| Download the amazing global Makindo app: Android | Apple | |
|---|---|
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: Educational use only. Not for diagnosis or management. See below for full disclaimer. |
Stroke and Vision
Related Subjects: |Anatomy the Medulla Oblongata |Anatomy of the Midbrain |Anatomy of the Pons
🧠 Introduction
🔹 About 30% of stroke patients develop post-stroke visual impairment. 🔹 Common symptoms: hemianopia, neglect, diplopia, ↓ visual acuity, ptosis, anisocoria, nystagmus. 🔹 Homonymous hemianopia affects ~8% of stroke patients – some may still be driving.
🧬 Aetiology
- 👁️ Homonymous hemianopia: Loss of the same right/left halves of the visual field in both eyes. ➡️ Cause: Stroke of optic radiation or occipital cortex (MCA or PCA infarcts). ➡️ Macular sparing may occur if dual MCA/PCA supply to occipital pole.
- ◼️ Quadrantanopia:
- 🌙 Superior quadrantanopia: Temporal lobe lesion (“pie in the sky”).
- 🌄 Inferior quadrantanopia: Parietal lobe lesion (“pie on the floor”).
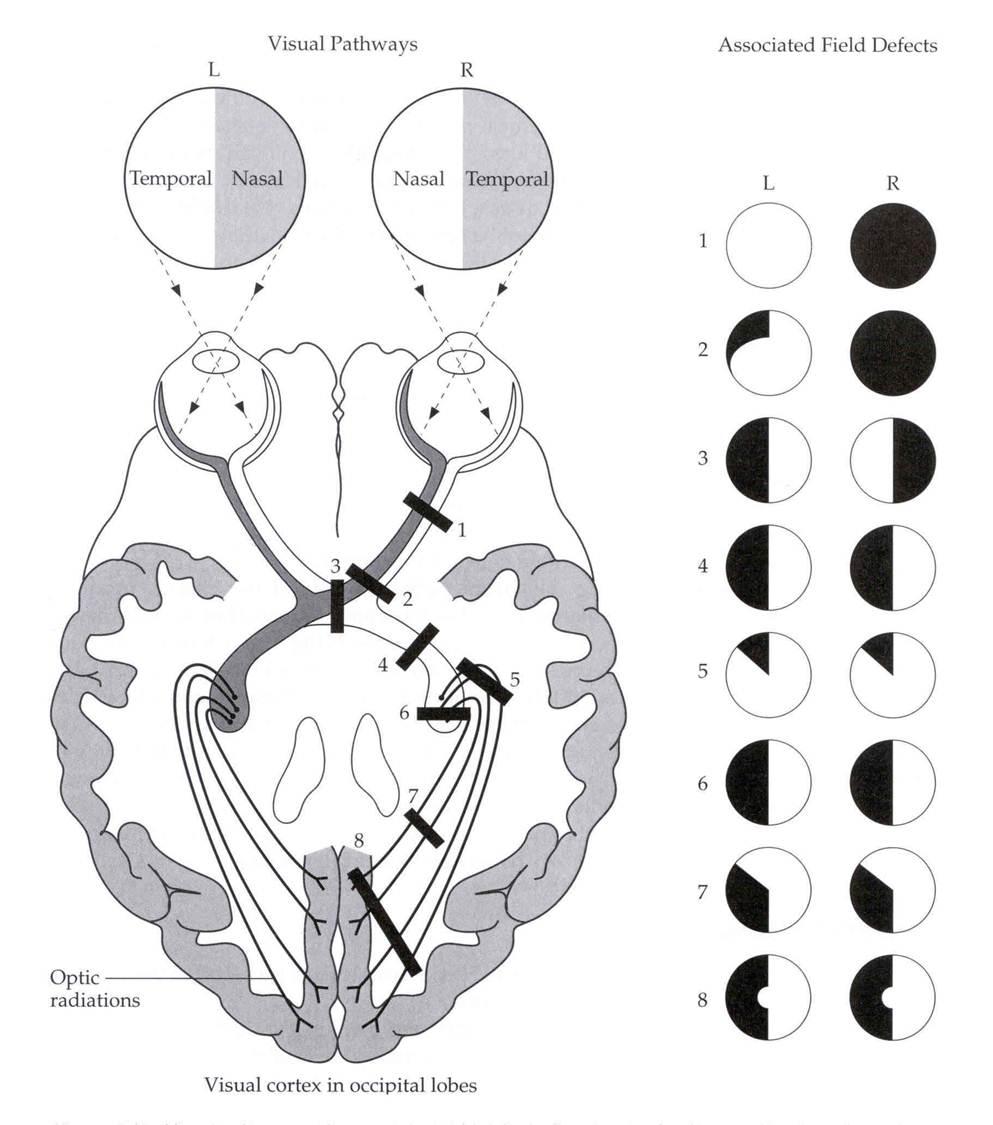
📊 Range of Visual Field Losses
| Visual Loss | Cause & Summary |
|---|---|
| Altitudinal defect | BRAO, optic neuropathy, retinal detachment, glaucoma |
| Central scotoma | Macular disease, optic neuritis/atrophy |
| Monocular blindness | CRAO, GCA, PMR, or vascular risk factors |
| Monocular quadrantanopia | Branch retinal artery occlusion |
| Dynamic loss (scotoma, aura) | Migraine with aura |
| Bitemporal hemianopia | Pituitary tumour, craniopharyngioma → MRI required |
| Lower homonymous quadrantanopia | Contralateral temporal lobe stroke |
| Upper homonymous quadrantanopia | Contralateral parietal lobe stroke |
| Complete homonymous hemianopia + motor/sensory deficit | Large MCA infarct |
| Complete homonymous hemianopia (no motor deficit) | PCA occipital infarct |
| Complete blindness | Rare, unless multiple bilateral lesions |
| Prosopagnosia | Inability to recognize faces (bilateral inferior occipital/temporal lesions) |
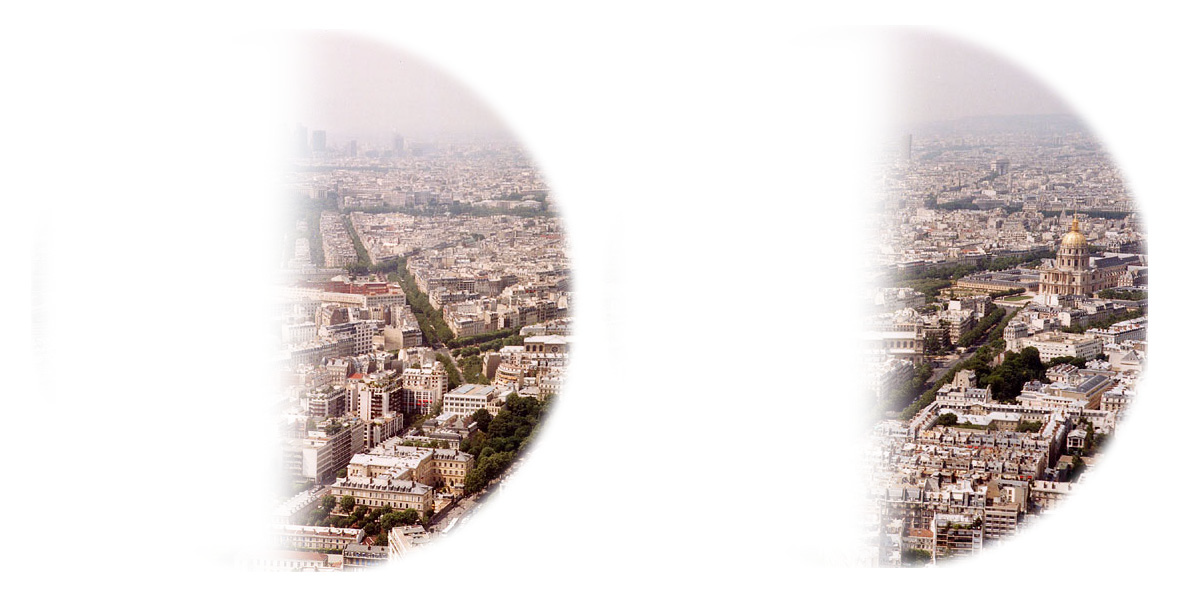
👁️ Left Homonymous Hemianopia (Patient’s View)

🔍 Visual Neglect
🧭 A parietal lobe syndrome → patients ignore one side (usually left). 🪒 May shave/eat only one side. 💡 Managed with occupational therapy & compensatory scanning strategies.
📖 Hemianopic Alexia
