| Download the amazing global Makindo app: Android | Apple | |
|---|---|
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: Educational use only. Not for diagnosis or management. See below for full disclaimer. |
Hepatic Encephalopathy
🧠 Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) is a neuropsychiatric syndrome due to liver dysfunction and portosystemic shunting, resulting in accumulation of neurotoxins (particularly ammonia) that impair cerebral function. Management focuses on correcting precipitating causes, reducing ammonia production and absorption, and supporting the failing liver.
| ⚕️ Hepatic Encephalopathy: Initial Management Summary |
|---|
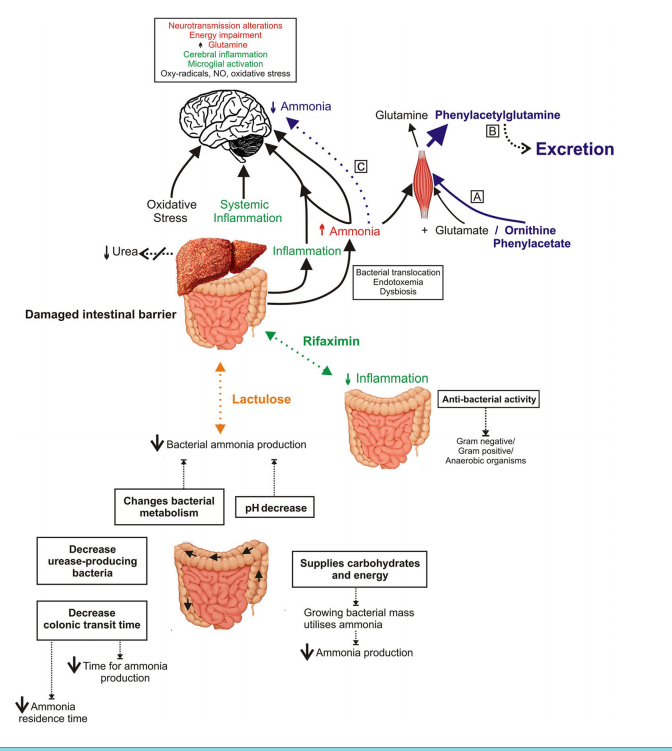
|
📖 About
- Occurs in advanced chronic liver disease or acute liver failure — a key sign of hepatic decompensation.
- Also termed portosystemic encephalopathy (PSE) when due to shunting of toxins around the liver.
- Reflects failure of the liver to detoxify nitrogenous substances absorbed from the gut.
- One of the major complications of cirrhosis alongside variceal bleeding and ascites.
🧬 Pathogenesis
- Ammonia and other nitrogenous toxins bypass hepatic metabolism and accumulate in systemic circulation.
- In the brain, ammonia is taken up by astrocytes → converted to glutamine → osmotic swelling → cerebral oedema and impaired neurotransmission.
- Altered GABAergic tone, false neurotransmitter accumulation (octopamine), and inflammation further contribute to neuronal dysfunction.
🧠 Asterixis (“liver flap”)
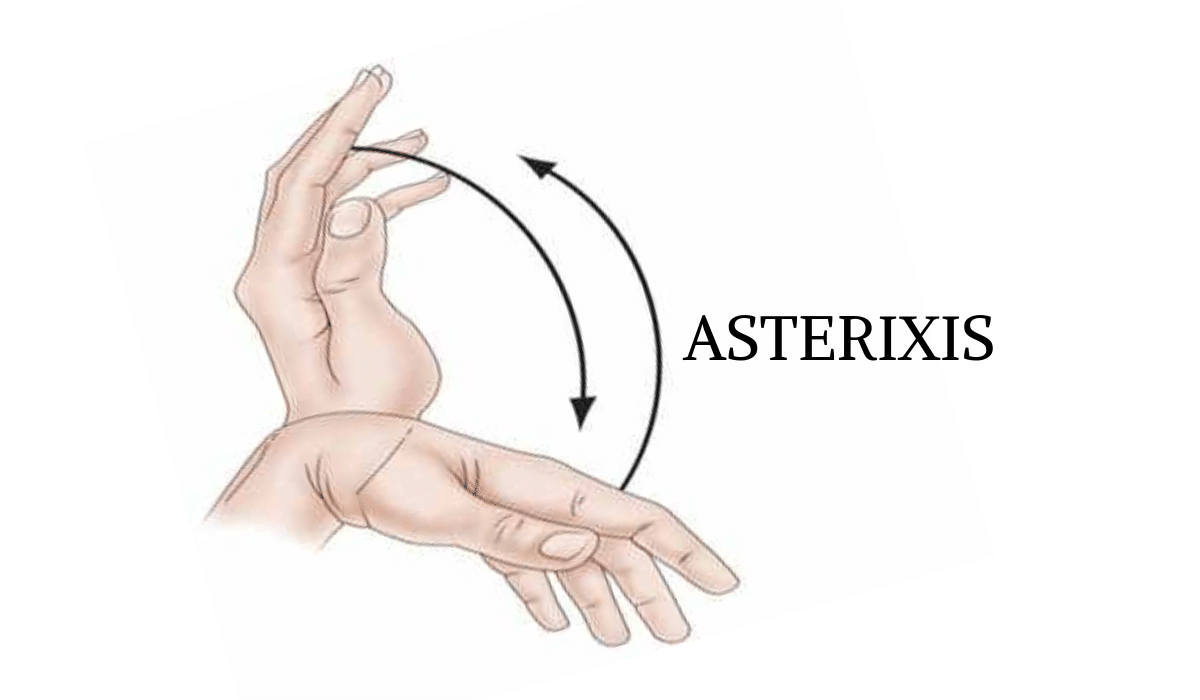
A classic sign of metabolic encephalopathy — a flapping tremor due to intermittent loss of postural muscle tone (“negative myoclonus”).
