| Download the amazing global Makindo app: Android | Apple | |
|---|---|
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: Educational use only. Not for diagnosis or management. See below for full disclaimer. |
Amoebiasis Amoebic (Entamoeba histolytica)
🦠 Entamoeba dispar looks identical to Entamoeba histolytica but is non-pathogenic. Pathogenic amoebiasis is caused only by E. histolytica.
📖 About
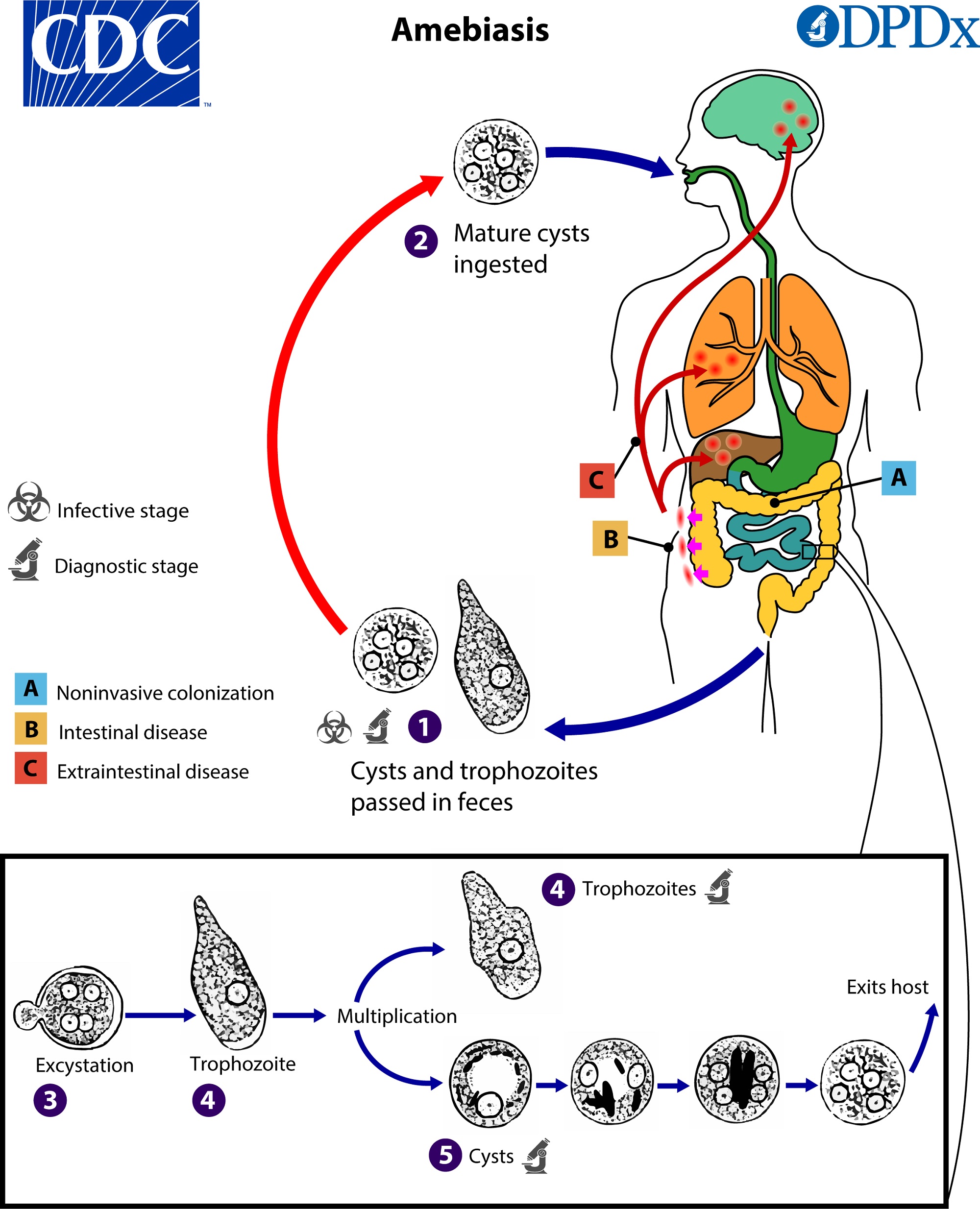
- 💩 Amoebiasis is caused by the protozoan Entamoeba histolytica.
