| Download the amazing global Makindo app: Android | Apple | |
|---|---|
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: Educational use only. Not for diagnosis or management. See below for full disclaimer. |
Massive Haemorrhage and Massive Transfusion Protocol (MTP)
Massive haemorrhage is one of the most life-threatening emergencies in medicine and surgery. It refers to uncontrolled, acute blood loss that overwhelms the body’s compensatory mechanisms. If not rapidly recognised and treated, it leads to hypovolaemic shock, multi-organ failure, and death. Understanding the causes, pathophysiology, clinical signs, and management is essential for safe practice.
🔬 Pathophysiology of Major Bleeding
- Circulatory compromise: Acute blood loss ↓ preload → ↓ cardiac output → tissue hypoperfusion.
- Compensatory response: Tachycardia, vasoconstriction, catecholamine surge initially maintain BP.
- Oxygen delivery: Reduced haemoglobin leads to anaerobic metabolism → lactic acidosis.
- Coagulopathy: Dilution by fluids, consumption of clotting factors, and hypothermia impair clot formation.
- Triad of death: Acidosis, hypothermia, coagulopathy → spiralling deterioration if not corrected.
🩸 Causes of Major Haemorrhage
- Trauma: Road traffic collisions, penetrating injuries, pelvic fractures.
- Surgical/iatrogenic: Intra-operative vascular injury, post-operative bleeding.
- Obstetric: Post-partum haemorrhage (PPH), placental abruption, uterine rupture.
- Gastrointestinal: Variceal bleed, peptic ulcer perforation, diverticular haemorrhage.
- Vascular pathology: Ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA), arterial rupture, aneurysm leak.
- Medical causes: Coagulopathy (anticoagulation, liver failure, DIC).
⚠️ Signs and Symptoms of Major Bleeding
- Early: Tachycardia, narrow pulse pressure, tachypnoea, pallor, sweating, anxiety.
- Progressive: Hypotension, confusion, oliguria, clammy skin.
- Late/decompensated: Coma, absent peripheral pulses, cardiac arrest (PEA common).
- Note: Elderly patients or those on β-blockers may not mount a tachycardic response — always assess perfusion and trend observations.
🛠️ Early Management Priorities
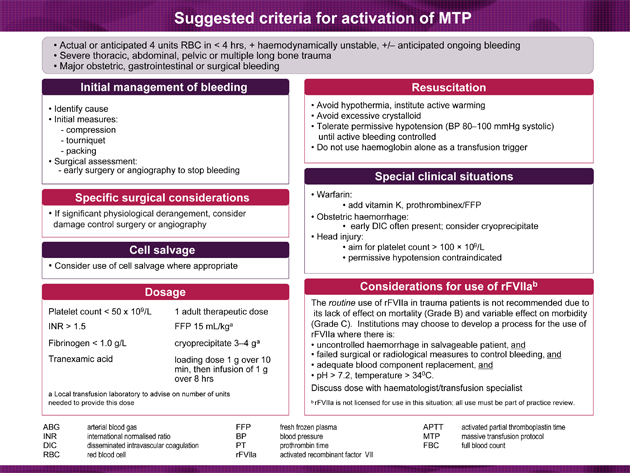
- 📞 Call for senior help & activate Massive Transfusion Protocol (MTP) early.
- 🫁 Airway & Breathing: Give high-flow O₂; intubate if airway threatened or GCS low.
- ❤️ Circulation: 2 large-bore IV lines (14–16G) or central access. Take bloods: FBC, U&E, coagulation, fibrinogen, group & save, crossmatch.
- 🦴 IV alternatives: Intraosseous access if IV fails.
- 🩹 Control bleeding: Direct pressure, tourniquet, pelvic binder, surgical packing, urgent surgical/IR referral.
- 💧 Limit crystalloids: Small boluses only → avoid dilution of clotting factors.
- 💊 Tranexamic acid (TXA): Give early in trauma (<3 hrs): 1 g IV bolus, then 1 g over 8 hrs.
- 🌡️ Prevent hypothermia: Forced-air warming blankets, warmed IV fluids/blood.
- 📈 Monitoring: ECG, SpO₂, NIBP/arterial line, catheter for urine output.
🩸 What is Massive Haemorrhage?
Defined as:
- Loss of one blood volume in 24 hrs, OR
- 50% blood volume in 3 hrs, OR
- Bleeding >150 ml/min.
It requires rapid activation of a Massive Transfusion Protocol (MTP) to restore volume, correct coagulopathy, and maintain tissue oxygenation.
📖 Principles of Safe Transfusion
- Always aim for ABO & Rhesus compatibility.
- Antibody screen: Detects red cell alloantibodies.
- Cross-match: Ensures safe donor-recipient match.
- ⚠️ Do not delay urgent transfusion in exsanguinating patients — group-specific or O negative should be given if necessary.
