| Download the amazing global Makindo app: Android | Apple | |
|---|---|
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: Educational use only. Not for diagnosis or management. See below for full disclaimer. |
Internal Jugular vein Cannulation
Related Subjects: Atropine |Acute Anaphylaxis |Basic Life Support |Advanced Life Support |Adrenaline/Epinephrine |Acute Hypotension |Cardiogenic shock |Distributive Shock |Hypovolaemic or Haemorrhagic Shock |Obstructive Shock |Septic Shock and Sepsis |Shock (General Assessment) |Toxic Shock Syndrome
Key Message (2025–2026 Guidelines): Real-time ultrasound guidance is the standard of care for IJV cannulation in adults and children (elective & most emergency cases). It significantly reduces mechanical complications (arterial puncture, pneumothorax), number of attempts, and time to success while improving first-pass rate (ASE 2025, ACS, Society of Hospital Medicine).
🔑 Preparation & Safety Principles
- Formal training & supervision required before independent attempts. Always assess necessity vs. risk – central lines have serious complications.
- Document clear justification (indication, risks discussed, consent obtained). Poor prognostic factors: emergency insertion, obesity (BMI >35), coagulopathy (INR >1.5, platelets <50,000), mechanical ventilation, hypotension/shock.
- Involve senior colleague if any doubt, anatomical variation, or high-risk patient.
- Use full aseptic technique (maximal barrier precautions: cap, mask, sterile gown/gloves, large drape, chlorhexidine skin prep).
✅ Indications
- Difficult/long-term peripheral IV access failure
- Infusion of irritant/vasoactive drugs (vasopressors, chemotherapy, TPN, high-concentration K+)
- Central venous pressure (CVP) monitoring
- Advanced haemodynamic monitoring (PiCCO, Swan-Ganz/PA catheter)
- ScvO₂ / central venous oxygen saturation monitoring
- Temporary cardiac pacing
- Extracorporeal therapies (CRRT, ECMO, plasmapheresis)
- Interventional procedures (IVC filter placement, venous stenting, catheter-directed thrombolysis)
🚫 Contraindications
- Absolute: Patient refusal/lack of consent (or best-interest form if lacking capacity), IJV thrombosis/obstruction (confirmed on US), local infection at site, inexperienced operator without supervision.
- Relative: Severe coagulopathy/bleeding risk (correct if possible; many guidelines now allow with precautions), raised ICP (avoid if pneumothorax risk high), severe respiratory failure, distorted anatomy (neck mass, clavicle fracture, previous surgery/radiation), uncooperative patient unable to tolerate position, contralateral pneumonectomy (avoid ipsilateral side).
📡 Equipment & Ultrasound Guidance (Mandatory Where Available)
- Real-time 2D ultrasound guidance with high-frequency linear probe (preferred over landmark technique – reduces arterial puncture by ~70%, overall complications by ~70%). Use sterile probe cover + gel.
- Distinguish vein vs. artery:
- Vein: larger, elliptical/collapsible, non-pulsatile, dilates with Valsalva/Trendelenburg, compressible.
- Artery: smaller, circular, pulsatile, non-compressible, pulsatile Doppler flow.
- Other equipment: sterile pack, lidocaine 1%, 18G introducer needle, guidewire, dilator, triple-lumen CVC (or appropriate catheter), suture kit, transparent dressing.
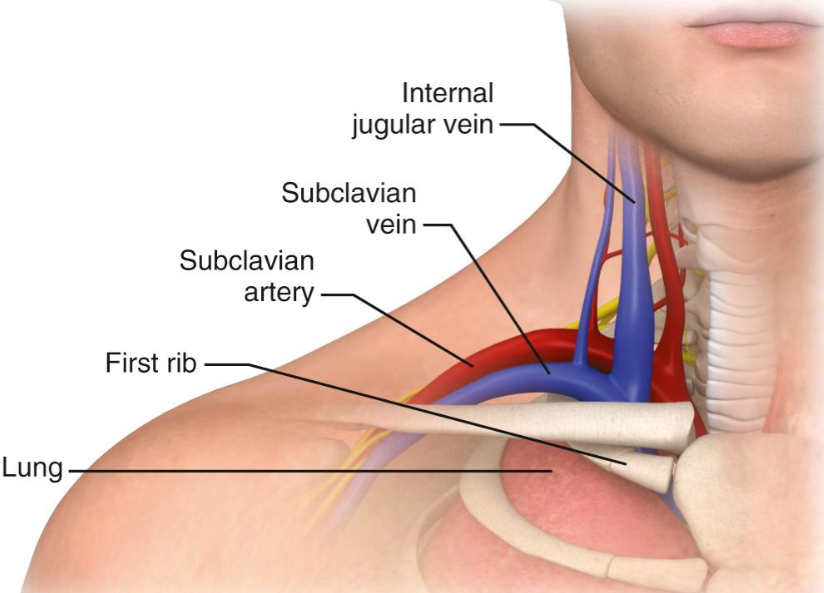
📍 Anatomy & Patient Positioning
- IJV: originates at jugular foramen, descends in carotid sheath (lateral to common carotid artery, anterior to vagus nerve), joins subclavian vein behind sternoclavicular joint to form brachiocephalic vein.