📚 Reading disorder post-stroke, usually left hemisphere → disrupts right visual field used for guiding eye movements. 🚨 Common, distressing, requires rehab input.
🚗 Driving & Visual Field Defects
Complete hemianopia = unsafe to drive. DVLA guidelines require assessment before resuming driving. DVLA guidance.
📏 DVLA Minimum Standards for Group 1 Drivers
- 120° horizontal field (≥50° left & right).
- No binocular defect within 20° of fixation.
- Homonymous/bitemporal defects close to fixation = not permitted.
DVLA testing includes: ✔️ Binocular Esterman field test (standard) ✔️ Monocular full-field charts (specific cases) ✔️ Goldmann perimetry (rare, strict criteria)
💊 Management of Visual Field Defects
- Multidisciplinary rehab: ophthalmology, orthoptics, OT, stroke physicians.
- Education + compensatory scanning strategies.
- Prism lenses → shift visual field.
- Refer to patient resources (Chest Heart & Stroke Scotland sheet).
- Prognosis variable → reassess at 2–3 months.
📚 References
- [1] Gilhotra JS, Mitchell P, Healey PR, et al. Homonymous visual field defects and stroke. Stroke 2002;33:2417-20.
- [2] Visual field defects after stroke. Aust Fam Physician, 2010.
- [3] DVLA Standards for Fitness to Drive.
Categories
- A Level
- About
- Acute Medicine
- Anaesthetics and Critical Care
- Anatomy
- Anatomy and Physiology
- Biochemistry
- Book
- Cardiology
- Collections
- CompSci
- Crib Sheets
- Crib sheets
- Dental
- Dermatology
- Differentials
- Drugs
- ENT
- Education
- Electrocardiogram
- Embryology
- Emergency Medicine
- Endocrinology
- Ethics
- Foundation Doctors
- GCSE
- Gastroenterology
- General Practice
- Genetics
- Geriatric Medicine
- Guidelines
- Gynaecology
- Haematology
- Hepatology
- Immunology
- Infectious Diseases
- Infographic
- Investigations
- Lists
- Mandatory Training
- Medical Students
- Microbiology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Nutrition
- OSCE
- OSCEs
- Obstetrics
- Obstetrics Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Medicine and Dentistry
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatrics
- Palliative
- Pathology
- Pharmacology
- Physiology
- Procedures
- Psychiatry
- Public Health
- Radiology
- Renal
- Respiratory
- Resuscitation
- Revision
- Rheumatology
- Statistics and Research
- Stroke
- Surgery
- Toxicology
- Trauma and Orthopaedics
- USMLE
- Urology
- Vascular Surgery
