| Download the amazing global Makindo app: Android | Apple | |
|---|---|
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: Educational use only. Not for diagnosis or management. See below for full disclaimer. |
Syphilis
Related Subjects: |Treponema |Bejel (Endemic syphilis) |Pinta |Yaws (Frambesia) |Syphilis |Non gonococcal urethritis
📜 Syphilis likely entered Europe in the late 15th century, spreading rapidly across the continent. It shaped society (handshakes instead of kisses, wigs to cover alopecia) and affected many historical figures including Henry VIII and Ivan the Terrible. The name "Syphilis" comes from a 1530 poem about a shepherd. Also known as “luetic disease.”
📖 About
- “To know syphilis is to know medicine.” – William Osler
- Caused by Treponema pallidum, a spiral-shaped spirochete bacterium 🌀.
- Cannot be cultured in vitro; spreads sexually and vertically (congenital syphilis).
- Cases are rising in the UK, especially linked to high-risk sexual networks.
- Always screen for 💉 HIV and other STIs when syphilis is suspected.
🩺 Clinical Stages
- Primary syphilis:
- Painless chancre (ulcer) at inoculation site (genitals, lips, anus).
- Heals spontaneously in weeks, but infection persists.
- Secondary syphilis: (2–6 weeks later)
- Flu-like illness: malaise, sore throat, lymphadenopathy.
- 🌸 Rash: widespread maculopapular, often palms/soles.
- Condylomata lata (moist, wart-like genital lesions).
- Nail track ulcers, patchy alopecia.
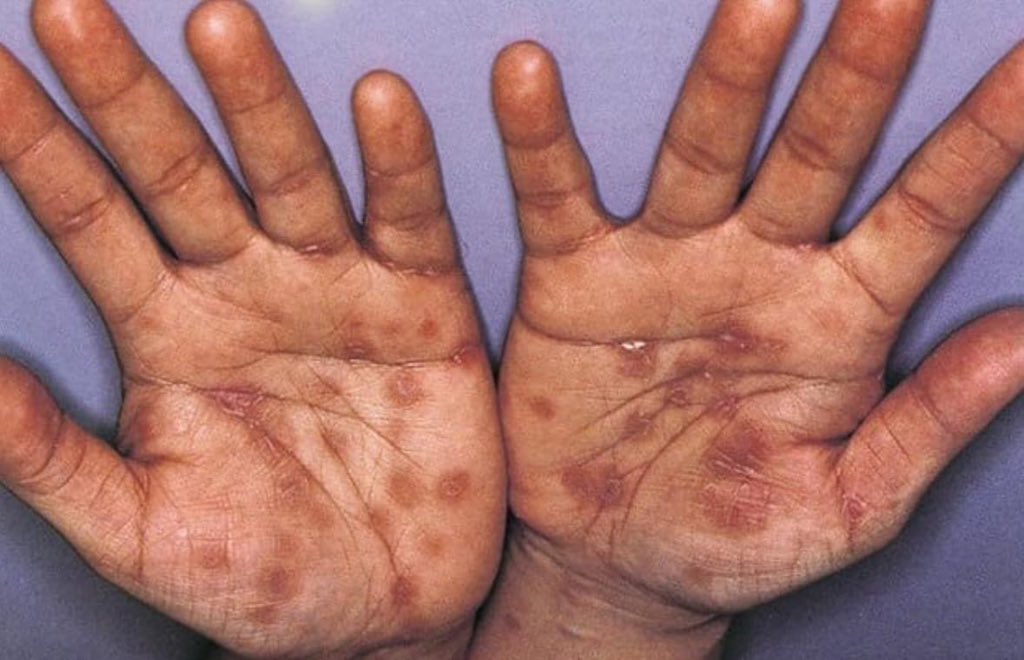
🌸 Symmetric, non-itchy rash of secondary syphilis affecting palms and soles.
⏳ Tertiary Syphilis (10+ years later)
- Neurosyphilis:
- Syphilitic meningitis (headache, neck stiffness).
- Meningovascular syphilis → strokes, seizures, cranial nerve palsies, Argyll Robertson pupils (“accommodates but does not react”).
- Tabes dorsalis: lightning pains, ataxia, sensory loss, positive Romberg’s.
- General paresis: dementia, personality change.
- Cardiovascular syphilis: Aortitis → aortic regurgitation, aneurysms.
- Gummas: Soft granulomatous lesions in skin, bone, liver, CNS.
👶 Congenital Syphilis
- Vertical transmission → ↑ risk of miscarriage, stillbirth, neonatal death.
- Early disease (2–6 weeks): snuffles (rhinitis), hepatosplenomegaly.
- Late stigmata:
- 🦷 Hutchinson’s teeth, Moon’s molars.
- 👃 Saddle nose.
- 👁️ Interstitial keratitis.
- 👂 Deafness (CN VIII damage).
- Bone deformities (saber shins, osteochondritis).
🔎 Investigations
- Dark ground microscopy: Spirochetes visible in lesion fluid.
- Screening: Treponemal EIA; confirm with TPHA/FTA.
- VDRL/RPR: Non-treponemal tests; positive after ~3 weeks, fall with treatment (but may persist in neurosyphilis).
- LP: If neurosyphilis suspected → raised protein & WCC.
- Always test for HIV & co-STIs.
💊 Management
- Primary/secondary: Procaine benzylpenicillin IM daily × 10 days OR doxycycline 100 mg BD × 14 days.
- Tertiary: Extended course – benzylpenicillin IM daily × 1 month.
- Congenital syphilis: Specialist-led IV penicillin therapy.
- Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction: Fever, chills, worsening rash hours after first dose due to spirochete die-off (cytokine mediated: TNF-α, IL-6, IL-8). Supportive management.
- Penicillin allergy: Doxycycline or ceftriaxone (but consider desensitisation if pregnant).
💡 Teaching pearl: Painless chancre → Rash (palms/soles) → Neurosyphilis/cardiac disease. “Think syphilis” in unexplained strokes in young adults, dementia with Argyll Robertson pupils, or atypical rashes.
Categories
- A Level
- About
- Acute Medicine
- Anaesthetics and Critical Care
- Anatomy
- Biochemistry
- Book
- Cardiology
- Collections
- CompSci
- Crib Sheets
- Dental
- Dermatology
- Differentials
- Drugs
- ENT
- Education
- Electrocardiogram
- Embryology
- Emergency Medicine
- Endocrinology
- Ethics
- Foundation Doctors
- GCSE
- Gastroenterology
- General Practice
- Genetics
- Geriatric Medicine
- Guidelines
- Gynaecology
- Haematology
- Hepatology
- Immunology
- Infectious Diseases
- Infographic
- Investigations
- Lists
- Mandatory Training
- Medical Students
- Microbiology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Nutrition
- OSCE
- OSCEs
- Obstetrics
- Obstetrics Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Medicine and Dentistry
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatrics
- Palliative
- Pathology
- Pharmacology
- Physiology
- Procedures
- Psychiatry
- Public Health
- Radiology
- Renal
- Respiratory
- Resuscitation
- Revision
- Rheumatology
- Statistics and Research
- Stroke
- Surgery
- Toxicology
- Trauma and Orthopaedics
- USMLE
- Urology
- Vascular Surgery
