Makindo Medical Notes"One small step for man, one large step for Makindo" |
|
|---|---|
| Download all this content in the Apps now Android App and Apple iPhone/Pad App | |
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: The contents are under continuing development and improvements and despite all efforts may contain errors of omission or fact. This is not to be used for the assessment, diagnosis, or management of patients. It should not be regarded as medical advice by healthcare workers or laypeople. It is for educational purposes only. Please adhere to your local protocols. Use the BNF for drug information. If you are unwell please seek urgent healthcare advice. If you do not accept this then please do not use the website. Makindo Ltd. |
Renal Anatomy
Related Subjects: |Metabolic acidosis |Lactic acidosis |Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) / Acute Renal Failure |Renal/Kidney Physiology |Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) |Anaemia in Chronic Kidney Disease |Analgesic Nephropathy |Medullary Sponge kidney |IgA Nephropathy (Berger's disease) |HIV associated nephropathy (HIVAN)
🔎 Overview of Renal Anatomy
The kidneys are a pair of bean-shaped organs located in the retroperitoneal space on either side of the spine. They filter blood, remove waste products, regulate electrolytes, and maintain fluid homeostasis. Each kidney measures roughly 10–12 cm × 5–7 cm × 3 cm.
🩻 Gross Anatomy of the Kidneys
- External Structure:
- Hilum: Medial concavity where renal artery, vein, ureter, lymphatics, and nerves enter/exit.
- Capsule: Fibrous capsule provides protection and maintains shape.
- Internal Structure:
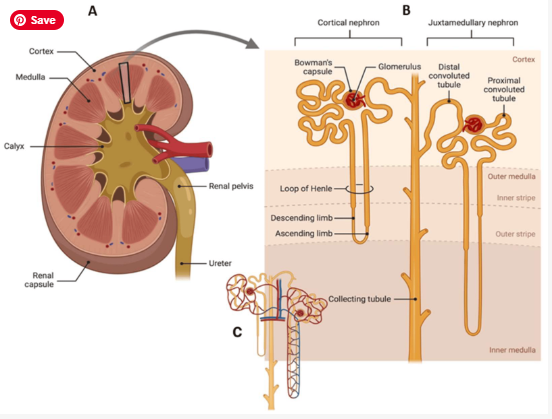
- Cortex: Outer region → contains glomeruli, PCT & DCT. Clinical note: most renal blood flow goes here, hence cortex is vulnerable in hypoperfusion.
- Medulla: 8–18 pyramids containing Loops of Henle & collecting ducts. Apex = papilla → drains into calyces.
- Renal Pelvis: Funnel-shaped, divided into major/minor calyces, continues as ureter.
🧪 Nephron: Functional Unit of the Kidney
- Each kidney has ~1–1.5 million nephrons.
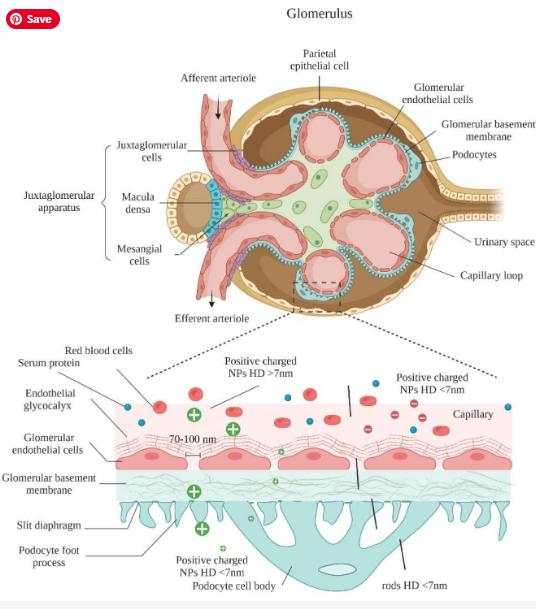
- Renal Corpuscle: Glomerulus + Bowman’s capsule → site of ultrafiltration.
- Renal Tubule:
- PCT: Bulk reabsorption of water, glucose, amino acids.
- Loop of Henle: Establishes medullary osmotic gradient. Descending limb = water permeable; ascending limb = solute transport only.
- DCT: Fine-tunes electrolytes, pH.
- Collecting Duct: Final site for water reabsorption (ADH sensitive).
🫀 Vascular Supply of the Kidneys
- Renal Artery: Branch of abdominal aorta → divides into segmental → interlobar → arcuate → interlobular arteries.
- Afferent Arterioles: Supply glomeruli.
- Efferent Arterioles: Exit glomeruli → form peritubular capillaries (cortex) & vasa recta (medulla). Vasa recta are essential for counter-current exchange and urine concentration.
- Renal Vein: Returns blood to the IVC.
🧠 Neural Supply of the Kidneys
- Sympathetic: Renal plexus (celiac + thoracic splanchnic). Controls renin release & blood flow.
- Parasympathetic: Vagus nerve (minor role).
- Sensory: Pain & reflex information carried via sympathetic pathways.
📊 Cortex vs Medulla – Quick Comparison
| Feature | Cortex | Medulla |
|---|---|---|
| Main Structures | Glomeruli, PCT, DCT | Loops of Henle, Collecting Ducts |
| Blood Flow | High (90% renal flow) | Low (10%) – vulnerable to hypoxia |
| Function | Filtration & bulk reabsorption | Urine concentration (counter-current) |
📝 Summary
The kidneys are vital for filtration, electrolyte balance, and volume regulation. Their anatomy includes cortex, medulla, and pelvis, with the nephron as the functional unit. Rich vascular supply and sympathetic regulation ensure fine-tuned control. Clinical pearl: cortical hypoperfusion → AKI; medullary hypoxia → concentrating defects.
Categories
-
| About | Anaesthetics and Critical Care | Anatomy | Biochemistry | Cardiology | Clinical Cases | CompSci | Crib | Dermatology | Differentials | Drugs | ENT | Electrocardiogram | Embryology | Emergency Medicine | Endocrinology | Ethics | Foundation Doctors | Gastroenterology | General Information | General Practice | Genetics | Geriatric Medicine | Guidelines | Haematology | Hepatology | Immunology | Infectious Diseases | Infographic | Investigations | Lists | Microbiology | Miscellaneous | Nephrology | Neuroanatomy | Neurology | Nutrition | OSCE | Obstetrics Gynaecology | Oncology | Ophthalmology | Oral Medicine and Dentistry | Paediatrics | Palliative | Pathology | Pharmacology | Physiology | Procedures | Psychiatry | Radiology | Respiratory | Resuscitation | Rheumatology | Statistics and Research | Stroke | Surgery | Toxicology | Trauma and Orthopaedics | Twitter | Urology