- Preferred side: Right IJV (straighter path to SVC, lower chylothorax risk, larger vein in most patients).
- Position: Supine, 10–15° Trendelenburg (increases vein diameter, reduces air embolism risk). Slight contralateral head turn (<30° – excessive rotation increases IJV-carotid overlap).
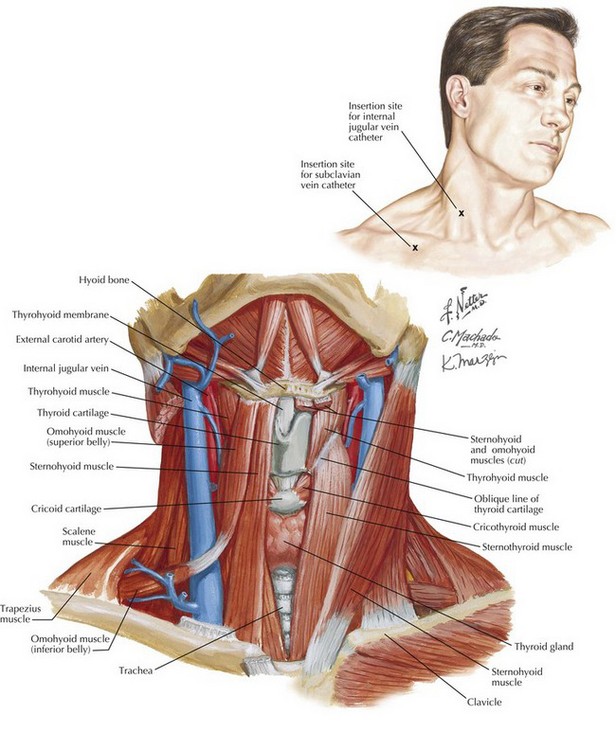
🧵 Technique (Real-Time US-Guided Seldinger – Preferred)
- Scan neck in transverse (short-axis) or longitudinal (long-axis) view to identify optimal puncture site (minimize IJV-carotid overlap, confirm patency/size >7 mm diameter ideal).
- Infiltrate local anaesthetic under US guidance.
- Insert 18G needle under real-time US (in-plane or out-of-plane technique) – confirm venous blood (non-pulsatile, dark).
- Advance guidewire (J-tip first) – monitor ECG for arrhythmias (withdraw if ectopics occur); avoid excessive depth.
- Dilate tract, advance catheter over wire (13–15 cm right IJV, 17–20 cm left to cavo-atrial junction/SVC above pericardial reflection).
- Aspirate all lumens, flush with saline, secure with sutures, apply occlusive dressing.
- Confirm tip position & exclude pneumothorax with CXR (or intra-procedural US/echo if available).
⚠️ Complications & Prevention
- 🫁 Pneumothorax/haemothorax (1–3% landmark, <1% US-guided) – higher approach, real-time US, avoid deep insertion.
- 💨 Air embolism – Trendelenburg, occlude needle hub, Valsalva if awake.
- ❤️ Arrhythmias – monitor ECG, limit guidewire depth (<20 cm).
- 🩸 Arterial puncture/cannulation (6–9% landmark, <1–2% US) – US identification, needle lateral to carotid, never force wire if resistance.
- 🍼 Chylothorax (left side, thoracic duct injury) – prefer right IJV.
- 🦠 Catheter-related bloodstream infection – maximal barriers, chlorhexidine, prompt removal when no longer needed.
- Other: hematoma, thrombosis, malposition, nerve injury (rare).
🖼️ Recommended Visual Resources
- NEJM Video: Ultrasound-Guided Internal Jugular Vein Cannulation (2010, still gold-standard technique) – Watch here
- NEJM Central Venous Catheterization Overview – Link
- Search for recent ASE 2025 guidelines figures or POCUS101 step-by-step images for updated diagrams.
📚 Key References (2025–2026)
- ASE Guidelines: Ultrasound-Guided Vascular Cannulation (2025)
- Association of Anaesthetists: Safe Vascular Access Guidelines (2025)
- ACS: Real-Time US Guidance for CVC Placement
- NEJM Videos (Ortega et al., 2010 – technique timeless)
- StatPearls / Merck Manuals / Hospital Procedures Consultants
Clinical Pearl:
Always use real-time US guidance – it's now recommended as standard (1A evidence for IJV). Prefer right IJV. Document everything: indication, consent, US findings, technique, complications, post-procedure CXR result. Remove line ASAP when no longer required to minimize infection/thrombosis risk.