🩺 Clinical Features
- Mild confusion, forgetfulness, personality change, or mood disturbance.
- Reversal of sleep–wake cycle and poor concentration.
- Slurred speech, slow responses, and impaired handwriting.
- Foetor hepaticus — sweet/musty odour of the breath (volatile thiols).
- Severe stages: asterixis, agitation, seizures, stupor → coma.
📊 Grades of Encephalopathy
- Grade I – Altered mood or sleep, mild confusion
- Grade II – Disorientation, lethargy, inappropriate behaviour
- Grade III – Somnolence, marked confusion, incoherent speech
- Grade IV – Coma (unresponsive to pain)
🔍 Investigations
- Bloods: FBC, U&E, LFTs, INR/PT, glucose, ammonia (limited correlation), CRP/ESR
- Renal: Creatinine (for hepatorenal syndrome), Urea (↑ with GI bleed)
- Sepsis screen: CXR, urinalysis, ascitic tap (for SBP), blood cultures
- Other: Paracetamol level, arterial lactate, ABG (metabolic alkalosis from diuretics or acidosis in sepsis)
- Imaging: Doppler US for Budd–Chiari, CT/MRI brain if diagnosis uncertain
⚠️ Common Precipitants
- Infection or sepsis (especially SBP, UTI, chest infection)
- GI bleed → protein load and ammonia rise
- Constipation or dehydration
- Excess diuretics → metabolic alkalosis, hypokalaemia
- Alcohol binge, sedatives (benzodiazepines), opiates
- Electrolyte imbalance, AKI, or hypoxia
- High protein intake or paracentesis without albumin replacement
🧩 Differential Diagnosis
- Hypoglycaemia
- Post-ictal state or status epilepticus
- Subdural haematoma or intracranial haemorrhage
- Drug or alcohol intoxication
- Delirium tremens or primary psychiatric disorders
💊 Management in Detail
| Treatment | Mechanism | Clinical Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Lactulose 30 mL BD–TDS | Non-absorbable disaccharide fermented in colon → acidifies gut → converts ammonia (NH₃) to ammonium (NH₄⁺), which is excreted. | First-line. Titrate to 2–3 soft stools/day. May give rectally if comatose. Excess causes dehydration and electrolyte loss. |
| Rifaximin 400 mg BD–TDS | Non-systemic antibiotic that suppresses ammonia-producing gut flora. | Add if recurrent HE or poor response to lactulose. Minimal systemic absorption; well tolerated. |
| Neomycin (≤4 g/day) | Reduces gut bacteria but nephrotoxic and ototoxic. | Rarely used now; reserved for refractory cases where rifaximin unavailable. |
| Protein management | Moderate protein intake (1.0–1.2 g/kg/day) focusing on vegetable/dairy proteins. | Avoid excessive restriction — malnutrition worsens prognosis. Branched-chain amino acids may help. |
| Correct precipitants | Treat infection, correct electrolytes, manage GI bleed, avoid sedatives. | Precipitant control often reverses HE without escalation. |
| Liver transplantation | Definitive treatment for irreversible hepatic failure. | Consider in recurrent/refractory HE and decompensated cirrhosis (high MELD/UKELD). |
🧠 Additional Supportive Measures
- Maintain airway and prevent aspiration if encephalopathic or comatose.
- Regular neuro-observation and ammonia-lowering therapy monitoring.
- Avoid sedatives; if required (e.g. agitation), use short-acting benzodiazepines in minimal doses.
- Ensure good nutrition and micronutrient replacement (thiamine, zinc).
📚 References
- Hepatic encephalopathy: A critical current review (Springer)
- British Society of Gastroenterology (BSG) Liver Failure Guidelines, 2023.
- NICE Clinical Knowledge Summaries: Cirrhosis & Encephalopathy.
- UpToDate: “Treatment and prevention of hepatic encephalopathy.”
Categories
- A Level
- About
- Acute Medicine
- Anaesthetics and Critical Care
- Anatomy
- Anatomy and Physiology
- Biochemistry
- Book
- Cardiology
- Collections
- CompSci
- Crib Sheets
- Dental
- Dermatology
- Differentials
- Drugs
- ENT
- Education
- Electrocardiogram
- Embryology
- Emergency Medicine
- Endocrinology
- Ethics
- Foundation Doctors
- GCSE
- Gastroenterology
- General Practice
- Genetics
- Geriatric Medicine
- Guidelines
- Gynaecology
- Haematology
- Hepatology
- Immunology
- Infectious Diseases
- Infographic
- Investigations
- Lists
- Mandatory Training
- Medical Students
- Microbiology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Nutrition
- OSCE
- OSCEs
- Obstetrics
- Obstetrics Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Medicine and Dentistry
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatrics
- Palliative
- Pathology
- Pharmacology
- Physiology
- Procedures
- Psychiatry
- Public Health
- Radiology
- Renal
- Respiratory
- Resuscitation
- Revision
- Rheumatology
- Statistics and Research
- Stroke
- Surgery
- Toxicology
- Trauma and Orthopaedics
- USMLE
- Urology
- Vascular Surgery
