| Download the amazing global Makindo app: Android | Apple | |
|---|---|
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: Educational use only. Not for diagnosis or management. See below for full disclaimer. |
Susac syndrome
Related Subjects: |Neurological History taking |Causes of Stroke |Ischaemic Stroke |Hypertension |CADASIL |CARASIL
🧠👁️👂 Susac's syndrome is a rare autoimmune microangiopathy affecting the brain, retina, and cochlea. 💡 Always consider in young women with hearing loss + visual disturbance + encephalopathy. Classical triad = 1) Sensorineural hearing loss, 2) Branched Retinal Artery Occlusions (BRAOs), 3) Encephalopathy.
📖 Introduction
- First described by John O. Susac in 1979.
- Autoimmune endotheliopathy causing microinfarctions in the cochlea, retina, and brain.
- Predominantly affects young women.
🔺 Classical Triad
- 🧠 Subacute encephalopathy.
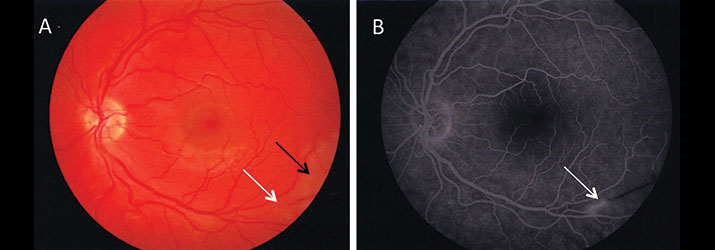
- 👁️ Retinal arteriolar branch occlusions (BRAOs).
- 👂 Sensorineural hearing loss.
🧬 Aetiology / Pathology
- Microangiopathy with microinfarcts in cochlea, retina, corpus callosum.
- Corpus callosum = most frequently affected region.
- Possible role of anti-endothelial cell antibodies.
🔎 Clinical Features
- 🧠 Cognitive changes: headache, memory loss, personality change, confusion, seizures.
- 🚶 Ataxia, migrainous headaches, delirium.
- 👁️ Acute visual loss from BRAOs.
- 👂 Asymmetric, bilateral sensorineural hearing loss (low-frequency loss).
- 📈 Typically monophasic, lasting 2–4 years; may relapse, especially in pregnancy.
🧪 Investigations
- 🧪 Bloods: Often normal (FBC, U&E, CRP).
- 💉 CSF: ↑ protein, mild lymphocytosis.
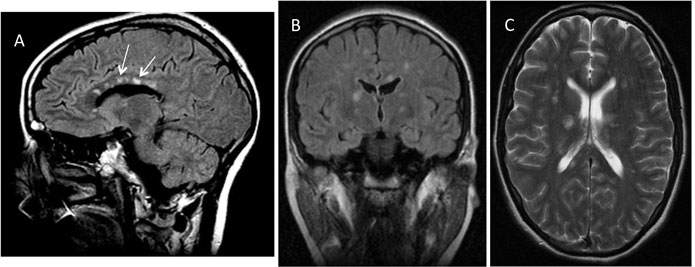
- 🧲 MRI: Pathognomonic findings:
- Central corpus callosum lesions ("snowball" lesions).
- “String of pearls” or “spoke lesions” along the callosal roof.
- Leptomeningeal enhancement (⅓ cases).
- 🌈 Fluorescein angiography: BRAOs.
- 🎧 Audiogram: Low-frequency sensorineural loss.
🖼️ Imaging Examples
 |
 |
⚖️ Differential Diagnoses
- Atypical MS or ADEM.
- CADASIL, SLE, APL syndrome, vasculitis.
- Neuro-Behçet’s disease.
- Lymphoma, temporal arteritis.
- Cogan’s syndrome (ocular + vestibuloauditory, no encephalopathy).
💊 Management
- 🎯 Immunotherapy (mainstay):
- IV methylprednisolone, then oral prednisolone taper.
- IVIG or plasmapheresis for refractory/active disease.
- Immunosuppressants: azathioprine, mycophenolate, rituximab, cyclophosphamide.
- 👂 Hearing loss: Intratympanic dexamethasone may give temporary relief.
- 🔄 Monitoring: Serial MRI, audiometry, and fluorescein angiography to track disease activity.
- 🧠 Course is usually self-limiting (2–4 yrs), but relapse prevention and close follow-up essential.
📚 References
Categories
- A Level
- About
- Acute Medicine
- Anaesthetics and Critical Care
- Anatomy
- Anatomy and Physiology
- Biochemistry
- Book
- Cardiology
- Collections
- CompSci
- Crib Sheets
- Crib sheets
- Dental
- Dermatology
- Differentials
- Drugs
- ENT
- Education
- Electrocardiogram
- Embryology
- Emergency Medicine
- Endocrinology
- Ethics
- Foundation Doctors
- GCSE
- Gastroenterology
- General Practice
- Genetics
- Geriatric Medicine
- Guidelines
- Gynaecology
- Haematology
- Hepatology
- Immunology
- Infectious Diseases
- Infographic
- Investigations
- Lists
- Mandatory Training
- Medical Students
- Microbiology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Nutrition
- OSCE
- OSCEs
- Obstetrics
- Obstetrics Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Medicine and Dentistry
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatrics
- Palliative
- Pathology
- Pharmacology
- Physiology
- Procedures
- Psychiatry
- Public Health
- Radiology
- Renal
- Respiratory
- Resuscitation
- Revision
- Rheumatology
- Statistics and Research
- Stroke
- Surgery
- Toxicology
- Trauma and Orthopaedics
- USMLE
- Urology
- Vascular Surgery
