Makindo Medical Notes"One small step for man, one large step for Makindo" |
|
|---|---|
| Download all this content in the Apps now Android App and Apple iPhone/Pad App | |
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: The contents are under continuing development and improvements and despite all efforts may contain errors of omission or fact. This is not to be used for the assessment, diagnosis, or management of patients. It should not be regarded as medical advice by healthcare workers or laypeople. It is for educational purposes only. Please adhere to your local protocols. Use the BNF for drug information. If you are unwell please seek urgent healthcare advice. If you do not accept this then please do not use the website. Makindo Ltd. |
Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT)
Related Subjects: |Wolff-Parkinson White syndrome (WPW) AVRT |Lown Ganong Levine Syndrome AVRT |Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT) |Atrioventricular Nodal Reentrant Tachycardia AVNRT |Atrial Flutter |Atrial Fibrillation |Sinus Tachycardia |Sinus Arrhythmia |Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia |Resuscitation - Adult Tachycardia Algorithm |Resuscitation - Advanced Life Support
⚡ Supraventricular Tachycardia (SVT) is a group of rapid heart rhythms originating above the ventricles (atria or AV node). 🫀 While usually benign, it can cause distressing symptoms (palpitations, dizziness, syncope) and occasionally serious complications. 🎯 Correct diagnosis and management are essential to relieve symptoms and prevent adverse outcomes.
📌 About
- SVT = any tachycardia arising from above the Bundle of His.
- Mainly includes reentrant tachycardias such as AVRT and AVNRT.
- 🚶 Generally benign, but can mimic panic attacks and be disabling.
- 💉 Often curable with catheter ablation, especially in Wolff-Parkinson-White (WPW).
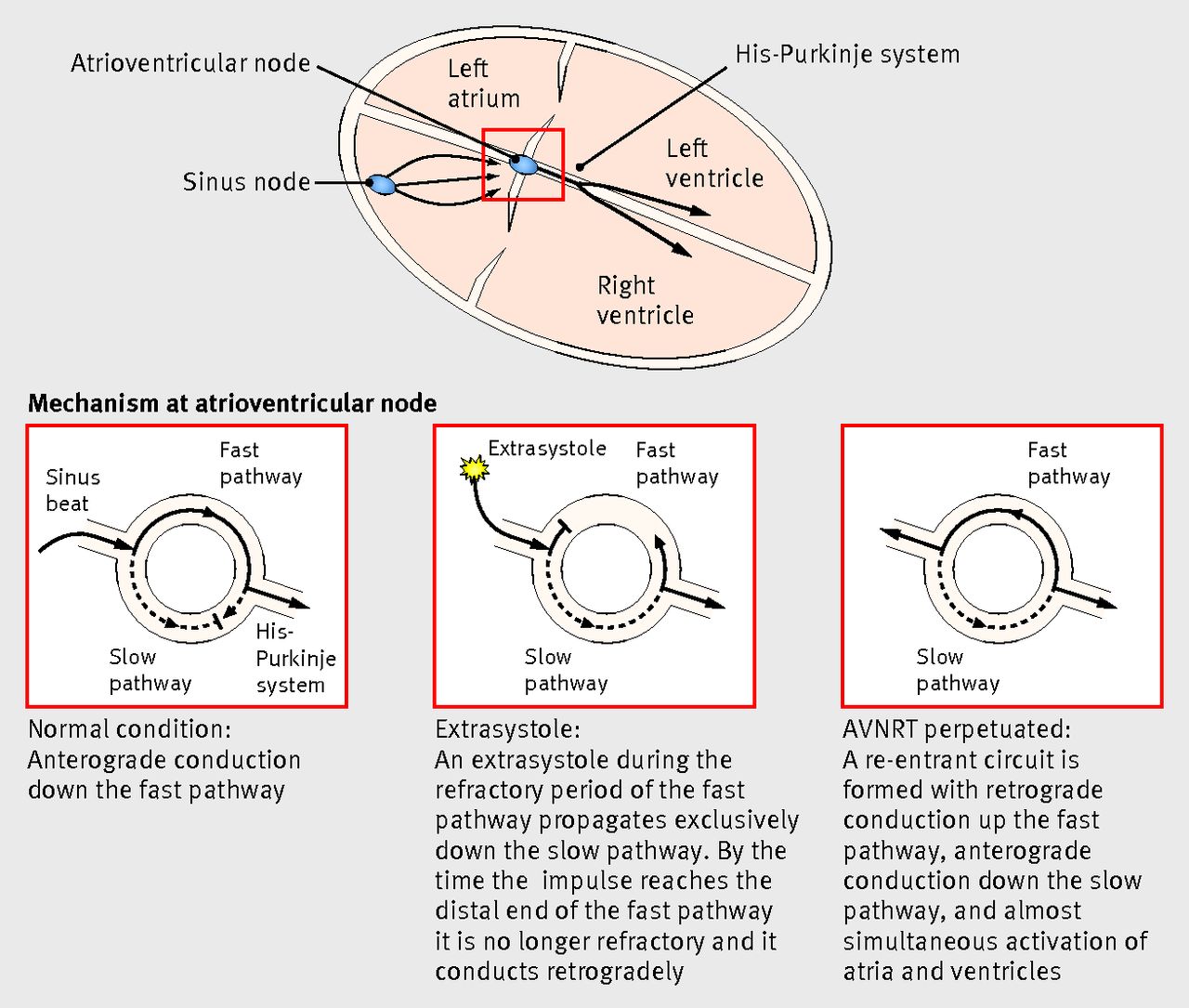
🔄 Aetiology of Reentrant SVT
- Needs two pathways (fast vs slow) ➝ reentrant circuit 🔄 like a Catherine wheel firework 🎆.
