| Download the amazing global Makindo app: Android | Apple | |
|---|---|
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: Educational use only. Not for diagnosis or management. See below for full disclaimer. |
Homocystinuria
Related Subjects:
|Osteoporosis
|Autosomal Dominant
|Autosomal Recessive
|X Linked Recessive
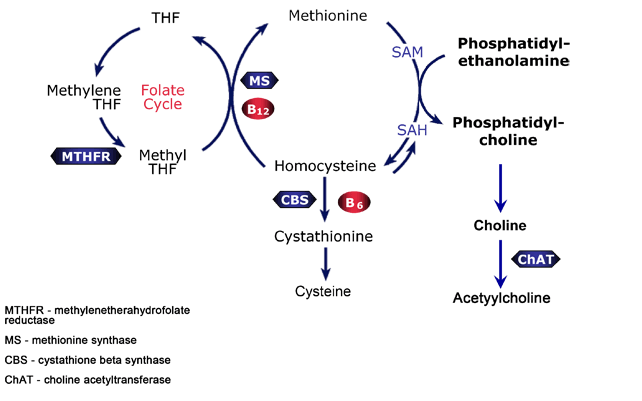
🧬 Homocystinuria is caused by reduced activity of cystathionine β-synthase (CBS), leading to accumulation of homocysteine and methionine. This disrupts collagen cross-linking and predisposes to vascular thrombosis — the cardinal feature.
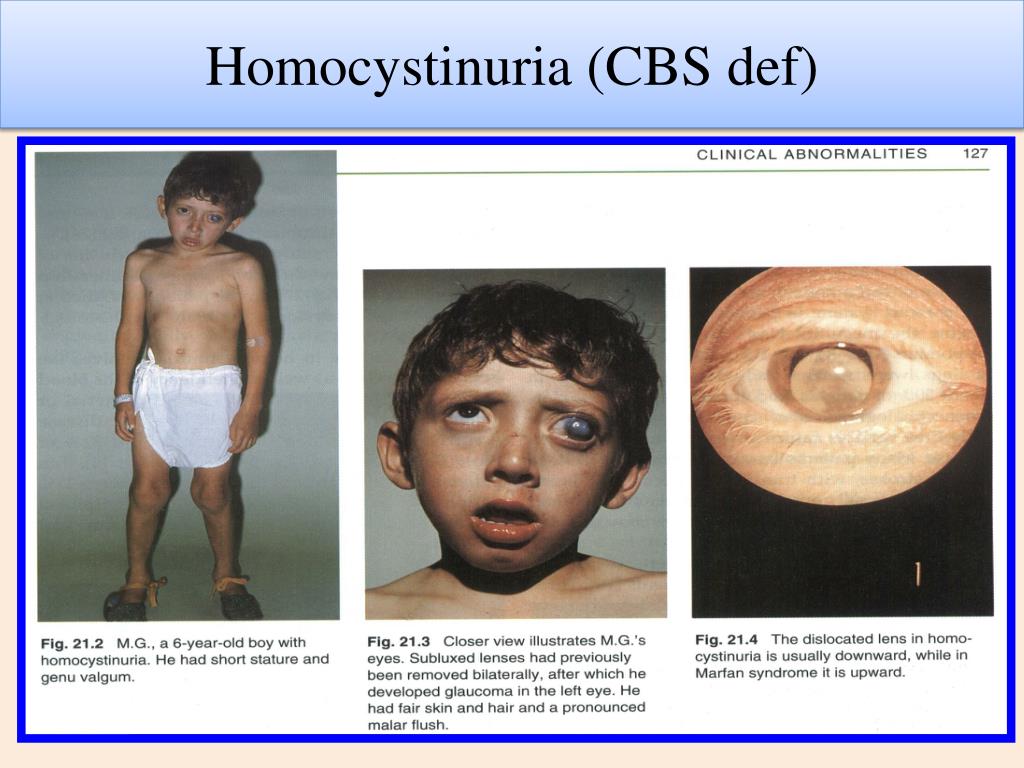
A 6-year-old boy is brought with learning difficulties, clumsiness, and tall, thin build with long fingers resembling Marfan’s habitus. He has fair hair and blue eyes. Ophthalmology finds downward lens dislocation (ectopia lentis). Blood tests show elevated plasma homocysteine. Management: 💊 High-dose pyridoxine (B6) in responsive patients, plus folate and B12 supplementation. Restrict methionine intake, supplement cysteine. Avoid: ❌ Missing diagnosis by assuming Marfan’s; avoid unmonitored protein-rich diets that worsen methionine load.
A 16-year-old girl presents with sudden left leg swelling and pain. Doppler ultrasound shows extensive DVT. She has mild learning difficulties and a history of lens surgery for dislocation. Labs: markedly raised homocysteine levels confirming homocystinuria. Management: 🩺 Anticoagulation for thrombosis, long-term homocysteine-lowering therapy (pyridoxine, folate, B12, betaine). Genetic counselling.
Avoid: ❌ Oestrogen-containing contraceptives (increase thrombotic risk). Avoid prolonged immobilisation without prophylaxis.
ℹ️ About
🧪 Aetiology
🔬 Biochemistry
🧬 Genetics
🩺 Clinical Features
🔍 Differential
🧾 Investigations
💊 Management
🩺 Case 1 — Child with Developmental Delay
🩺 Case 2 — Teen with Thromboembolism
Categories
- A Level
- About
- Acute Medicine
- Anaesthetics and Critical Care
- Anatomy
- Anatomy and Physiology
- Biochemistry
- Book
- Cardiology
- Collections
- CompSci
- Crib Sheets
- Crib sheets
- Dental
- Dermatology
- Differentials
- Drugs
- ENT
- Education
- Electrocardiogram
- Embryology
- Emergency Medicine
- Endocrinology
- Ethics
- Foundation Doctors
- GCSE
- Gastroenterology
- General Practice
- Genetics
- Geriatric Medicine
- Guidelines
- Gynaecology
- Haematology
- Hepatology
- Immunology
- Infectious Diseases
- Infographic
- Investigations
- Lists
- Mandatory Training
- Medical Students
- Microbiology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Nutrition
- OSCE
- OSCEs
- Obstetrics
- Obstetrics Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Medicine and Dentistry
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatrics
- Palliative
- Pathology
- Pharmacology
- Physiology
- Procedures
- Psychiatry
- Public Health
- Radiology
- Renal
- Respiratory
- Resuscitation
- Revision
- Rheumatology
- Statistics and Research
- Stroke
- Surgery
- Toxicology
- Trauma and Orthopaedics
- USMLE
- Urology
- Vascular Surgery
