| Download the app: Android | Apple | |
|---|---|
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: Educational use only. Not for diagnosis or management. |
Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis (FSGS)
Related Subjects: |Metabolic acidosis |Lactic acidosis |Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) / Acute Renal Failure |Renal/Kidney Physiology |Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) |Anaemia in Chronic Kidney Disease |Analgesic Nephropathy |Medullary Sponge kidney |IgA Nephropathy (Berger's disease) |HIV associated nephropathy (HIVAN) |Balkan endemic nephropathy (BEN) |Adult Polycystic kidney disease |Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis (FSGS)
🧪 Focal Segmental Glomerulosclerosis (FSGS) is a major cause of nephrotic syndrome and chronic kidney disease worldwide. "Focal" → only some glomeruli are affected. "Segmental" → only part of each affected glomerulus shows sclerosis.
📘 About
- One of the most common causes of end-stage renal disease (ESRD) globally.
- Presents with proteinuria — nephrotic (>3.5 g/day) or sub-nephrotic.
- Incidence is rising, with a significant public health burden.
🧬 Aetiology & Pathophysiology
- Podocyte injury and depletion are the central mechanism → impaired filtration barrier → proteinuria.
- Likely immune-mediated: possible circulating plasma factor (explains recurrence post-transplant & steroid responsiveness).
- Genetic forms seen especially in children and young adults (e.g., podocin or nephrin mutations).
- Shares features with Minimal Change Disease (MCD) but biopsy reveals segmental sclerosis.
🔍 Microscopy (Biopsy)
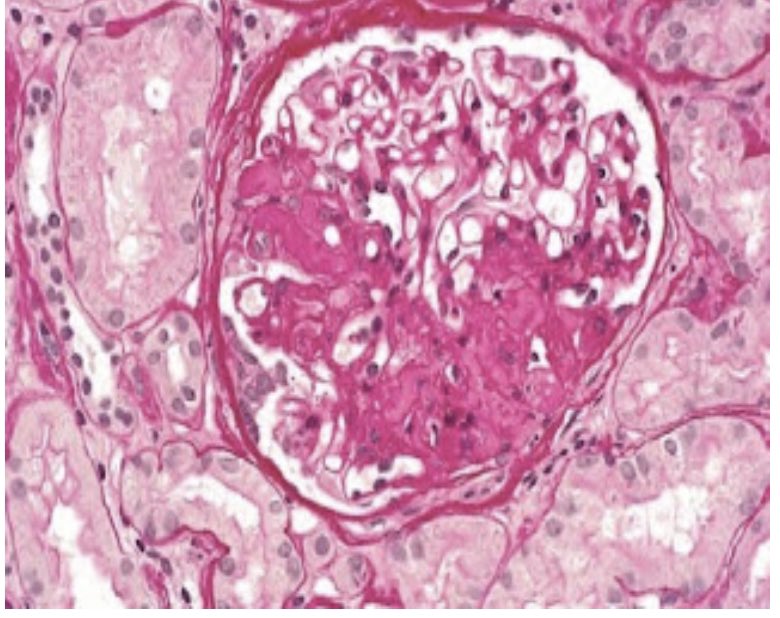
🎯 Renal biopsy: segmental sclerosis, hyalinosis, and podocyte effacement (on EM). Immunofluorescence may show IgM and C3 deposits.
📎 Associations
- 🏥 Nephropathies: reflux nephropathy, analgesic nephropathy.
- 🦠 Infections: HIV, malaria.
- 💉 Substances: IV heroin use.
- 🧬 Haemoglobinopathies: sickle cell disease.
- ⚖️ Other: severe obesity, adaptive response to reduced nephron mass.
- 🔄 Post-transplant recurrence: occurs in up to 30% of patients, often leading to graft loss.
👩⚕️ Clinical Presentation
- Nephrotic syndrome: oedema, frothy urine, hypoalbuminaemia, hyperlipidaemia.
- Hypertension is common (especially adults).
- Microscopic haematuria in some cases.
- Prothrombotic tendency → ↑ risk of DVT, PE, or renal vein thrombosis.
🔬 Investigations
- Dipstick: proteinuria ± blood.
- 24h urine protein: quantifies nephrotic-range proteinuria.
- U&Es: rising creatinine → renal impairment.
- USS: kidneys usually normal size/echogenicity.
- Biopsy (gold standard): focal & segmental sclerosis of glomerular tufts, mesangial expansion.
💊 Management
- Immunosuppression:
- 1st-line: high-dose steroids (response variable).
- Ciclosporin or tacrolimus for steroid-resistant cases (monitor nephrotoxicity).
- Other agents: cyclophosphamide, mycophenolate (selected cases).
- Supportive:
- ACE inhibitors / ARBs → reduce proteinuria and control BP.
- Lifestyle: weight reduction in obesity-related FSGS.
- Statins for dyslipidaemia.
- Anticoagulation if thrombosis risk high.
- Advanced disease: dialysis or renal transplantation (but beware recurrence).
📉 Prognosis
- Variable course: some remit, many progress to CKD/ESRD within 5–10 years.
- Poor prognostic factors: high baseline proteinuria, resistance to steroids, renal impairment at diagnosis.
📖 References
Categories
- A Level
- About
- Acute Medicine
- Anaesthetics and Critical Care
- Anatomy
- Biochemistry
- Book
- Cardiology
- Collections
- CompSci
- Crib Sheets
- Dental
- Dermatology
- Differentials
- Drugs
- ENT
- Education
- Electrocardiogram
- Embryology
- Emergency Medicine
- Endocrinology
- Ethics
- Foundation Doctors
- GCSE
- Gastroenterology
- General Practice
- Genetics
- Geriatric Medicine
- Guidelines
- Gynaecology
- Haematology
- Hepatology
- Immunology
- Infectious Disease
- Infectious Diseases
- Infographic
- Investigations
- Lists
- Mandatory Training
- Medical Students
- Microbiology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Nutrition
- OSCE
- Obstetrics
- Obstetrics Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Medicine and Dentistry
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatrics
- Palliative
- Pathology
- Pharmacology
- Physiology
- Procedures
- Psychiatry
- Public Health
- Radiology
- Renal
- Respiratory
- Resuscitation
- Revision
- Rheumatology
- Statistics and Research
- Stroke
- Surgery
- Toxicology
- Trauma and Orthopaedics
- USMLE
- Urology
