Related Subjects: Asthma
|Acute Severe Asthma
|Exacerbation of COPD
|Pulmonary Embolism
|Cardiogenic Pulmonary Oedema
|Pneumothorax
⚠️ HIV patients are at ↑ risk of bacterial infections (e.g., Strep. pneumoniae, H. influenzae, Moraxella catarrhalis) and opportunistic infections like PCP.
📖 About
- 🦠 Formerly called Pneumocystis carinii, renamed P. jirovecii. The acronym PCP (Pneumocystis pneumonia) remains in use.
- 🍄 It is a fungus but lacks ergosterol → resistant to conventional antifungals.
🧪 Aetiology
- Occurs when immunocompromised → especially in HIV/AIDS with CD4 < 200 cells/mm³.
- Seen at HIV diagnosis or when ART is interrupted.
- Also in patients on long-term steroids, transplants, chemotherapy, or autoimmune therapy.
🩺 Clinical
- Gradual onset: breathlessness, fever 🌡️, dry cough, malaise.
- Non-HIV patients may deteriorate more acutely.
- Findings: tachypnoea, hypoxia, fine crackles.
- ⬇️ O₂ sats on exertion = classic clue.
- ⚡ Pneumothorax is a severe complication.
🔍 Investigations
- Sputum induction + IF staining (or PCR) → may detect organism.
- BAL via bronchoscopy = gold standard if sputum negative.
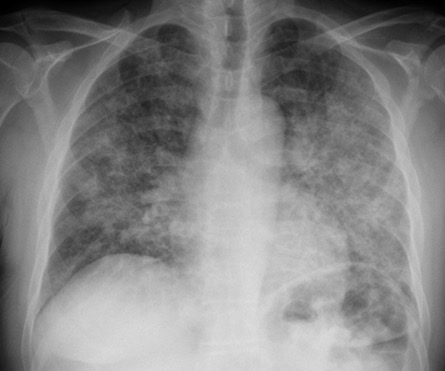
- CXR/CT: diffuse bilateral ground-glass opacities 🌫️, sometimes pneumatocele/cystic changes.
- LDH ↑ (>500 U/L, nonspecific marker).
- ABG: PaO₂ ≤ 9.3 kPa → severe disease.
- Beta-D-glucan ↑ (fungal marker, nonspecific).
- Always do HIV test + CD4 count + viral load.
🧾 Differentials
- Bacterial/viral pneumonia (incl. COVID-19, influenza).
- Pulmonary embolism 🫀 (if hypoxia unexplained).
- Asthma (though minimal wheeze here).
- Pulmonary oedema 💧 (radiology overlap).
- HIV-related TB or atypical mycobacteria.
💊 Management
- Stabilise with O₂, monitor, urgent HIV referral.
- Prophylaxis: Co-trimoxazole 960 mg OD (or 3x weekly) if CD4 < 200 or previous PCP.
- Treatment – Mild/Moderate:
- Co-trimoxazole PO 1920 mg TDS x 21d.
- Atovaquone 750 mg BD with fatty meal 🍳 if intolerant.
- Dapsone 100 mg OD + Trimethoprim (20 mg/kg/day).
- Treatment – Severe:
- IV Co-trimoxazole 120 mg/kg/day (→ 90 mg/kg after 3 days).
- Clindamycin IV + Primaquine PO.
- Pentamidine IV (third-line).
- 💊 Steroids: If PaO₂ ≤ 9.3 kPa or sats < 92%.
Prednisolone 40 mg BD → taper over 21 days.
IV methylprednisolone if unable to take PO.
- 🚨 Monitor for complications esp. pneumothorax.
- Ventilatory support if progressive RF (but risk of barotrauma).
- Start/optimise HAART to restore CD4 >200 and prevent relapse.
📉 Prognosis & Complications
- Untreated → very high mortality. Early Rx improves survival.
- Relapse risk if ART adherence poor.
- Pneumothorax in 5–10% → poor prognosis.
- Secondary bacterial/mycobacterial infections common.
🛡️ Prevention & Long-Term
- Continue Co-trimoxazole prophylaxis until CD4 >200 for 3–6 months on ART.
- Education on ART adherence + follow-up.
- Monitor lung function + imaging if residual damage.
📚 References
3 Clinical Cases — Pneumocystis jirovecii Pneumonia (PJP) 🫁🦠
- Case 1 — HIV-related PJP 🧬: A 32-year-old man with untreated HIV presents with 3 weeks of progressive exertional dyspnoea, dry cough, and low-grade fever. Oxygen saturations fall from 94% at rest to 82% on exertion. CXR: bilateral perihilar ground-glass infiltrates. Teaching: PJP is a classic opportunistic infection when CD4 <200 cells/µL. Hypoxia may be disproportionate to auscultatory findings. Diagnosis by induced sputum/BAL PCR. First-line treatment: high-dose co-trimoxazole ± corticosteroids if hypoxic.
- Case 2 — Post-transplant PJP 💉: A 54-year-old renal transplant recipient on tacrolimus and prednisolone presents with fever, breathlessness, and non-productive cough. CXR shows diffuse interstitial infiltrates; HRCT reveals ground-glass opacities. Teaching: PJP also occurs in solid organ transplant patients due to immunosuppression. Prophylaxis with low-dose co-trimoxazole is standard post-transplant. BAL is gold-standard for diagnosis.
- Case 3 — Iatrogenic immunosuppression 💊: A 61-year-old woman with rheumatoid arthritis on methotrexate and long-term prednisolone presents with acute hypoxaemia, fever, and cough. CXR shows bilateral diffuse infiltrates. Teaching: Non-HIV immunosuppressed patients (steroids, chemotherapy, biologics) are at risk. Presentation is often more acute and severe than in HIV. Requires early treatment with co-trimoxazole, consider adjunctive steroids if PaO₂ <9.3 kPa.

