| Download the amazing global Makindo app: Android | Apple | |
|---|---|
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: Educational use only. Not for diagnosis or management. See below for full disclaimer. |
Eosinophilic Oesophagitis
📖 About
- Eosinophilic Oesophagitis (EoE) = chronic, immune-mediated inflammation of the oesophagus.
- First recognised as a distinct disease in the 1990s.
- Food antigens (🥛 milk, 🌾 wheat, 🍳 eggs, 🐟 seafood, 🌱 soy) strongly implicated.
- Pathology = infiltration of eosinophils → mucosal inflammation → fibrosis → stricturing.
📊 Incidence
- Predominantly affects white men aged 30–50.
- Estimated incidence ≈ 7 per 100,000 per year (rising with improved recognition).
🧬 Aetiology & Pathophysiology
- Genetics: Variants in CAPN14 and TSLP (thymic stromal lymphopoietin) genes increase susceptibility.
- Barrier dysfunction: Loss of anti-proteases → increased epithelial permeability → allergen penetration.
- Immune signalling: ↑ eotaxin-3 expression → recruitment of eosinophils → chronic inflammation.
- Result = mucosal fibrosis, trachealisation of oesophagus, stricture formation.
🧾 Diagnostic Criteria
- Symptoms of oesophageal dysfunction (e.g. dysphagia, food bolus impaction).
- > 15 eosinophils / high power field on oesophageal biopsy 🔬.
- Persistent eosinophilia despite 8-week PPI trial 💊.
- Exclusion of secondary causes of eosinophilia (see below).
🩺 Clinical Features
- Dysphagia (solids > liquids) 🍞🥩
- Food bolus impaction 🍗 (often requiring A&E attendance)
- Chest pain or reflux-like symptoms despite PPI use
- Narrow-calibre oesophagus → slow eating, avoidance of hard textures
- Children may present with feeding difficulties, failure to thrive
🔬 Investigations
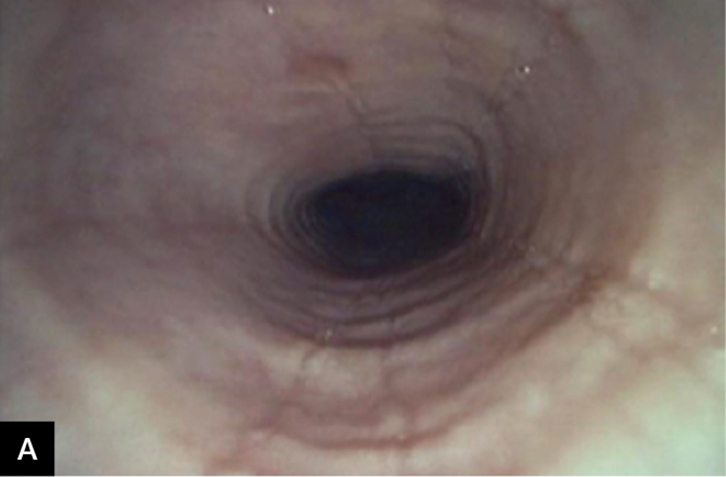
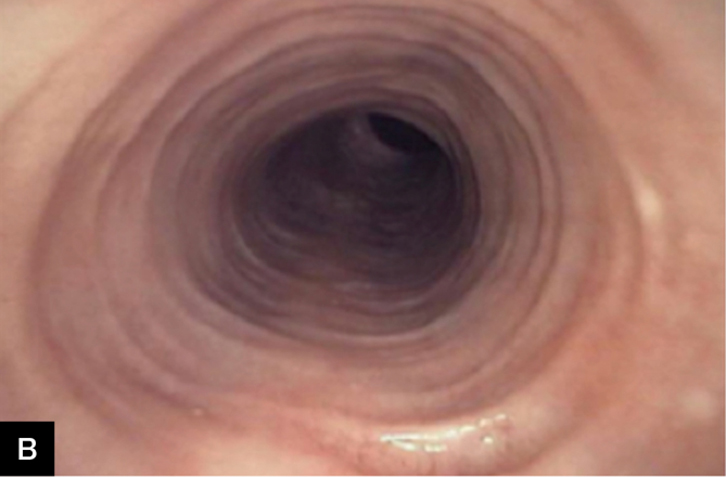
- Endoscopy (OGD):
- Rings (“trachealisation” of oesophagus) 🔄
- Linear furrows 📏
- White exudates ❄️
- Friability, mucosal oedema, loss of vascular pattern
- Fixed strictures in advanced disease
- Biopsy: > 15 eosinophils/hpf confirms diagnosis (after PPI trial).
- Bloods: May show peripheral eosinophilia, but not diagnostic.
📌 Causes of Oesophageal Eosinophilia
- Eosinophilic oesophagitis ✅
- GORD (reflux disease)
- PPI-responsive oesophageal eosinophilia
- Achalasia
- Crohn’s disease
- Parasitic infection 🪱
- Drug hypersensitivity 💊
- Connective tissue disease (e.g. scleroderma, dermatomyositis)
- Coeliac disease 🌾
- Hypereosinophilic syndrome
💡 Exam tip: A PPI trial (8 weeks) is essential before diagnosing EoE to exclude GORD.
💊 Management
- Dietary modification:
- Empirical elimination diet (milk, wheat, eggs, soy, seafood) 🍞🥛🍳
- Elemental diet in severe cases
- Consider formal allergy testing
- Pharmacological:
- High-dose PPI (also helps differentiate from GORD)
- Topical swallowed steroids (fluticasone, budesonide via inhaler MDI without spacer) → reduce inflammation
- Course: typically 8 weeks, then re-scope
- Endoscopic intervention:
- Dilatation for strictures 🚑
- Reserved for refractory or critically narrowed oesophagus
📋 References
Categories
- A Level
- About
- Acute Medicine
- Anaesthetics and Critical Care
- Anatomy
- Anatomy and Physiology
- Biochemistry
- Book
- Cardiology
- Collections
- CompSci
- Crib Sheets
- Crib sheets
- Dental
- Dermatology
- Differentials
- Drugs
- ENT
- Education
- Electrocardiogram
- Embryology
- Emergency Medicine
- Endocrinology
- Ethics
- Foundation Doctors
- GCSE
- Gastroenterology
- General Practice
- Genetics
- Geriatric Medicine
- Guidelines
- Gynaecology
- Haematology
- Hepatology
- Immunology
- Infectious Diseases
- Infographic
- Investigations
- Lists
- Mandatory Training
- Medical Students
- Microbiology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Nutrition
- OSCE
- OSCEs
- Obstetrics
- Obstetrics Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Medicine and Dentistry
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatrics
- Palliative
- Pathology
- Pharmacology
- Physiology
- Procedures
- Psychiatry
- Public Health
- Radiology
- Renal
- Respiratory
- Resuscitation
- Revision
- Rheumatology
- Statistics and Research
- Stroke
- Surgery
- Toxicology
- Trauma and Orthopaedics
- USMLE
- Urology
- Vascular Surgery
