🦠 Coronavirus SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19): As of October 2020, there are insufficient data to recommend for or against specific antiviral or immune-based therapies for patients with mild COVID-19. Management is largely supportive except in severe/critical illness.
📖 About
- COVID-19 is caused by SARS-CoV-2, a novel coronavirus identified in late 2019.
- It spreads via droplets, aerosols, and fomites, with a high potential for human-to-human transmission.
🌍 Origin
- First identified in Wuhan, China, December 2019, linked to wet markets with close contact between humans and live animals.
🔬 Aetiology
- SARS-CoV-2 has four key structural proteins:
- Spike (S) 🗝️ – binds ACE2 receptors (lungs, GI, kidneys, brain).
- Envelope (E) 📦 – viral assembly & release.
- Matrix (M) 🧱 – structural stability.
- Nucleocapsid (N) 🧬 – protects viral RNA.
- Primary pathology = viral pneumonia, mortality ≈ 1% (higher in elderly/comorbid).
🧫 Pathology
- Hyaline membranes, pneumocyte desquamation, mononuclear infiltrates, and fibroblastic proliferation.
- ACE2 receptor expression beyond lungs explains multi-organ involvement (kidneys, heart, brain, liver).
⚠️ Groups at Higher Risk
- 👵 Elderly & nursing home residents.
- Comorbidities: diabetes, obesity, hypertension, chronic lung disease, cancer, immunosuppression.
- Higher risk in some ethnic groups (South Asian, Afro-Caribbean).
- Possible role of low vitamin D and immune variation under study.
🩺 Clinical Features
- Incubation: 2–14 days (avg ~5 days).
- Common: fever 🌡️, dry cough, dyspnoea, fatigue, myalgia, headache, confusion.
