| Download the amazing global Makindo app: Android | Apple | |
|---|---|
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: Educational use only. Not for diagnosis or management. See below for full disclaimer. |
Watershed Infarcts
🧠 Watershed infarcts occur in the border zones between two or more cerebral arterial territories. These regions are particularly vulnerable to hypoperfusion 🌊, especially during systemic hypotension or severe carotid disease. 💡 They account for ~10% of all ischemic strokes.
📖 About
- 🧩 Found at junctions of major arteries (ACA, MCA, PCA).
- Two main types: Cortical Border-Zone (CBZ) & Internal Border-Zone (IBZ).
- Pathophysiology: ↓ cerebral perfusion ± microemboli.
⚠️ Aetiology
- Severe systemic hypotension (e.g. shock, perioperative drops).
- Carotid artery stenosis or occlusion.
- 💉 Microemboli contributing to cortical infarcts.
🗺️ Cortical Border-Zone Infarcts
- Between distal ACA–MCA–PCA territories.
- Wedge-shaped infarcts in parietal/frontal cortex.
- Often unilateral, linked to hypoperfusion or emboli.
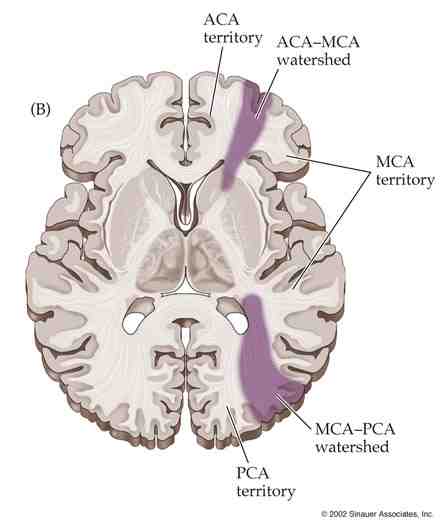
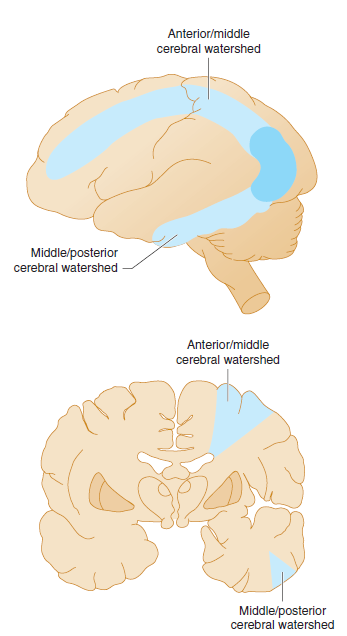
🏞️ Internal Border-Zone Infarcts
- Between cortical vessels & deep perforators (lenticulostriate, Heubner).
- Often due to profound hypotension or severe carotid/MCA stenosis.
- Appear as linear/band-like lesions parallel to lateral ventricles.
🧩 Risk Factors
- Rapid BP reduction in hypertensives.
- Perioperative hypotension 🛠️.
- Shock (cardiac arrest, sepsis, dehydration).
- Severe carotid stenosis.
- Low cardiac output (e.g. heart failure).
🩺 Clinical Presentation
- Varies by cortical/subcortical area affected.
- Common: weakness/paralysis, sensory loss, visual field defects, aphasia.
- “Man-in-the-barrel” syndrome 🧍♂️: proximal upper & lower limb weakness > distal.
🔬 Investigations
- 🧪 Bloods: FBC, U&E, LFTs, glucose, cardiac enzymes, lactate.
- 🖥️ Imaging: MRI-DWI (gold standard), CT, CTA/MRA.
- 🩻 Carotid duplex for stenosis, echo for embolic source, ECG for arrhythmias.
💊 Management
- 💧 Restore perfusion: cautious BP optimisation, fluids for hypovolaemia.
- 🫀 Treat underlying cause: carotid revascularisation, cardiac management.
- 🛡️ Secondary prevention: antiplatelets, statins, BP control, lifestyle modification.
- 🧑⚕️ Rehabilitation: physio, OT, speech therapy as needed.
📈 Prognosis
- Outcome depends on infarct size & speed of perfusion restoration.
- Early rehab improves recovery 💪.
📚 References
- Caplan LR, Hennerici M. Arch Neurol. 1998;55(11):1475-1482.
- Derdeyn CP, Powers WJ. In: Barnett's Stroke, 5th ed. Elsevier Saunders; 2011.
- Bladin CF, Chambers BR. Stroke. 1993;24(12):1925-1932.
Categories
- A Level
- About
- Acute Medicine
- Anaesthetics and Critical Care
- Anatomy
- Anatomy and Physiology
- Biochemistry
- Book
- Cardiology
- Collections
- CompSci
- Crib Sheets
- Crib sheets
- Dental
- Dermatology
- Differentials
- Drugs
- ENT
- Education
- Electrocardiogram
- Embryology
- Emergency Medicine
- Endocrinology
- Ethics
- Foundation Doctors
- GCSE
- Gastroenterology
- General Practice
- Genetics
- Geriatric Medicine
- Guidelines
- Gynaecology
- Haematology
- Hepatology
- Immunology
- Infectious Diseases
- Infographic
- Investigations
- Lists
- Mandatory Training
- Medical Students
- Microbiology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Nutrition
- OSCE
- OSCEs
- Obstetrics
- Obstetrics Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Medicine and Dentistry
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatrics
- Palliative
- Pathology
- Pharmacology
- Physiology
- Procedures
- Psychiatry
- Public Health
- Radiology
- Renal
- Respiratory
- Resuscitation
- Revision
- Rheumatology
- Statistics and Research
- Stroke
- Surgery
- Toxicology
- Trauma and Orthopaedics
- USMLE
- Urology
- Vascular Surgery
