| Download the amazing global Makindo app: Android | Apple | |
|---|---|
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: Educational use only. Not for diagnosis or management. See below for full disclaimer. |
Shoulder Joint Structure and Form
Related Subjects: |Shoulder Joint Structure and Form |Knee Joint Structure and Form |Wrist Joint Structure and Form
The shoulder is the most mobile joint complex in the human body, designed to position the hand in almost any direction in space. This mobility comes at the expense of inherent stability. It consists of four articulations: the glenohumeral, acromioclavicular, sternoclavicular, and scapulothoracic joints. Stability depends heavily on soft tissues rather than bony congruence.
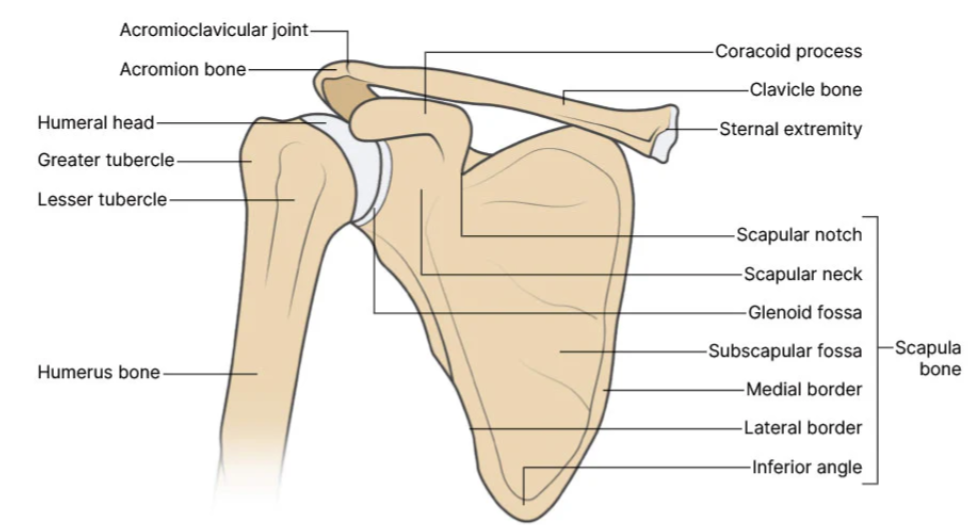
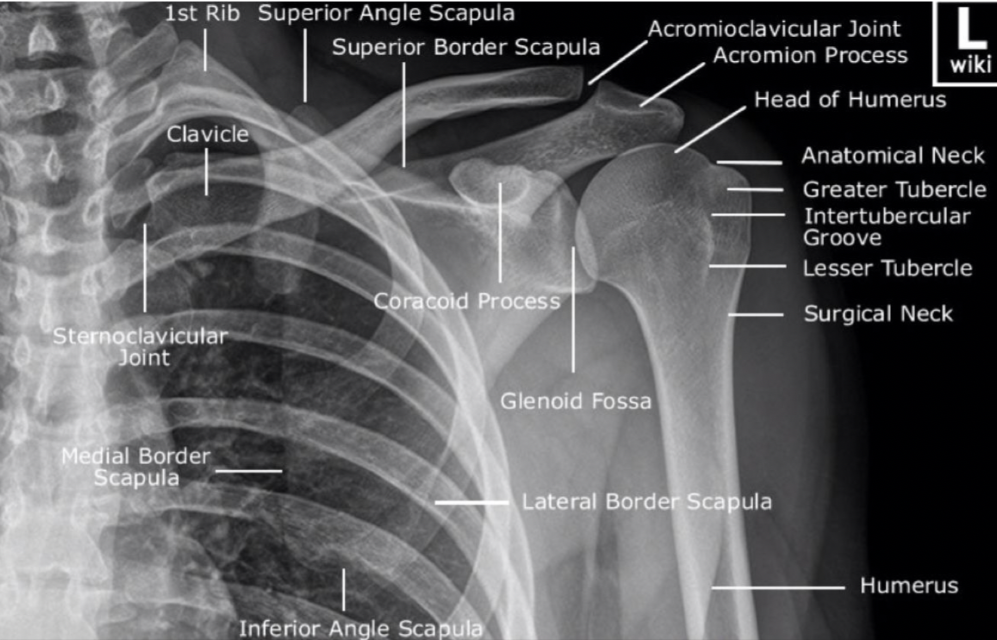
🦴 Bony Anatomy
- Clavicle 🦴 – acts as a strut holding the upper limb away from the thorax; transmits force to axial skeleton.
- Scapula 🦴 – flat triangular bone with:
- Glenoid cavity (shallow socket)
- Acromion (forms AC joint)
- Coracoid process (ligament and muscle attachment)
- Spine of scapula
- Humerus 🦴 – head articulates with glenoid; greater and lesser tubercles for cuff attachment; surgical neck clinically important.

🔗 Joints of the Shoulder
- Glenohumeral joint ⚙️ – synovial ball-and-socket; wide ROM (flexion, extension, abduction, rotation).
