| Download the amazing global Makindo app: Android | Apple | |
|---|---|
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: Educational use only. Not for diagnosis or management. See below for full disclaimer. |
Wernicke Korsakoff Syndrome
Related Subjects: |Psychiatric Emergencies |Depression |Mania |Schizophrenia |Suicide |Acute Psychosis |Delusions |General Anxiety Disorder |Obsessive-Compulsive disorder |Wernicke Korsakoff Syndrome |Medically Unexplained symptoms |Postpartum/Postnatal Depression |Postpartum / Postnatal Psychosis |Eating disorders in Children
⚠️ Always give Pabrinex (parenteral thiamine) to anyone who is malnourished, alcoholic, or has hyperemesis — before giving carbohydrates or glucose. If not available then IV Thiamine 300-500 mg three times daily for 3 days should be prescribed and should be given by infusion over 30 minutes. 💉 Pabrinex (10 ml) contains: Ascorbic acid 500 mg, Glucose 1 g, Nicotinamide 160 mg, Pyridoxine 50 mg, Riboflavin 4 mg, Thiamine 250 mg. 🚨 Untreated Wernicke’s encephalopathy can progress to Korsakoff’s syndrome a chronic, often irreversible amnestic state.
| 🚑 Initial Management Summary |
|---|
|
📖 About
- 🧑🔬 First described by Carl Wernicke in 1881.
- 🧠 Classic triad: confusion, ataxia, ophthalmoplegia (but present in <20% cases).
- ⚡ Caused by thiamine deficiency (body stores last ~18 days).
- 🔎 Associated with memory impairment, nystagmus, and confabulation.
👁️ Clinical Signs of Acute Wernicke’s Encephalopathy
- 👀 Ophthalmoplegia → diplopia, horizontal/vertical nystagmus.
- 👁️ Weakness of lateral rectus or impaired conjugate gaze.
- 🚶 Ataxia → unsteady gait and stance.
- 🌀 Confusion, poor attention, possible confabulation.
- 🧩 May coexist with peripheral neuropathy or cerebellar signs.
➡️ If Untreated → Chronic Korsakoff’s Syndrome
- 🧠 Severe memory loss (anterograde > retrograde).
- 📖 Confabulation (fabricated stories to fill memory gaps).
- 👓 Hallucinations, disorientation.
- 🛑 Irreversible amnestic state → lifelong disability.
🛑 Causes / Precipitants
- 🍺 Alcohol misuse → impaired absorption, reduced hepatic storage.
- 🥀 Malnutrition → starvation, anorexia nervosa.
- 🤰 Hyperemesis gravidarum.
- ⚖️ Rapid weight loss or bariatric surgery.
- 🦠 Malabsorption syndromes (IBD, coeliac).
- 💉 Precipitated by infection, surgery, trauma, or carbohydrate load.
🔎 Differentials
- 🩸 Hepatic encephalopathy (↑ ammonia).
- 🦠 Encephalitis (LP/MRI if suspected).
- 🍷 Alcoholic neuropathy or cranial nerve palsies.
- 🧠 Hypothalamic tumours/lesions.
- 🧾 Syphilis, CO poisoning, subarachnoid haemorrhage, head trauma.
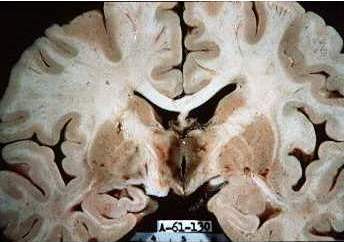
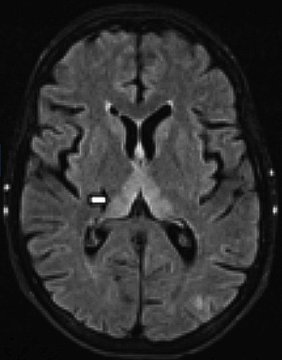
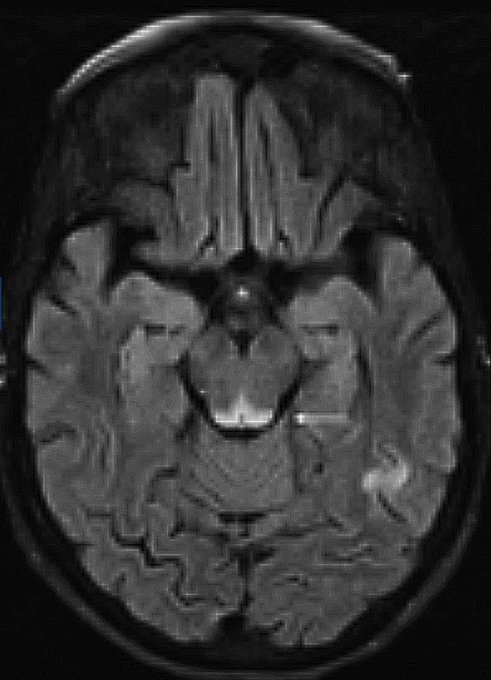
🧩 Pathology: Lesions in mamillary bodies, medial thalamus, hypothalamus, and periaqueductal grey. 🧲 MRI: T2/FLAIR hyperintensities ± diffusion restriction in these regions.
