| Download the amazing global Makindo app: Android | Apple | |
|---|---|
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: Educational use only. Not for diagnosis or management. See below for full disclaimer. |
Eczema/Dermatitis
Related Subjects: |Nikolsky's sign |Koebner phenomenon |Psoriatic Arthritis |Psoriasis |Eczema/Dermatitis |Anatomy of Skin | Topical Steroids
💡 Red flag: Widespread herpes simplex infection (eczema herpeticum) should be suspected in any patient with rapidly worsening atopic eczema ⚡. This is a dermatological emergency → immediate referral to dermatology/paediatrics.
📖 About
- Chronic inflammatory skin disease with intense pruritus and eczematous lesions in characteristic sites:
- 👶 Infants: face, scalp, extensor surfaces
- 🧒 Children/adults: flexural surfaces (elbows, knees, neck)
🧬 Aetiology
- Combination of genetic and environmental factors.
- Defects in skin barrier proteins (e.g., filaggrin) → ↑ permeability, sensitivity to allergens, irritants, microbes.
- Often associated with the atopic triad: eczema, asthma, allergic rhinitis 🤧.
📊 Epidemiology
- 15–20% of school-aged children 👦
- 2–10% of adults 👩
- Frequently improves with age, but some persist into adulthood.
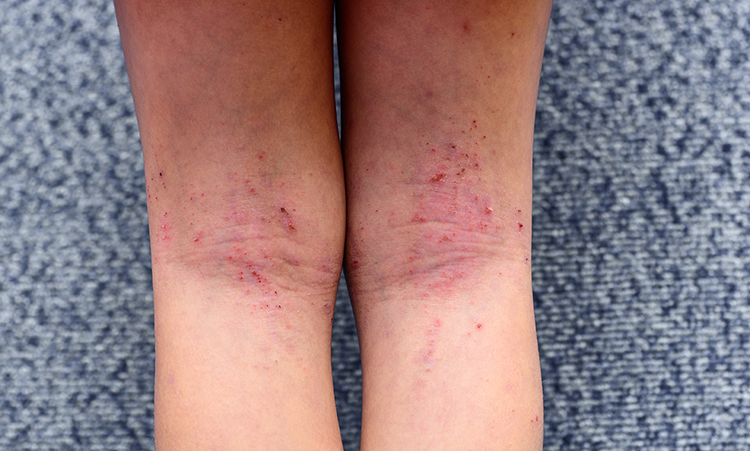
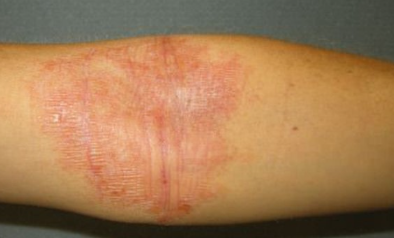
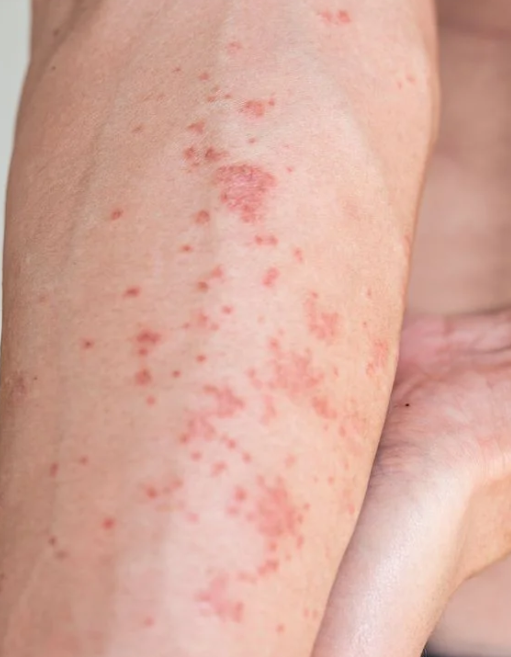
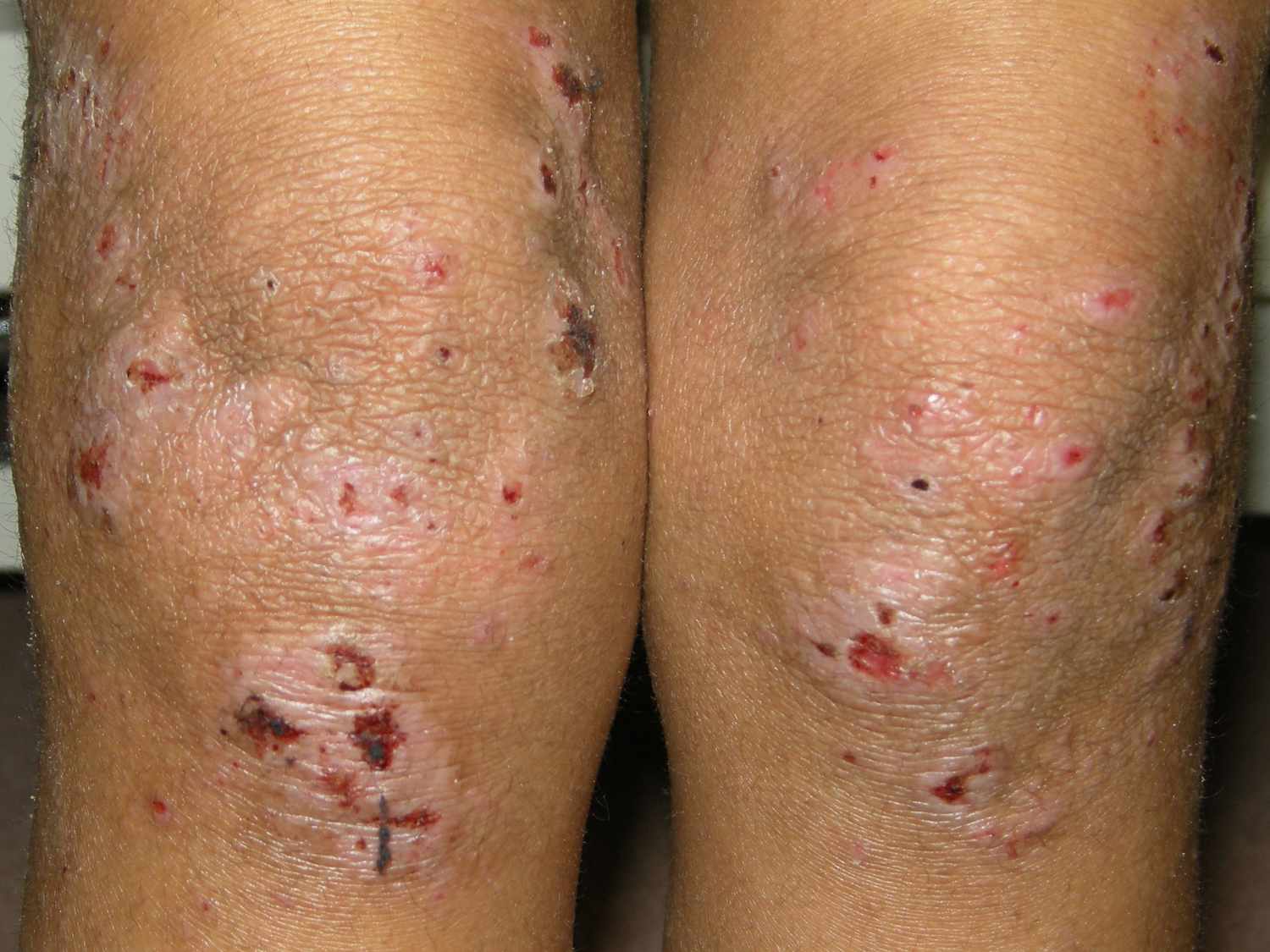
🩺 Clinical Presentation
- Dry, itchy 🔥, erythematous skin with papules, vesicles, excoriations.
- Flexural distribution common; severe disease → lichenification, cracking, oozing.
- Complications: bacterial infection (impetiginisation), eczema herpeticum (HSV), widespread fungal infections.
📏 Severity Classification
- ✅ Clear: Normal skin
- 🙂 Mild: Small patches, occasional itching
- 😣 Moderate: Frequent itching, redness, excoriations
- 🚨 Severe: Widespread, thickened skin, bleeding/oozing, sleep disturbance
🔎 Clinical Forms
- Atopic dermatitis: Flexural eczema, chronic relapsing course
- Contact dermatitis: Allergic or irritant trigger (nickel, detergents)
- Seborrhoeic dermatitis: Scalp/face involvement; “cradle cap” in infants
