| Download the app: Android | Apple | |
|---|---|
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: Educational use only. Not for diagnosis or management. |
Small vessel disease
Related Subjects: |Neurological History taking |Causes of Stroke |Ischaemic Stroke |Hypertension |Small Vessel Disease |Vascular Dementia |Dementias |CADASIL |CARASIL
🧠 Introduction
- Cerebral Small Vessel Disease (SVD) causes ~25% of all ischaemic strokes and >40% of dementia cases.
- It contributes to cognitive decline, gait impairment, mood disturbance, and vascular dementia.
- Common in the elderly on CT/MRI, but imaging–clinical correlation is variable (asymptomatic → gait dyspraxia → dementia).
- Underlying pathology for many deep haemorrhages (see haemorrhagic stroke chapter).
- Strongly linked to hypertension and other vascular risk factors.
- SVD itself cannot be directly imaged — instead, we use markers: lacunes, microbleeds, WMHs.
⚙️ Aetiology & Pathology
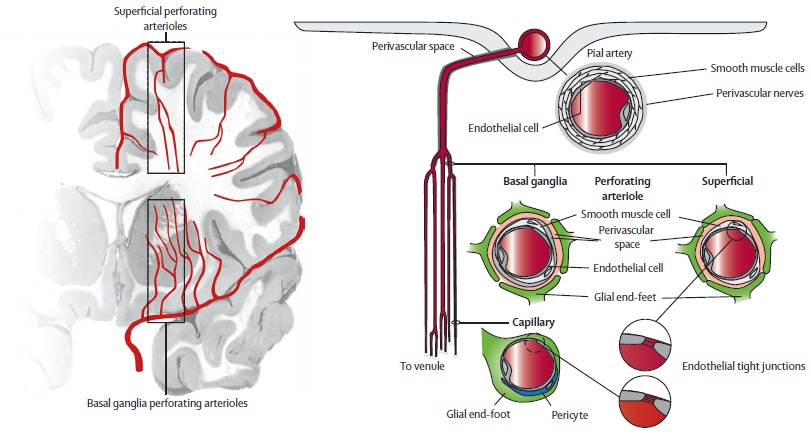
- A disease of small penetrating arterioles (<800 µm), branching from the Circle of Willis and vertebrobasilar system.
- Exposed to high pressures → prone to injury.
- Key mechanisms:
- 🩸 Lipohyalinosis (degenerative, different to atherosclerosis).
- 🧠 Amyloid angiopathy (elderly, lobar bleeds).
- 🧬 Inherited genetic defects (CADASIL, Fabry’s, CARASIL).
- 🦠 Vasculitis (autoimmune/inflammatory).
- End result → white matter demyelination, axonal loss, gliosis, and small deep strokes (lacunes <15 mm).
- Risk factors: age, hypertension, diabetes.
💡 Clinical pearl: Multiple acute lacunar infarcts → think embolism (not pure SVD).
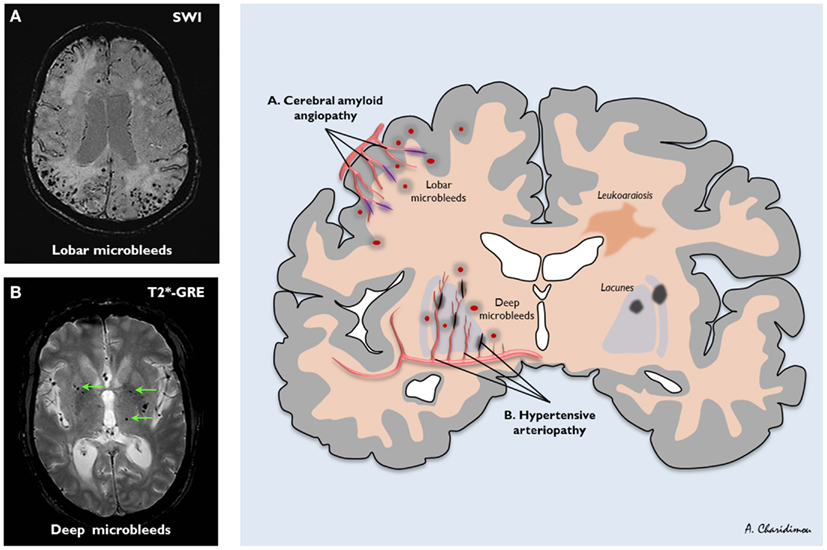
🔬 Imaging Features
- CT: Periventricular hypodensity, often with atrophy.
