Related Subjects:
|Iron deficiency Anaemia
|Haemolytic anaemia
|Macrocytic anaemia
|Megaloblastic anaemia
|Microcytic anaemia
|Myelodysplasia
|Myelofibrosis
🩸 Haemoglobin is a vital protein in red blood cells that transports oxygen from the lungs to tissues and returns carbon dioxide for exhalation. It is essential for maintaining tissue oxygenation and overall metabolic function.
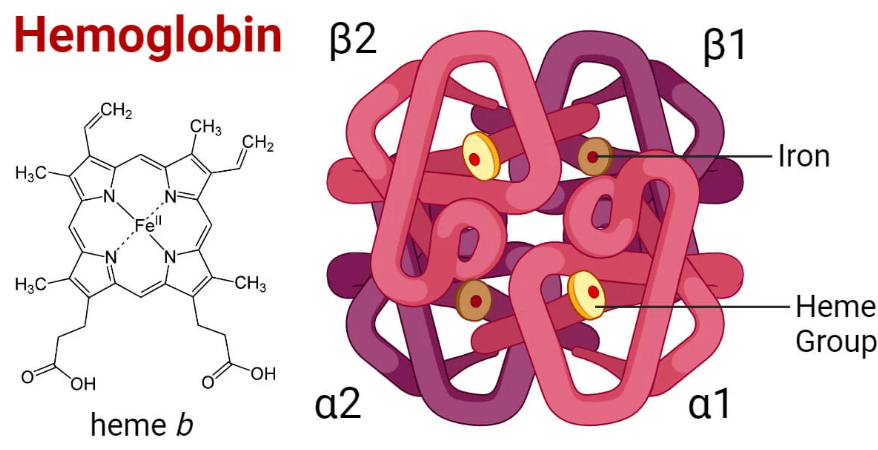
🔬 Structure of Haemoglobin
- Haemoglobin is a tetrameric protein with four subunits:
- Each subunit contains a heme group and a globin chain.
- Heme = porphyrin ring + iron (Fe²⁺) ion, binding one O₂ molecule.
- Globin = polypeptide chains supporting structure & regulating oxygen binding/release.
- Most common in adults = HbA (α₂β₂).
⚙️ Formation of Haem
💡 Key Point: Haem is essential not only for haemoglobin but also for myoglobin and cytochromes. Synthesis occurs in the bone marrow & liver.
🧪 Steps in Haem Synthesis
- δ-Aminolevulinic Acid (ALA) Formation: Glycine + Succinyl-CoA → ALA via ALA synthase (rate-limiting, requires Vit B6).
- ALA → Porphobilinogen (PBG): Catalysed by ALA dehydratase (inhibited by lead).
- Uroporphyrinogen III Formation: Hydroxymethylbilane → uroporphyrinogen III.
- Coproporphyrinogen III Formation: Decarboxylation step.
- Protoporphyrinogen IX: Conversion inside mitochondria.
- Protoporphyrin IX: Formed by oxidation.
- Final Step: Ferrochelatase inserts Fe²⁺ into protoporphyrin IX → Haem.
⚖️ Regulation
- Controlled at ALA synthase step.
- ⬆️ Anaemia → ↑ ALA synthase activity.
- ⬆️ Haem → negative feedback on ALA synthase.
📚 Clinical Relevance of Haem Synthesis
- Porphyrias = enzyme deficiencies → neuro/skin symptoms.
- Lead poisoning = inhibits ALA dehydratase + ferrochelatase → anaemia, neurological features.
🧬 Types of Haemoglobin
| Type | Composition | Normal Proportion | Key Features |
|---|
| HbA | α₂β₂ | ~97% | Normal adult haemoglobin |
| HbA₂ | α₂δ₂ | ~2-3% | Slightly higher in β-thalassemia trait |
| HbF | α₂γ₂ | <1% adults
Predominant in fetus | Higher O₂ affinity → helps placental transfer |
| HbS | Mutated β chain | Pathological | Sickle cell disease |
| HbC | Mutated β chain | Pathological | HbC disease with haemolysis |
🧭 Function of Haemoglobin
- O₂ Transport: Lungs → tissues (oxyhaemoglobin).
- CO₂ Transport: Tissues → lungs (carbaminohaemoglobin).
- Buffering: Binds H⁺ to maintain pH stability.
📈 Oxygen–Haemoglobin Dissociation Curve
- S-shaped (sigmoidal) curve showing % saturation vs pO₂.
- Right Shift = ⬇️ O₂ affinity → easier release to tissues (↑ CO₂, ↑ H⁺, ↑ temp, ↑ 2,3-BPG).
- Left Shift = ⬆️ O₂ affinity → easier loading in lungs (↓ CO₂, ↓ H⁺, ↓ temp, ↓ 2,3-BPG, HbF).
💡 Exam Tip: “Right shift = Release” (easy way to remember).
🩸 Clinical Relevance
- Anaemias: Nutritional (iron, B12, folate), genetic (thalassemia, sickle cell), chronic disease.
- Haemoglobinopathies: HbS, HbC, thalassemias → haemolysis, anaemia, organ damage.
- CO Poisoning: CO binds Hb with 200x affinity vs O₂ → tissue hypoxia.
- Methaemoglobinemia: Fe³⁺ form cannot bind O₂ → hypoxia despite normal O₂ levels.
📝 Summary
Haemoglobin = 🩸 oxygen transporter, CO₂ remover, and pH buffer.
Its complex structure allows precise regulation. Disorders of synthesis (porphyrias, lead poisoning) or structure (sickle cell, thalassemias) underline its clinical importance.
Understanding shifts in the O₂ curve and genetic variants is high-yield for exams and practice.