- Xerotic eczema: Dry skin–related, common in elderly
🛠️ Management
- 💧 Emollients: Foundation of care; applied liberally & often, including soap substitutes
- 💊 Topical corticosteroids: Step-up by potency depending on site/severity; “fingertip unit” rule for dosing
- 🧴 Topical calcineurin inhibitors: (tacrolimus, pimecrolimus) for steroid-sparing use
- 🦠 Infection control: Treat secondary bacterial infection (flucloxacillin); oral antibiotics NOT for routine use
- 💤 Antihistamines: Sedating antihistamines for severe nocturnal itch
- ☀️ Phototherapy / Immunosuppressants: Consider if severe refractory disease (dermatology-led)
- 🥛 Diet/environment: Avoid known triggers; routine exclusion diets not recommended unless proven allergy
📌 Exam Tips
- Always mention emollients + steroid ladder as first-line 🪜
- Know red flags: eczema herpeticum, recurrent infections
- Remember psychosocial impact → poor sleep, bullying, school issues
📚 References
Categories
- A Level
- About
- Acute Medicine
- Anaesthetics and Critical Care
- Anatomy
- Anatomy and Physiology
- Biochemistry
- Book
- Cardiology
- Collections
- CompSci
- Crib Sheets
- Dental
- Dermatology
- Differentials
- Drugs
- ENT
- Education
- Electrocardiogram
- Embryology
- Emergency Medicine
- Endocrinology
- Ethics
- Foundation Doctors
- GCSE
- Gastroenterology
- General Practice
- Genetics
- Geriatric Medicine
- Guidelines
- Gynaecology
- Haematology
- Hepatology
- Immunology
- Infectious Diseases
- Infographic
- Investigations
- Lists
- Mandatory Training
- Medical Students
- Microbiology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Nutrition
- OSCE
- OSCEs
- Obstetrics
- Obstetrics Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Medicine and Dentistry
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatrics
- Palliative
- Pathology
- Pharmacology
- Physiology
- Procedures
- Psychiatry
- Public Health
- Radiology
- Renal
- Respiratory
- Resuscitation
- Revision
- Rheumatology
- Statistics and Research
- Stroke
- Surgery
- Toxicology
- Trauma and Orthopaedics
- USMLE
- Urology
- Vascular Surgery