- 🍽️ Infection occurs via ingestion of food or water contaminated with cysts.
🔄 Transmission
- 🚰 Faecal–oral spread through contaminated food or water.
- ❤️ Oral–anal sexual contact can transmit cysts.
- 🪰 Insects may contaminate food with cysts.
🔬 Pathology
- 🟢 Cysts = infective stage; trophozoites = invasive stage.
- Ingested cysts release trophozoites in the small intestine → colon invasion → “flask-shaped ulcers.”
- Via portal vein, trophozoites may reach the liver → amoebic liver abscess.
🌍 Epidemiology
- 🌴 Prevalent in tropical & subtropical regions.
- 📑 Notifiable disease in many countries due to public health significance.
🩺 Clinical Features
- 🚽 Amoebic dysentery: bloody diarrhoea, abdominal pain, fever, weight loss. Complications → toxic megacolon, strictures, severe GI bleeding.
- ⚠️ Amoeboma: inflammatory mass (sigmoid/caecum) mimicking malignancy.
- 🩸 Amoebic liver abscess: fever, RUQ pain, tender hepatomegaly; risk of rupture → empyema, peritonitis, pericarditis.
- ❤️ Pericardial amoebiasis: due to ruptured liver abscess → chest pain, dyspnoea, hypotension.
- 🧠 Brain abscess: headache, fever, focal neurology (resembles pyogenic abscess).
- 🩹 Cutaneous amoebiasis: painful ulcers near anus or genitals.
🧪 Investigations
- 📉 FBC: anaemia, leukocytosis.
- 🧫 Serology: fluorescent antibody test positive in most liver disease cases.
- 🔍 Stool microscopy: motile trophozoites with ingested RBCs; cysts.
- 🧾 Colonic biopsy: flask-shaped ulcers ± strictures.
- 🩻 Chest X-ray: elevated right diaphragm, right pleural effusion (liver abscess complication).
- 🖥️ USS/CT abdomen: liver abscess (often right lobe), raised ALP possible.
- 🧠 CT/MRI head: for suspected brain abscess.
🔍 Differential Diagnosis
- 🩺 Inflammatory bowel disease.
- 🦠 Bacillary dysentery.
- 🐔 Salmonella infection.
- 💊 Pseudomembranous colitis.
🧾 Differential Diagnosis of Liver Abscess
- 🧫 Pyogenic abscess.
- 🐑 Hydatid cyst.
- 🎗️ Primary/secondary liver tumour.
💊 Management
- Metronidazole 800 mg PO TDS × 5 days → amoebic colitis.
- Metronidazole 400 mg PO TDS × 10–14 days → liver abscess, then Diloxanide 500 mg TDS × 10 days to eradicate cysts.
- 🪣 Liver aspiration if risk of rupture or poor response to therapy → “anchovy paste” aspirate.
🛡️ Prevention
- 🚱 Safe water: bottled/boiled in endemic areas.
- 🧼 Good hygiene and sanitation.
- ❌ No effective vaccine currently available.
Categories
- A Level
- About
- Acute Medicine
- Anaesthetics and Critical Care
- Anatomy
- Anatomy and Physiology
- Biochemistry
- Book
- Cardiology
- Collections
- CompSci
- Crib Sheets
- Dental
- Dermatology
- Differentials
- Drugs
- ENT
- Education
- Electrocardiogram
- Embryology
- Emergency Medicine
- Endocrinology
- Ethics
- Foundation Doctors
- GCSE
- Gastroenterology
- General Practice
- Genetics
- Geriatric Medicine
- Guidelines
- Gynaecology
- Haematology
- Hepatology
- Immunology
- Infectious Diseases
- Infographic
- Investigations
- Lists
- Mandatory Training
- Medical Students
- Microbiology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Nutrition
- OSCE
- OSCEs
- Obstetrics
- Obstetrics Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Medicine and Dentistry
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatrics
- Palliative
- Pathology
- Pharmacology
- Physiology
- Procedures
- Psychiatry
- Public Health
- Radiology
- Renal
- Respiratory
- Resuscitation
- Revision
- Rheumatology
- Statistics and Research
- Stroke
- Surgery
- Toxicology
- Trauma and Orthopaedics
- USMLE
- Urology
- Vascular Surgery
