| Download the amazing global Makindo app: Android | Apple | |
|---|---|
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: Educational use only. Not for diagnosis or management. See below for full disclaimer. |
Vaginal Prolapse
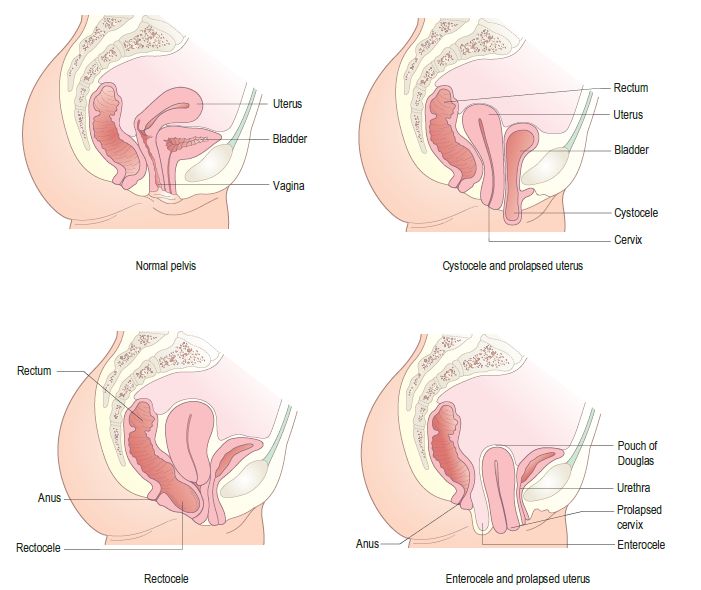
🌸 Vaginal prolapse (Pelvic Organ Prolapse) occurs when the muscles, fascia, and ligaments of the pelvic floor weaken, causing pelvic organs (bladder, uterus, rectum, or small bowel) to descend into or outside the vagina. ⚠️ Common in postmenopausal women but can affect younger women, especially after childbirth. 💡 Early recognition improves quality of life and prevents complications.
🔎 Types of Vaginal Prolapse
- 💧 Cystocele (Bladder prolapse): Bladder bulges into anterior vaginal wall.
- 🍑 Rectocele: Rectum pushes into posterior vaginal wall → constipation symptoms.
- 🧷 Uterine prolapse: Uterus descends into/through vaginal canal.
- 🌐 Enterocele: Small bowel herniates into upper posterior vaginal wall.
- 🏔️ Vaginal vault prolapse: Descent of the vaginal apex (esp. after hysterectomy).
⚠️ Risk Factors
- 👶 Childbirth: Vaginal deliveries (especially multiple or instrumental).
- 🎂 Ageing & Menopause: ↓ Oestrogen → weaker pelvic tissues.
- ⚖️ Obesity: Chronic ↑ intra-abdominal pressure.
- 😮💨 Chronic strain: Constipation, cough, heavy lifting.
- 🔪 Pelvic surgery: Hysterectomy can disrupt support structures.
🩺 Clinical Presentation
- ⬇️ Pelvic pressure/heaviness: Worse on standing, lifting, or end of day.
- 👀 Vaginal bulge: Visible/“something coming down.”
- 💧 Urinary: Frequency, urgency, incontinence, incomplete emptying, recurrent UTIs.
- 💩 Bowel: Constipation, incomplete evacuation, need to press on perineum (rectocele).
- ❤️ Sexual dysfunction: Dyspareunia, reduced satisfaction.
🧪 Diagnostic Evaluation
- 👩⚕️ Pelvic exam: Direct visual and bimanual exam.
- 📊 POP-Q system: Standardised staging of prolapse severity.
- 🖥️ Imaging: Ultrasound or MRI for unclear cases/surgical planning.
⚕️ Management Options
🌿 A. Conservative
- 🏋️ Pelvic floor exercises (Kegels): Improve tone in mild cases.
- 🛑 Pessary: Vaginal device to support organs — especially if unfit for surgery.
- ⚖️ Lifestyle: Weight loss, treat cough/constipation, avoid heavy lifting.
- 💊 Vaginal oestrogen: Improves tissue health post-menopause.
🔪 B. Surgical
- 🧵 Anterior/posterior repair: Reinforce vaginal walls for cystocele/rectocele.
- 🏥 Hysterectomy: For uterine prolapse in women not desiring fertility.
- 🪢 Sacrocolpopexy: Mesh/tissue to support vaginal vault.
- 🚫 Colpocleisis: Vaginal closure (for women no longer sexually active).
⚠️ Complications
- 🩹 Ulceration/infection: From exposed tissues or pessary use.
- 💧 Urinary retention: From urethral compression.
- 💩 Chronic constipation: With rectocele.
🔄 Follow-Up & Prevention
- 👩⚕️ Regular review: Especially if using a pessary.
- 🏋️ Continue pelvic floor exercises post-treatment.
- ⚖️ Maintain healthy weight & bowel habits.
💡 Key Point: Management should be individualised, balancing severity of symptoms, patient preference, sexual activity, and surgical fitness. 👩⚕️ Both conservative and surgical options can dramatically improve quality of life.
Categories
- A Level
- About
- Acute Medicine
- Anaesthetics and Critical Care
- Anatomy
- Anatomy and Physiology
- Biochemistry
- Book
- Cardiology
- Collections
- CompSci
- Crib Sheets
- Crib sheets
- Dental
- Dermatology
- Differentials
- Drugs
- ENT
- Education
- Electrocardiogram
- Embryology
- Emergency Medicine
- Endocrinology
- Ethics
- Foundation Doctors
- GCSE
- Gastroenterology
- General Practice
- Genetics
- Geriatric Medicine
- Guidelines
- Gynaecology
- Haematology
- Hepatology
- Immunology
- Infectious Diseases
- Infographic
- Investigations
- Lists
- Mandatory Training
- Medical Students
- Microbiology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Nutrition
- OSCE
- OSCEs
- Obstetrics
- Obstetrics Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Medicine and Dentistry
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatrics
- Palliative
- Pathology
- Pharmacology
- Physiology
- Procedures
- Psychiatry
- Public Health
- Radiology
- Renal
- Respiratory
- Resuscitation
- Revision
- Rheumatology
- Statistics and Research
- Stroke
- Surgery
- Toxicology
- Trauma and Orthopaedics
- USMLE
- Urology
- Vascular Surgery