- Acromioclavicular joint 🔩 – plane synovial; allows scapular adjustment.
- Sternoclavicular joint 🔗 – saddle-type; only true bony link to axial skeleton.
- Scapulothoracic articulation 🫁 – functional sliding articulation over rib cage.
🛡️ Static Stabilising Structures
- Glenoid labrum 🧵 – fibrocartilage that deepens the socket (~50%).
- Joint capsule – lax inferiorly to allow abduction.
- Glenohumeral ligaments – superior, middle, inferior (IGHL prevents anterior dislocation).
- Coracoacromial arch 🏗️ – protects against superior displacement.
- Coracoclavicular ligaments – conoid + trapezoid stabilise AC joint.
💪 Dynamic Stabilisation – Rotator Cuff (SITS)
- Supraspinatus ⬆️ – initiates abduction (0–15°); suprascapular nerve (C5–C6).
- Infraspinatus 🔄 – external rotation; suprascapular nerve.
- Teres minor 🔄 – external rotation; axillary nerve.
- Subscapularis 🔁 – internal rotation; upper/lower subscapular nerves.
The cuff compresses the humeral head into the glenoid (“concavity compression”) to counteract the superior pull of the deltoid.
🏋️ Major Movers of the Glenohumeral Joint
- Deltoid 💥 – main abductor after 15°; axillary nerve (C5–C6).
- Pectoralis major 🤲 – adduction + internal rotation; medial/lateral pectoral nerves.
- Latissimus dorsi 🏊 – extension + adduction; thoracodorsal nerve.
- Teres major – adduction; lower subscapular nerve.
- Biceps (long head) 💪 – assists flexion; stabilises humeral head; musculocutaneous nerve.
- Triceps (long head) – assists extension; radial nerve.
🦾 Scapular Stabilising Muscles
- Trapezius 🎯 – elevation, retraction, upward rotation; spinal accessory nerve (CN XI).
- Serratus anterior 🪽 – protraction; prevents winging; long thoracic nerve (C5–C7).
- Rhomboids – retraction; dorsal scapular nerve.
- Levator scapulae – elevation; dorsal scapular nerve.
🩸 Arterial Supply
- Axillary artery branches supply the region.
- Anterior + posterior circumflex humeral arteries encircle surgical neck.
- Suprascapular + dorsal scapular arteries contribute to scapular anastomosis.
⚡ Nerve Supply (Plexus Relations)
- Axillary nerve (C5–C6) – deltoid, teres minor; surgical neck relation.
- Suprascapular nerve (C5–C6) – supraspinatus, infraspinatus; suprascapular notch.
- Long thoracic nerve (C5–C7) – serratus anterior; superficial on chest wall.
- Thoracodorsal nerve – latissimus dorsi.
- Musculocutaneous nerve – biceps brachii.
📍 Important Spaces & Relations
- Quadrangular space 📦 – axillary nerve + posterior circumflex humeral artery.
- Triangular interval 🔺 – radial nerve + profunda brachii artery.
- Subacromial space – supraspinatus tendon + subacromial bursa (impingement site).
- Surgical neck fracture ⚠️ – risk to axillary nerve.
🔄 Biomechanics & Function
Full abduction requires coordinated scapulohumeral rhythm (approximately 2:1 glenohumeral to scapular movement beyond 30°). The rotator cuff provides dynamic centring of the humeral head. Disruption of this balance leads to impingement, instability, or rotator cuff pathology.
🩺 Clinical Correlations
- Anterior dislocation – most common; damages inferior glenohumeral ligament and possibly axillary nerve.
- Rotator cuff tear – especially supraspinatus (painful arc 60–120°).
- Long thoracic nerve injury – winged scapula.
- AC joint separation – fall onto shoulder.
- Frozen shoulder (adhesive capsulitis) – global restriction due to capsular fibrosis.
Categories
- A Level
- About
- Acute Medicine
- Anaesthetics and Critical Care
- Anatomy
- Biochemistry
- Book
- Cardiology
- Collections
- CompSci
- Crib Sheets
- Dental
- Dermatology
- Differentials
- Drugs
- ENT
- Education
- Electrocardiogram
- Embryology
- Emergency Medicine
- Endocrinology
- Ethics
- Foundation Doctors
- GCSE
- Gastroenterology
- General Practice
- Genetics
- Geriatric Medicine
- Guidelines
- Gynaecology
- Haematology
- Hepatology
- Immunology
- Infectious Diseases
- Infographic
- Investigations
- Lists
- Mandatory Training
- Medical Students
- Microbiology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Nutrition
- OSCE
- OSCEs
- Obstetrics
- Obstetrics Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Medicine and Dentistry
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatrics
- Palliative
- Pathology
- Pharmacology
- Physiology
- Procedures
- Psychiatry
- Public Health
- Radiology
- Renal
- Respiratory
- Resuscitation
- Revision
- Rheumatology
- Statistics and Research
- Stroke
- Surgery
- Toxicology
- Trauma and Orthopaedics
- USMLE
- Urology
- Vascular Surgery
