| Download the amazing global Makindo app: Android | Apple | |
|---|---|
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: Educational use only. Not for diagnosis or management. See below for full disclaimer. |
Ectopic Pregnancy
⚠️ An ectopic pregnancy must be suspected in any woman with a positive pregnancy test, amenorrhoea, abdominal/pelvic pain, or PV bleeding. A delayed or missed diagnosis can be fatal.
📖 About
- 🚺 Ectopic pregnancy is the leading cause of maternal death in the first trimester.
- 💡 Classic triad: positive β-HCG, amenorrhoea, and empty uterus on ultrasound.
- 🧪 In a normal pregnancy, serum β-HCG doubles approximately every 48 hours. A plateau or slow rise is suspicious.
- ⚠️ Digital vaginal examination should be deferred until resuscitation is available, as it can precipitate rupture.
🧬 Aetiology
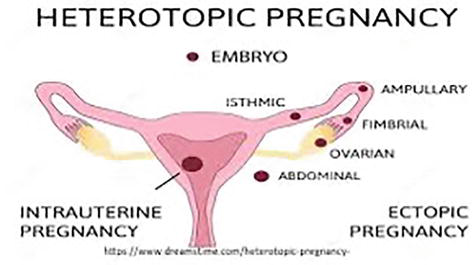
- Occurs when the embryo implants outside the uterus.
- 📍 90% occur in the fallopian tube (most often ampullary region).
- Incidence: ~1 in 200 pregnancies; risk rises with maternal age.
🔬 Physiology
- Fertilisation normally occurs in the fallopian tube → zygote travels to uterine cavity.
- 🩹 Scarring, infection, or surgery can disrupt this process → ectopic implantation.
⚡ Risk Factors
- Previous ectopic pregnancy
- PID, endometriosis, IUCD use
- Previous abdominal or pelvic surgery
- Reversal of sterilisation or IVF
- Ovarian/uterine tumours or cysts
- Smoking 🚬
🩺 Clinical Features (Pre-Rupture)
- Amenorrhoea (5–8 weeks post-LMP)
- Unilateral lower abdominal pain (sharp, stabbing)
- PV bleeding with “prune juice” appearance
- Pregnancy symptoms: breast tenderness, nausea
- Vasovagal episodes, collapse, or shock if ruptured
- Shoulder-tip pain (from diaphragmatic irritation)
- Peritonitis if rupture occurs → 🚨 emergency
🧪 Investigations
- Serum β-HCG: Serial levels (abnormal rise suggests ectopic).
- Transvaginal ultrasound: Empty uterus, adnexal mass, free fluid.
- Rhesus status: Anti-D may be required in Rh-negative women.
- Laparoscopy: Definitive diagnosis if uncertainty remains.
🔍 Differential Diagnosis
- Acute appendicitis
- Acute PID
- Threatened or incomplete miscarriage
💊 Management
- Medical (stable, early cases):
- 📉 β-HCG < 1500 IU/L, sac < 4 cm, no rupture → Methotrexate ± Misoprostol.
- Monitor β-HCG until resolution. Side effects: nausea, mucositis, fatigue.
- Surgical:
- 🚑 Emergency laparotomy + salpingectomy if unstable/ruptured.
- 💉 Laparoscopic salpingotomy or salpingectomy in stable patients.
- Conservative:
- For small (<2 cm), asymptomatic masses with β-HCG < 1000 IU/L.
- Close follow-up: β-HCG should fall ≥15% per visit.
- Other:
- Rhesus-negative → give Anti-D prophylaxis (250 IU).
- Ongoing EPAU follow-up until β-HCG negative.
📚 References
Categories
- A Level
- About
- Acute Medicine
- Anaesthetics and Critical Care
- Anatomy
- Anatomy and Physiology
- Biochemistry
- Book
- Cardiology
- Collections
- CompSci
- Crib Sheets
- Dental
- Dermatology
- Differentials
- Drugs
- ENT
- Education
- Electrocardiogram
- Embryology
- Emergency Medicine
- Endocrinology
- Ethics
- Foundation Doctors
- GCSE
- Gastroenterology
- General Practice
- Genetics
- Geriatric Medicine
- Guidelines
- Gynaecology
- Haematology
- Hepatology
- Immunology
- Infectious Diseases
- Infographic
- Investigations
- Lists
- Mandatory Training
- Medical Students
- Microbiology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Nutrition
- OSCE
- OSCEs
- Obstetrics
- Obstetrics Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Medicine and Dentistry
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatrics
- Palliative
- Pathology
- Pharmacology
- Physiology
- Procedures
- Psychiatry
- Public Health
- Radiology
- Renal
- Respiratory
- Resuscitation
- Revision
- Rheumatology
- Statistics and Research
- Stroke
- Surgery
- Toxicology
- Trauma and Orthopaedics
- USMLE
- Urology
- Vascular Surgery