- Pathway properties:
- 🐢 Slow Pathway: Long refractory period.
- 🐇 Fast Pathway: Short refractory period.
- Classifications:
- ✅ Slow-Fast AVNRT: Most common (>90%).
- ⚡ Fast-Slow AVRT: 10–15%.
- 🔸 Slow-Slow AVRT: Rare (<5%).
 >
>
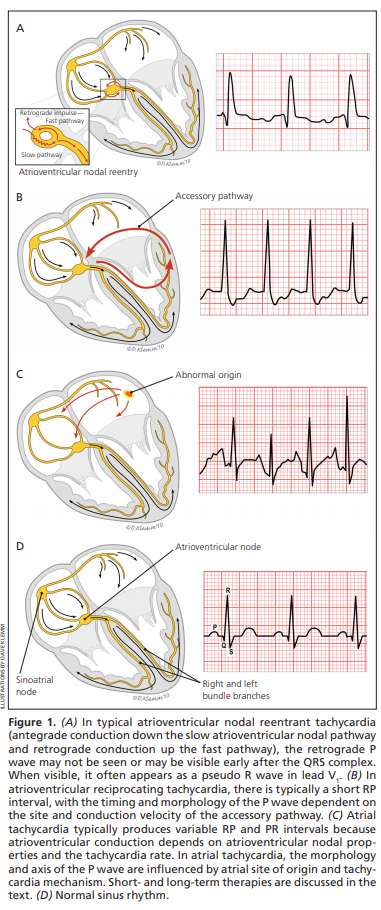
📊 Diagram – Pathways of AVRT and AVNRT
 >
>
📖 Definition Includes
- ❤️ Sinus Tachycardia – from sinus node.
- ⚡ Atrial Tachycardia – ectopic atrial focus.
- 🎯 Multifocal Atrial Tachycardia – multiple atrial foci.
- ♻️ Atrial Fibrillation – chaotic atrial activity.
- 🔄 Atrial Flutter – reentry circuit, regular.
- But in practice, “SVT” usually means:
- AVNRT
- AVRT (often with WPW)
🧑⚕️ Clinical Features
- Seen in all ages; more common in women (M:F ~1:2).
- Symptoms:
- 💓 Palpitations
- 😵 Dizziness/lightheadedness
- 🫁 Dyspnoea
- 💢 Chest pain
- 💫 Syncope/presyncope
- Common triggers: ☕ caffeine, 🍷 alcohol, 🚬 smoking, stress, 💊 drugs.
🔍 Investigations
- 📊 ECG: Key test. Narrow complex tachycardia (120–240 bpm), may mimic VT if bundle branch block.
- 📈 Holter / Event Recorder: For transient episodes.
- 🧪 Labs: FBC, U&E, TFTs, LFTs.
- 🫀 Echocardiogram: Rule out structural disease.
- 🩻 CXR: Exclude lung causes if relevant.
- Consider 💡 pheochromocytoma if hypertension + SVT (rare).
💡 Clinical Pearls
- ⏱️ Sudden onset + sudden termination → classic PSVT.
- 👕 “Shirt-flapping” or “neck pounding” → highly suggestive of AVNRT.
- ⚠️ Hypotension/syncope → unstable → urgent treatment/referral.
- 🩺 WPW with delta waves → high risk ➝ ablation referral.
