| Download the amazing global Makindo app: Android | Apple | |
|---|---|
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: Educational use only. Not for diagnosis or management. See below for full disclaimer. |
Ulnar nerve
Related Subjects: |Radial Nerve |Median Nerve |Ulnar Nerve |Musculocutaneous nerve |Axillary nerve |Brachial plexus
✋ Although the 4th & 5th digits are held in the clawed position when the ulnar nerve is injured at the wrist, a high lesion (above elbow) paralyses the long flexors → loss of this sign. This is called the ulnar paradox 🧩.
🩻 Anatomy of the Ulnar Nerve
- Origin: medial cord of brachial plexus (C8, T1).
- Course:
- Descends medial arm → passes posterior to medial epicondyle (“funny bone”).
- Runs between flexor carpi ulnaris & FDP in forearm.
- Enters hand via Guyon’s canal near pisiform.
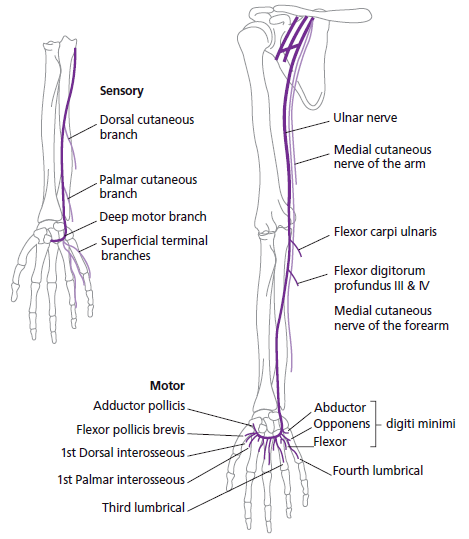
The ulnar nerve is a major nerve of the upper limb, originating from the brachial plexus (C8–T1). It supplies key forearm flexors and most intrinsic hand muscles, as well as sensation to the medial 1½ fingers.
🌿 Branches
- Forearm muscular: flexor carpi ulnaris, medial half of FDP.
- Hand muscular: hypothenar muscles, interossei, medial 2 lumbricals, adductor pollicis.
- Sensory:
- Dorsal cutaneous branch → dorsum medial 1½ fingers.
- Palmar cutaneous branch → palmar medial 1½ fingers.
⚙️ Functions
- Motor: finger ab/adduction (interossei), grip & pinch strength, wrist flexion (FCU), DIP flexion of 4th & 5th (FDP).
- Sensory: medial hand + medial 1½ digits (palmar & dorsal).
🚨 Clinical Relevance
- Ulnar nerve entrapment:
- Elbow → cubital tunnel syndrome.
- Wrist → Guyon’s canal syndrome.
- Symptoms: paraesthesia in medial 1½ digits, weak grip, hand intrinsic wasting.
- Ulnar nerve injury:
- High lesion (elbow/humerus): FCU + FDP (digits 4–5) + intrinsic hand weakness → less obvious clawing (ulnar paradox).
- Low lesion (wrist): long flexors intact, intrinsic weakness → claw hand deformity of digits 4–5.
- Froment’s sign: thumb IP flexes (FPL via median nerve) when trying to pinch a paper due to weak adductor pollicis (ulnar).
- Claw hand deformity:
- Hyperextension of MCP + flexion of IP joints (digits 4–5).
- Caused by unopposed extensor digitorum + FDP action.
🧪 Investigations
- Clinical exam: interossei (finger ab/adduction), Froment’s sign, sensory testing.
- Nerve conduction studies / EMG.
- MRI/US if structural entrapment suspected.
💊 Management
- Conservative: activity modification, splints, physio, NSAIDs.
- Neuropathic pain management if required.
- Surgical decompression (cubital tunnel release, Guyon’s canal release) for persistent/severe cases.
📚 Summary
🔑 The ulnar nerve (C8–T1) supplies most intrinsic hand muscles and sensation to the medial 1½ digits. 👉 Low lesion → classic claw hand. 👉 High lesion → less clawing (ulnar paradox). 👉 Froment’s sign = key clinical test for adductor pollicis weakness.
Categories
- A Level
- About
- Acute Medicine
- Anaesthetics and Critical Care
- Anatomy
- Anatomy and Physiology
- Biochemistry
- Book
- Cardiology
- Collections
- CompSci
- Crib Sheets
- Crib sheets
- Dental
- Dermatology
- Differentials
- Drugs
- ENT
- Education
- Electrocardiogram
- Embryology
- Emergency Medicine
- Endocrinology
- Ethics
- Foundation Doctors
- GCSE
- Gastroenterology
- General Practice
- Genetics
- Geriatric Medicine
- Guidelines
- Gynaecology
- Haematology
- Hepatology
- Immunology
- Infectious Diseases
- Infographic
- Investigations
- Lists
- Mandatory Training
- Medical Students
- Microbiology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Nutrition
- OSCE
- OSCEs
- Obstetrics
- Obstetrics Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Medicine and Dentistry
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatrics
- Palliative
- Pathology
- Pharmacology
- Physiology
- Procedures
- Psychiatry
- Public Health
- Radiology
- Renal
- Respiratory
- Resuscitation
- Revision
- Rheumatology
- Statistics and Research
- Stroke
- Surgery
- Toxicology
- Trauma and Orthopaedics
- USMLE
- Urology
- Vascular Surgery