🧪 Investigations
- 🧮 Routine confusion screen: U&E, Mg, LFTs.
- 🔬 Specific: ↓ red cell transketolase, ↓ thiamine, ↑ pyruvate.
- 🧠 CT head: exclude bleed or subdural haematoma.
- 🧲 MRI brain: thalamic/periaqueductal changes; diencephalic atrophy in Korsakoff’s.
- 🌬️ ABG: exclude hypoxia, hypercarbia, COHb.
- ⚰️ Post-mortem: punctate haemorrhages around 3rd/4th ventricles & aqueduct.
Prevention of Wernicke’s encephalopathy
- People at high risk of Wernicke’s encephalopathy can have a range of conditions, including: significant weight loss poor diet, low BMI (<18), other signs of malnutrition, memory disturbance, peripheral neuropathy, previous history of Wernicke’s encephalopathy
- NICE CG100(opens in a new tab) recommends to offer prophylactic parenteral thiamine followed by oral thiamine(opens in a new tab) to harmful or dependent drinkers if they: are malnourished or at risk of malnourishment or have decompensated liver disease and in addition. They attend an emergency department or are admitted to hospital with an acute injury or illness
- Consider IV or IM thiamine(opens in a new tab) 200 to 300mg once daily for at least 3 days in high risk and then oral
💊 Management of Wernicke’s encephalopathy
- 💉 Thiamine replacement
- Pabrinex IV for 3 days (2–3 pairs TDS) → then oral thiamine lifelong.
- Thiamine 300-500 mg IV TDS for 2–3 days. Continue thiamine 400 mg IV three times daily on day 4 and 5 switch to oral thiamine if appropriate. Day 6 give oral thiamine if appropriate or give thiamine 400 mg IV once daily until cognition plateaus.
- Ensure magnesium is monitored, and corrected if necessary, during Pabrinex or thiamine treatment
- ⚠️ Rare risk: anaphylaxis to parenteral thiamine.
- ⚡ Correct electrolytes: esp. magnesium & potassium.
- 🍺 Address alcohol dependence → detox programme, community support.
- 🧠 Psychiatric and cognitive support for long-term sequelae.
💡 Teaching Pearl: Always give thiamine before glucose in any patient at risk. NICE/UK guidance emphasises routine use of IV Pabrinex in alcohol withdrawal with malnutrition, preventing irreversible brain injury.
Cases — Wernicke–Korsakoff Syndrome
- Case 1 — Acute Wernicke’s encephalopathy 🍺: A 52-year-old man with chronic alcohol misuse is admitted with confusion, unsteady gait, and horizontal nystagmus. Exam: ataxia and ophthalmoplegia. Diagnosis: Wernicke’s encephalopathy (thiamine deficiency). Treated urgently with IV thiamine before glucose to prevent progression.
- Case 2 — Korsakoff’s psychosis 🧠: A 47-year-old woman with long-standing alcohol dependence is found to have profound memory impairment. She fills in memory gaps with fabricated stories (confabulation). She recalls her childhood but cannot remember events from the previous day. Diagnosis: Korsakoff’s syndrome. Managed with thiamine supplementation and abstinence, but cognitive impairment often persists.
- Case 3 — Non-alcoholic cause ⚕️: A 60-year-old man following prolonged total parenteral nutrition without adequate vitamin supplementation develops confusion, ataxia, and diplopia. MRI: mammillary body changes. Diagnosis: Wernicke’s encephalopathy secondary to malnutrition. Treated with IV thiamine, with partial neurological recovery.
Teaching Point 🩺: Wernicke–Korsakoff is due to thiamine (vitamin B1) deficiency, classically from alcohol misuse but also malnutrition, hyperemesis, or TPN. Wernicke’s = triad of ophthalmoplegia, ataxia, confusion (acute, reversible). Korsakoff’s = chronic amnesia + confabulation (often irreversible). Always give IV thiamine before glucose.
Categories
- A Level
- About
- Acute Medicine
- Anaesthetics and Critical Care
- Anatomy
- Anatomy and Physiology
- Biochemistry
- Book
- Cardiology
- Collections
- CompSci
- Crib Sheets
- Crib sheets
- Dental
- Dermatology
- Differentials
- Drugs
- ENT
- Education
- Electrocardiogram
- Embryology
- Emergency Medicine
- Endocrinology
- Ethics
- Foundation Doctors
- GCSE
- Gastroenterology
- General Practice
- Genetics
- Geriatric Medicine
- Guidelines
- Gynaecology
- Haematology
- Hepatology
- Immunology
- Infectious Diseases
- Infographic
- Investigations
- Lists
- Mandatory Training
- Medical Students
- Microbiology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Nutrition
- OSCE
- OSCEs
- Obstetrics
- Obstetrics Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Medicine and Dentistry
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatrics
- Palliative
- Pathology
- Pharmacology
- Physiology
- Procedures
- Psychiatry
- Public Health
- Radiology
- Renal
- Respiratory
- Resuscitation
- Revision
- Rheumatology
- Statistics and Research
- Stroke
- Surgery
- Toxicology
- Trauma and Orthopaedics
- USMLE
- Urology
- Vascular Surgery