- Less common: sore throat, rhinorrhoea, chest pain, diarrhoea, nausea/vomiting.
- Complications: viral pneumonia → type 1 RF, myocarditis ❤️, AKI 🧽.
📊 Severity Classification
- Asymptomatic: PCR+ but no symptoms.
- Mild: fever/cough, no hypoxia.
- Moderate: lower respiratory disease, SpO₂ ≥94% RA.
- Severe: RR >30, SpO₂ <94%, PaO₂/FiO₂ <300, >50% lung infiltrates.
- Critical: respiratory failure, septic shock, MODS.
🚑 Complications
- Cytokine Storm 🌪️ – hyperinflammatory response → ARDS, shock.
- Cardiac ❤️ – myocarditis, arrhythmias, ACS-like syndromes.
- Renal/Liver 🧽 – AKI, liver enzyme rise; ~15% critical cases need renal replacement therapy.
🔍 Investigations
- Bloods: lymphopenia, ↑ CRP, ↑ D-dimer, ± deranged LFTs.
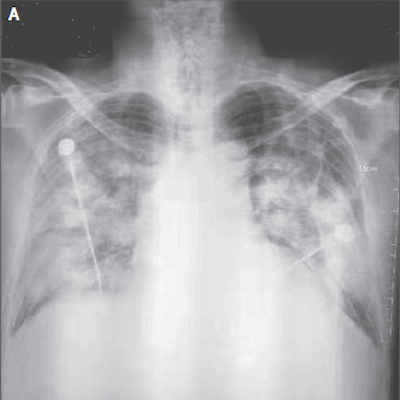
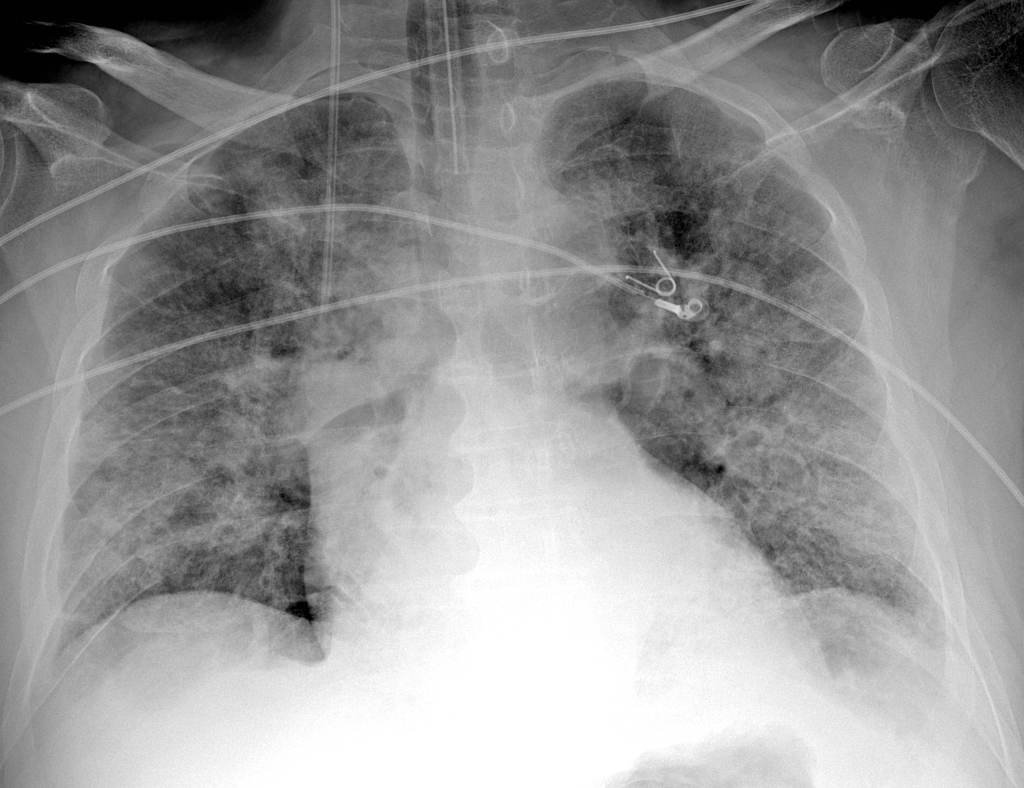
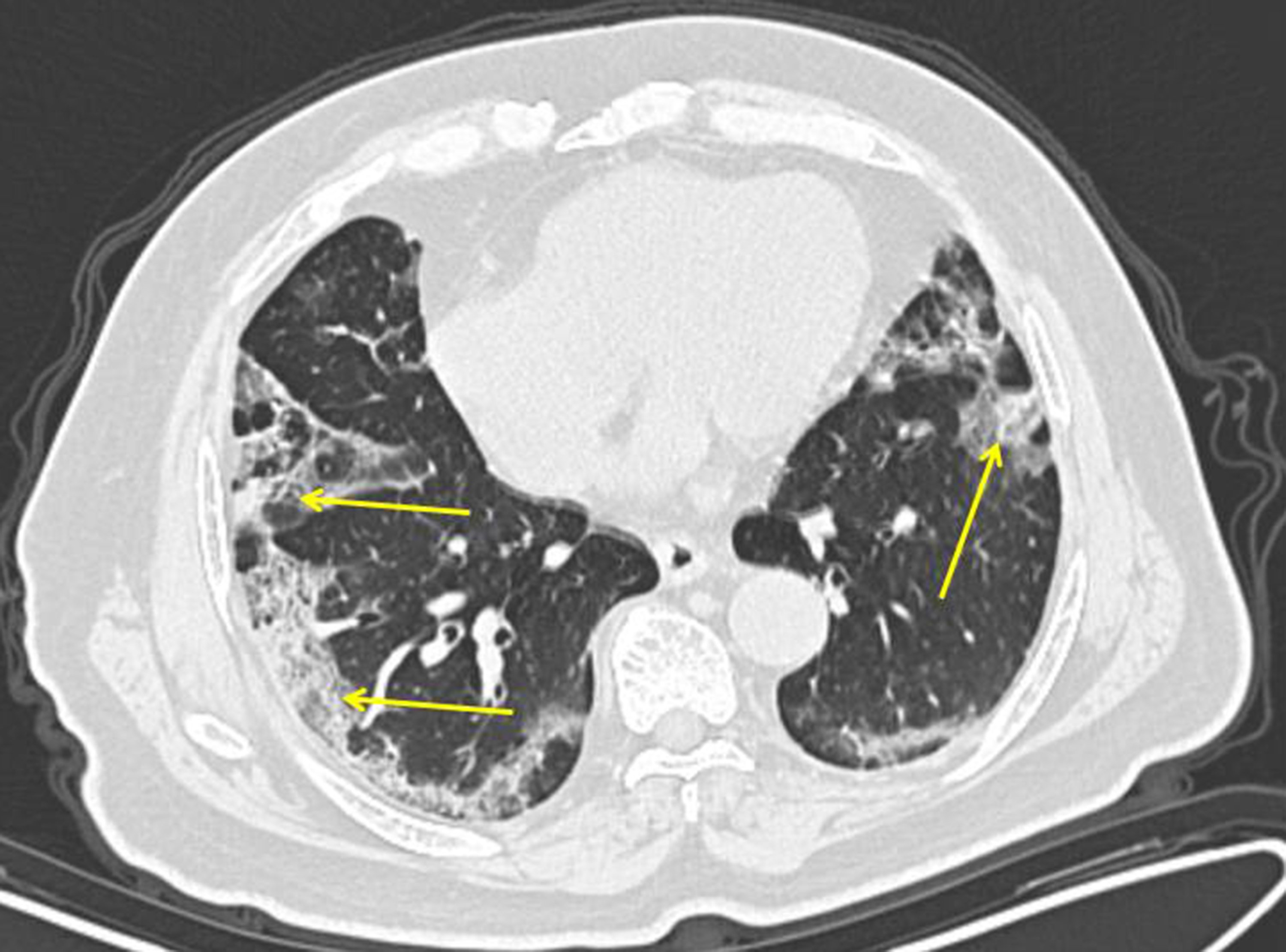
- Imaging: CXR → patchy bilateral opacities. CT → ground-glass opacities 🌫️. CTPA → rule out PE (common complication).
- Diagnostic: RT-PCR nasal/throat swabs; antibody testing (past exposure).
- Biomarkers: ↑ troponin/BNP if cardiac involvement.
🛡️ Prevention
- 😷 Masks, 🤲 hand hygiene, ↔️ social distancing.
- 📞 Contact tracing & isolation of exposures.
- Environmental: PPE, aseptic technique, waste & linen safety, regular cleaning/disinfection.
💊 Management
- Supportive: IV fluids, O₂ therapy 🎭, treat sepsis.
- Respiratory support: – High-flow O₂ / NIV 😷 if needed. – Intubation/ventilation in critical cases (low tidal volume + prone).
- Drugs: – Dexamethasone 6 mg OD × up to 10 days if requiring O₂ e.g. sats < 92-94%. – Remdesivir = limited/experimental.
- Thromboprophylaxis 🩸: LMWH due to high VTE risk.
