| Download the amazing global Makindo app: Android | Apple | |
|---|---|
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: Educational use only. Not for diagnosis or management. See below for full disclaimer. |
Calcium Physiology
🔗 Related Subjects: Calcium Physiology
🦴 Calcium is an essential mineral that underpins bone health, muscle contraction, nerve transmission, blood clotting, and cellular signaling. About 99% of calcium is stored in bones and teeth, while 1% circulates or sits in soft tissues for vital metabolic processes.
📊 Distribution of Calcium
- Calcium distribution in the body:
- 🦷 99% in bones and teeth → provides structure and acts as a calcium reservoir.
- 💉 1% in extracellular fluid and soft tissues → supports nerve, muscle, and clotting functions.
- ⚖️ Normal serum calcium range: 2.1–2.6 mmol/L (8.5–10.5 mg/dL), tightly regulated.
⚡ Functions of Calcium
- Bone Health 🦴 :
- Combines with phosphate to form hydroxyapatite crystals → bone strength.
- Bone acts as a reservoir, buffering blood calcium fluctuations.
- Muscle Contraction 💪 :
- Calcium binds to troponin, enabling actin–myosin interaction.
- Essential for skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle activity.
- Nerve Transmission 🧠 :
- Triggers neurotransmitter release at synapses.
- Supports rapid communication across the nervous system.
- Blood Clotting 🩸 :
- Acts as a cofactor in multiple clotting cascade steps.
- Cellular Signaling 📡 :
- Serves as a “second messenger” in hormonal and metabolic pathways.
⚖️ Regulation of Calcium Levels
- Maintained by interplay of hormones and organs:
- Parathyroid Hormone (PTH) ⬆️ :
- Released when calcium is low.
- Stimulates bone resorption, kidney reabsorption, and vitamin D activation.
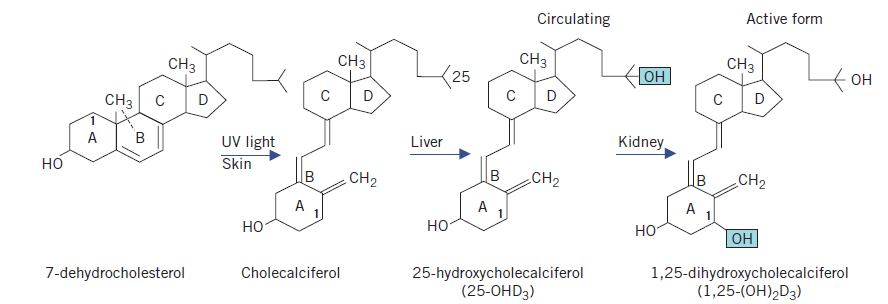
- Calcitriol (Active Vitamin D) 🌞 :
- Produced in kidneys under PTH control.
- Enhances intestinal calcium absorption and kidney retention.
- Calcitonin ⬇️ :
- Secreted by thyroid C cells when calcium is high.
- Inhibits bone resorption and promotes renal excretion.
- Parathyroid Hormone (PTH) ⬆️ :
- Balance also depends on diet, renal excretion, and bone turnover.
🏥 Clinical Relevance
- Hypocalcemia ⬇️ :
- Causes: Hypoparathyroidism, vitamin D deficiency, CKD, medications.
- Symptoms: Muscle cramps, tetany, seizures, paraesthesia, arrhythmias.
- Treatment: IV or oral calcium, plus correction of underlying cause.
- Hypercalcemia ⬆️ :
- Causes: Primary hyperparathyroidism, malignancy, vitamin D excess.
- Symptoms: “Stones, bones, groans, and psychiatric overtones” → renal stones, bone pain, constipation, confusion.
- Treatment: IV fluids, bisphosphonates, calcitonin, treat underlying cause.
- Osteoporosis 🦴 :
- Reduced bone density and fracture risk.
- Common in aging and post-menopause.
- Treatment: Calcium + vitamin D, exercise, bisphosphonates, SERMs.
- Rickets & Osteomalacia ☀️ :
- Vitamin D deficiency → poor bone mineralization.
- Rickets in children (bowed legs), osteomalacia in adults (bone pain, fragility).
- Treatment: Vitamin D and calcium replacement.
📝 Summary
Calcium is central to skeletal strength, neuromuscular activity, clotting, and intracellular signaling. Its levels are finely tuned by PTH, calcitriol, and calcitonin. Disorders of calcium balance can present dramatically (tetany, arrhythmia, confusion), making it a cornerstone concept in both physiology and clinical medicine.
Categories
- A Level
- About
- Acute Medicine
- Anaesthetics and Critical Care
- Anatomy
- Anatomy and Physiology
- Biochemistry
- Book
- Cardiology
- Collections
- CompSci
- Crib Sheets
- Crib sheets
- Dental
- Dermatology
- Differentials
- Drugs
- ENT
- Education
- Electrocardiogram
- Embryology
- Emergency Medicine
- Endocrinology
- Ethics
- Foundation Doctors
- GCSE
- Gastroenterology
- General Practice
- Genetics
- Geriatric Medicine
- Guidelines
- Gynaecology
- Haematology
- Hepatology
- Immunology
- Infectious Diseases
- Infographic
- Investigations
- Lists
- Mandatory Training
- Medical Students
- Microbiology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Nutrition
- OSCE
- OSCEs
- Obstetrics
- Obstetrics Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Medicine and Dentistry
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatrics
- Palliative
- Pathology
- Pharmacology
- Physiology
- Procedures
- Psychiatry
- Public Health
- Radiology
- Renal
- Respiratory
- Resuscitation
- Revision
- Rheumatology
- Statistics and Research
- Stroke
- Surgery
- Toxicology
- Trauma and Orthopaedics
- USMLE
- Urology
- Vascular Surgery