- MRI T2/FLAIR: White matter hyperintensities (WMHs) in periventricular & deep regions.
- DWI: Detects acute lacunes (≤1.5 cm).
- Gradient echo / SWI: Microbleeds (siderosis).
- Appearance can mimic demyelination (MS).
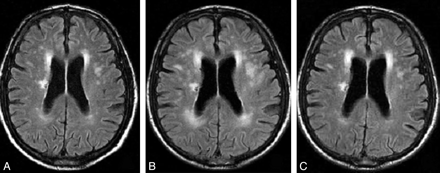
📏 Fazekas Scale
Grades WMHs severity:
PVWM 0–3 (caps → halo → extension) and DWM 0–3 (punctate → confluent).
Used more in research than routine practice.
🧩 Clinical Spectrum
- Often subclinical, but may present as:
- Classical lacunar syndromes:
- Pure motor or pure sensory stroke.
- Sensorimotor stroke.
- Ataxic hemiparesis.
- Dysarthria–clumsy hand.
- Hemichorea / hemiballismus.
- Chronic manifestations: Vascular dementia, gait apraxia, vascular parkinsonism.
📚 Pantoni’s Classification (2010)
SVD is heterogeneous — multiple pathologies converge on small vessels:
- 🩸 Arteriosclerosis: Lipohyalinosis, microaneurysms (HTN, diabetes, age).
- 🧠 Amyloid angiopathy: β-amyloid deposition, lobar bleeds, Alzheimer link.
- 🧬 Inherited: CADASIL, CARASIL, Fabry’s, MELAS, COL4A1 mutations.
- 🦠 Vasculitis/Immune: SLE, RA, ANCA vasculitides, Sneddon’s syndrome.
- Other: post-radiation angiopathy, venous collagenosis.
🩺 Management
- No specific cure — focus is on risk factor modification.
- 🎯 Control hypertension, diabetes, lipids, smoking.
- 💊 Antiplatelet therapy: Aspirin first-line. SPS3 trial: no benefit of dual therapy (aspirin+clopidogrel).
- 🏃 Lifestyle: exercise, diet, vascular prevention.
- 🔍 Consider genetic causes if young onset (e.g. CADASIL, Fabry’s).
- In acute stroke → thrombolysis is not contraindicated in lacunar infarction.
💡 Exam Pearl: SVD is the main cause of lacunar stroke, vascular dementia, gait apraxia, and deep haemorrhage. Think “small deep vessel” whenever you see a lacunar infarct on CT/MRI.
Categories
- A Level
- About
- Acute Medicine
- Anaesthetics and Critical Care
- Anatomy
- Biochemistry
- Book
- Cardiology
- Collections
- CompSci
- Crib Sheets
- Dental
- Dermatology
- Differentials
- Drugs
- ENT
- Education
- Electrocardiogram
- Embryology
- Emergency Medicine
- Endocrinology
- Ethics
- Foundation Doctors
- GCSE
- Gastroenterology
- General Practice
- Genetics
- Geriatric Medicine
- Guidelines
- Gynaecology
- Haematology
- Hepatology
- Immunology
- Infectious Disease
- Infectious Diseases
- Infographic
- Investigations
- Lists
- Mandatory Training
- Medical Students
- Microbiology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Nutrition
- OSCE
- Obstetrics
- Obstetrics Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Medicine and Dentistry
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatrics
- Palliative
- Pathology
- Pharmacology
- Physiology
- Procedures
- Psychiatry
- Public Health
- Radiology
- Renal
- Respiratory
- Resuscitation
- Revision
- Rheumatology
- Statistics and Research
- Stroke
- Surgery
- Toxicology
- Trauma and Orthopaedics
- USMLE
- Urology