📊 Examples
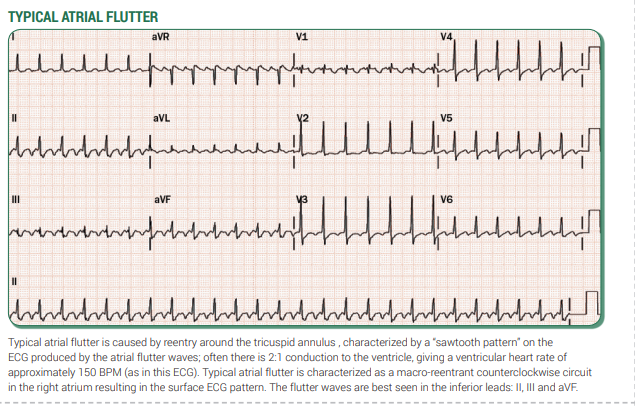
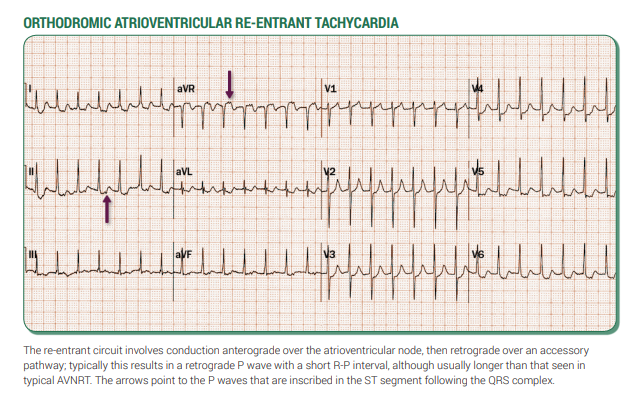
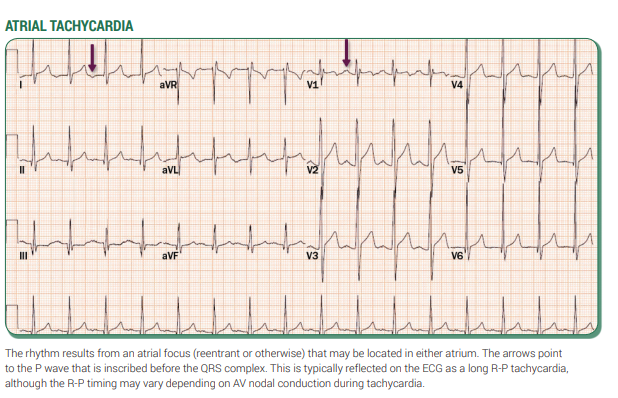
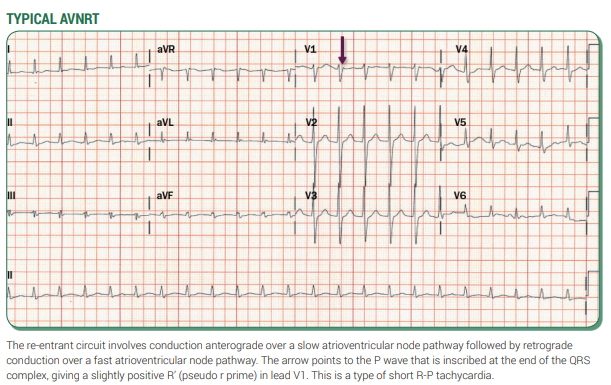
🛠️ Management
- 🚑 Initial Assessment: ABC, IV access, urgent DC cardioversion if unstable.
- 🙂 Stable SVT:
- 🙌 Vagal manoeuvres (Valsalva, carotid sinus massage, cold water face immersion).
- 💉 If fails → IV Adenosine (6 mg, then 12 mg if needed; warn about flushing & chest tightness).
- 💊 Drugs:
- 📉 Calcium channel blockers (IV verapamil, diltiazem).
- 🛡️ Beta-blockers in some cases (avoid in WPW + AF).
- ⚡ Amiodarone for broad/unstable SVT.
- ❌ Special Situations:
- WPW + AF ➝ avoid AV nodal blockers (adenosine, beta-blocker, digoxin, verapamil) ➝ use flecainide/propafenone/amiodarone or cardiovert.
- 🏥 Long-term:
- Electrophysiology referral for ablation in recurrent cases.
- Nodal ablation as last resort.
📚 References
Categories
-
| About | Anaesthetics and Critical Care | Anatomy | Biochemistry | Cardiology | Clinical Cases | CompSci | Crib | Dermatology | Differentials | Drugs | ENT | Electrocardiogram | Embryology | Emergency Medicine | Endocrinology | Ethics | Foundation Doctors | Gastroenterology | General Information | General Practice | Genetics | Geriatric Medicine | Guidelines | Haematology | Hepatology | Immunology | Infectious Diseases | Infographic | Investigations | Lists | Microbiology | Miscellaneous | Nephrology | Neuroanatomy | Neurology | Nutrition | OSCE | Obstetrics Gynaecology | Oncology | Ophthalmology | Oral Medicine and Dentistry | Paediatrics | Palliative | Pathology | Pharmacology | Physiology | Procedures | Psychiatry | Radiology | Respiratory | Resuscitation | Rheumatology | Statistics and Research | Stroke | Surgery | Toxicology | Trauma and Orthopaedics | Twitter | Urology