| Download the amazing global Makindo app: Android | Apple | |
|---|---|
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: Educational use only. Not for diagnosis or management. See below for full disclaimer. |
Ventricular Septal defect (VSD) 💔
Related Subjects: |Congenital Acyanotic Heart Disease |Congenital Cyanotic Heart Disease |Cardiac Embryology |Cyanosis - Central and Peripheral |Down's syndrome (Trisomy 21) |Tetralogy of Fallot |Patent Foramen Ovale (PFO) |Ventricular Septal defect (VSD)
🫀 Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD) is the most common congenital heart defect (≈2/1000 live births). Small VSDs often 🎶 produce loud murmurs but are well tolerated, while large VSDs may be quieter but cause heart failure by 6–8 weeks. Many small muscular defects close spontaneously.
📌 About
- Abnormal shunt between LV → RV.
- Classic finding: harsh pansystolic murmur ± thrill at lower left sternal edge.
- Symptomatic infants: poor weight gain, tachypnoea, feeding fatigue.
🧬 Aetiology & Pathophysiology
- Size of defect + pulmonary pressures dictate severity.
- Large, uncorrected defects → pulmonary hypertension → reversal of shunt = Eisenmenger’s syndrome (cyanosis, clubbing, ↓ murmur).
- High risk of endocarditis – vigilance required.
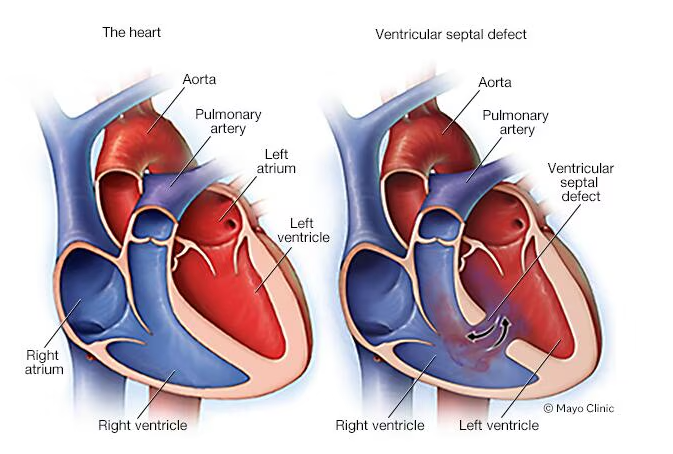
🔎 Anatomical Types
- Perimembranous – most common; near valves; may close spontaneously; risk aortic regurgitation.
- Muscular – “Swiss cheese”; high chance of closure.
- Inlet (AV canal) – linked with Down syndrome; often surgical.
- Outlet (subarterial) – more frequent in Asia; risk aortic cusp prolapse → early surgery.
- Gerbode – rare LV→RA defect.
🩺 Clinical Features
- 🎶 Loud pansystolic murmur ± thrill (small VSD louder than large).
- Hyperdynamic apex beat, pulmonary overcirculation signs.
- Failure to thrive, recurrent chest infections.
- Eisenmenger’s: RV lift, cyanosis, murmur softens/disappears.
🧪 Investigations
- Bloods: FBC (anaemia), CRP/ESR if ?endocarditis.
- CXR: Normal in small; cardiomegaly & pulmonary plethora in large.
- ECG: Normal if small; LVH + RVH if large.
- Echocardiography: 🥇 gold standard – defect site, shunt size, PA pressure.
💊 Management
- Observation 👀: Most small VSDs close spontaneously → regular follow-up.
- Medical: Diuretics, ACE inhibitors, digoxin for symptomatic infants awaiting repair.
- Surgical Repair 🩻: Patch closure for large, symptomatic, or failing to thrive defects (often in early childhood).
- Device Closure: Via catheter – mainly muscular VSDs.
- Endocarditis Prophylaxis: NICE: only if previous endocarditis or prosthetic material used. But clinicians must remain alert 🚨.
- Long-term follow-up: Monitor for arrhythmias, residual defects, pulmonary hypertension.
⚠️ Complications
- Infective endocarditis
- Heart failure & pulmonary hypertension
- Arrhythmias (esp. post-surgery)
- Eisenmenger’s syndrome
🔍 Comparison: ASD vs VSD vs PDA
| Feature | ASD | VSD | PDA |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | Abnormal communication between atria (usually secundum type). | Shunt between LV → RV (most common congenital defect). | Persistent communication between aorta & pulmonary artery. |
| Murmur | 🌬️ Fixed split S2 + ejection systolic murmur (↑ flow across pulmonary valve). | 🎶 Harsh pansystolic murmur ± thrill at LLSB (small = louder). | 🔄 Continuous “machinery” murmur below left clavicle. |
| Clinical Features | Often asymptomatic in childhood; recurrent chest infections; exercise intolerance in adults. | Failure to thrive, HF by 6–8 weeks if large; recurrent chest infections; FTT. | Bounding pulses, wide pulse pressure, HF in infancy if large. |
| ECG | RAD, RBBB pattern (esp. secundum ASD). | LVH ± RVH in large defects; normal if small. | LVH ± RVH in large ducts. |
| CXR | Cardiomegaly, prominent pulmonary arteries. | Small: normal; Large: cardiomegaly, pulmonary plethora. | Cardiomegaly, ↑ pulmonary markings. |
| Complications | Paradoxical emboli, pulmonary hypertension, arrhythmias (AF). | Endocarditis, Eisenmenger’s, arrhythmias, HF. | Endocarditis, Eisenmenger’s (late), HF. |
| Management | Device/surgical closure if large shunt or symptomatic. | Observe if small; surgery/device closure if symptomatic/large. | Indomethacin/ibuprofen (in neonates) or surgical/device closure if persistent. |
Categories
- A Level
- About
- Acute Medicine
- Anaesthetics and Critical Care
- Anatomy
- Anatomy and Physiology
- Biochemistry
- Book
- Cardiology
- Collections
- CompSci
- Crib Sheets
- Crib sheets
- Dental
- Dermatology
- Differentials
- Drugs
- ENT
- Education
- Electrocardiogram
- Embryology
- Emergency Medicine
- Endocrinology
- Ethics
- Foundation Doctors
- GCSE
- Gastroenterology
- General Practice
- Genetics
- Geriatric Medicine
- Guidelines
- Gynaecology
- Haematology
- Hepatology
- Immunology
- Infectious Diseases
- Infographic
- Investigations
- Lists
- Mandatory Training
- Medical Students
- Microbiology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Nutrition
- OSCE
- OSCEs
- Obstetrics
- Obstetrics Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Medicine and Dentistry
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatrics
- Palliative
- Pathology
- Pharmacology
- Physiology
- Procedures
- Psychiatry
- Public Health
- Radiology
- Renal
- Respiratory
- Resuscitation
- Revision
- Rheumatology
- Statistics and Research
- Stroke
- Surgery
- Toxicology
- Trauma and Orthopaedics
- USMLE
- Urology
- Vascular Surgery
