presyncope, fatigue, palpitations, syncope (if long pauses).
- Signs: Bradycardia, irregular pauses on auscultation or telemetry.
🔎 Investigations
- 24-Hour Holter / Event Recorder: For intermittent blocks.
- Electrolytes: Look for hyperkalemia, magnesium/calcium disturbances.
- Thyroid Function: Both hypo- and hyperthyroidism can precipitate bradyarrhythmia.
- Echocardiography: If structural disease is suspected.
⚕️ Management
- Review and withdraw offending drugs if possible.
- Correct reversible causes (electrolytes, thyroid, myocarditis).
- Pacemaker: Indicated for symptomatic patients (e.g., syncope, presyncope, heart failure) or if pauses >3 seconds, in line with ESC/NICE pacing guidelines.
🚨 Key Clinical Pearl: Symptomatic SA block is considered part of the "sick sinus syndrome" spectrum and usually requires pacing. Asymptomatic pauses <3 seconds may not need intervention.