📊 Summary Table – Major Haemorrhage
| Cause | Key Signs & Symptoms | Initial Management | Advanced Management |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trauma 🚗🔪 | External bleeding, hypovolaemia, shock | Direct pressure, tourniquet, pelvic binder, activate MTP | Damage-control surgery, interventional radiology, balanced transfusion |
| Obstetric 👩🍼 | Postpartum haemorrhage, uterine atony, shock | Uterine massage, IV access, fluids, TXA, activate obstetric MTP | Surgical repair, hysterectomy, cryoprecipitate for fibrinogen replacement |
| GI Bleed 🍷 | Haematemesis, melaena, shock, anaemia | Resuscitate, IV access, O₂, NG tube, TXA (if trauma-related only) | Endoscopy, banding/sclerotherapy, surgery, MTP if massive |
| Vascular (AAA rupture) 💔 | Pulsatile abdominal mass, collapse, severe pain | Permissive hypotension, call vascular team, rapid transfusion | Emergency vascular repair (open/endovascular), massive transfusion |
| Surgical/Iatrogenic 🏥 | Intra/post-operative bleeding, drains filling rapidly | Call senior help, compress if possible, resuscitate | Return to theatre, haemostasis, balanced transfusion |
| Medical (Coagulopathy, DIC) 🧪 | Oozing wounds, mucosal bleeding, prolonged clotting | Stop anticoagulants, send coagulation screen, vitamin K if appropriate | FFP, cryoprecipitate, platelets, haematology input |
🚨 Emergency Transfusion Strategy
- Permissive hypotension: SBP 80–100 mmHg until bleeding controlled (unless head injury — keep normotension).
- Head injury: Maintain normotension and platelets >75–100 ×10⁹/L.
- Obstetrics: Anticipate DIC → give fibrinogen/cryoprecipitate early.
- Group-specific blood: Fastest safe option if blood group known.
- Uncrossmatched blood: O negative RBCs for females of childbearing age; O positive acceptable in adult males.
- Transfuse as fast as required for haemodynamic stability.
💉 Massive Transfusion Protocol (MTP)
- Balanced transfusion: RBC : FFP : Platelets ≈ 1:1:1 (some centres 6:4:1).
- Tranexamic acid: Give early in trauma (<3 hrs).
- Haematological targets:
- Hb > 80 g/L
- Platelets > 50 ×10⁹/L (≥100 ×10⁹/L if CNS bleeding)
- Fibrinogen > 1.5 g/L (cryoprecipitate if low)
- INR/PT ratio < 1.5
- Adjuncts:
- Calcium replacement (prevent citrate toxicity from transfusion).
- Warm all fluids and blood → prevent hypothermia.
- Monitor for hyperkalaemia (stored blood).
- Repeat bloods every 30–60 min: FBC, coagulation, fibrinogen, ABG, lactate, calcium.
📊 Physiological Targets (Damage Control Resuscitation)
- Temperature > 35 °C
- pH > 7.2
- Base excess > -6
- Lactate < 4 mmol/L
- Ionised Ca²⁺ normal
- Platelets > 50 ×10⁹/L
- Fibrinogen > 1.5 g/L
🧠 Key Concept: “Triad of Death”
🔻 Hypothermia
🔻 Acidosis
🔻 Coagulopathy
These factors worsen one another in a vicious cycle.
Prevent by early balanced transfusion, correction of acidosis, active warming, and minimal crystalloid.
📚 Clinical Pearls
- 🚨 Think haemorrhage first in trauma or post-op collapse until proven otherwise.
- Never delay surgery/IR for cross-match — haemostasis saves lives.
- Coagulopathy kills more often than anaemia — monitor clotting closely.
- In obstetrics, anticipate DIC early.
- Debrief and audit every MTP activation for learning and quality improvement.
Categories
- A Level
- About
- Acute Medicine
- Anaesthetics and Critical Care
- Anatomy
- Anatomy and Physiology
- Biochemistry
- Book
- Cardiology
- Collections
- CompSci
- Crib Sheets
- Crib sheets
- Dental
- Dermatology
- Differentials
- Drugs
- ENT
- Education
- Electrocardiogram
- Embryology
- Emergency Medicine
- Endocrinology
- Ethics
- Foundation Doctors
- GCSE
- Gastroenterology
- General Practice
- Genetics
- Geriatric Medicine
- Guidelines
- Gynaecology
- Haematology
- Hepatology
- Immunology
- Infectious Diseases
- Infographic
- Investigations
- Lists
- Mandatory Training
- Medical Students
- Microbiology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Nutrition
- OSCE
- OSCEs
- Obstetrics
- Obstetrics Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Medicine and Dentistry
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatrics
- Palliative
- Pathology
- Pharmacology
- Physiology
- Procedures
- Psychiatry
- Public Health
- Radiology
- Renal
- Respiratory
- Resuscitation
- Revision
- Rheumatology
- Statistics and Research
- Stroke
- Surgery
- Toxicology
- Trauma and Orthopaedics
- USMLE
- Urology
- Vascular Surgery
