| Download the amazing global Makindo app: Android | Apple | |
|---|---|
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: Educational use only. Not for diagnosis or management. See below for full disclaimer. |
Hepatocellular Carcinoma
🌍 Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most common primary liver cancer, frequently arising in patients with cirrhosis. Biannual ultrasound ± alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) screening is recommended in high-risk groups to allow diagnosis at an early stage when potentially curative therapies are feasible.
📖 About
- HCC is a leading cause of cancer deaths worldwide.
- Highest incidence: Southeast Asia & sub-Saharan Africa 🌏.
- Not all cases arise in cirrhosis — HBV can predispose directly via viral DNA integration.
⚠️ Risk Factors
- Chronic hepatitis B or C infection 🦠
- Alcoholic liver disease 🍺
- Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH, metabolic syndrome link) 🍔
- Haemochromatosis 🩸
- Aflatoxin B exposure (contaminated grains/nuts in endemic regions) 🌽
- Primary biliary cholangitis (rare cause)
🩺 Clinical Features
- Systemic: Weight loss, anorexia, fever, fatigue.
- Hepatic: Right upper quadrant pain, hepatomegaly, jaundice in late disease.
- Background of cirrhosis (ascites, varices, encephalopathy).
🔎 Screening
- Surveillance: Ultrasound ± AFP every 6 months for cirrhotics or HBV carriers at risk.
- Helps detect subclinical disease when resection/transplant is feasible.
🧪 Investigations
- Bloods: FBC, U&E, LFTs, coagulation, CRP.
- Tumour marker: Alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), though not diagnostic alone.
- Ultrasound: Initial modality to detect lesions.
- Triple-phase CT / MRI: Gold standard to confirm arterial enhancement & venous washout.
- Biopsy: Usually avoided due to seeding risk unless diagnosis uncertain.
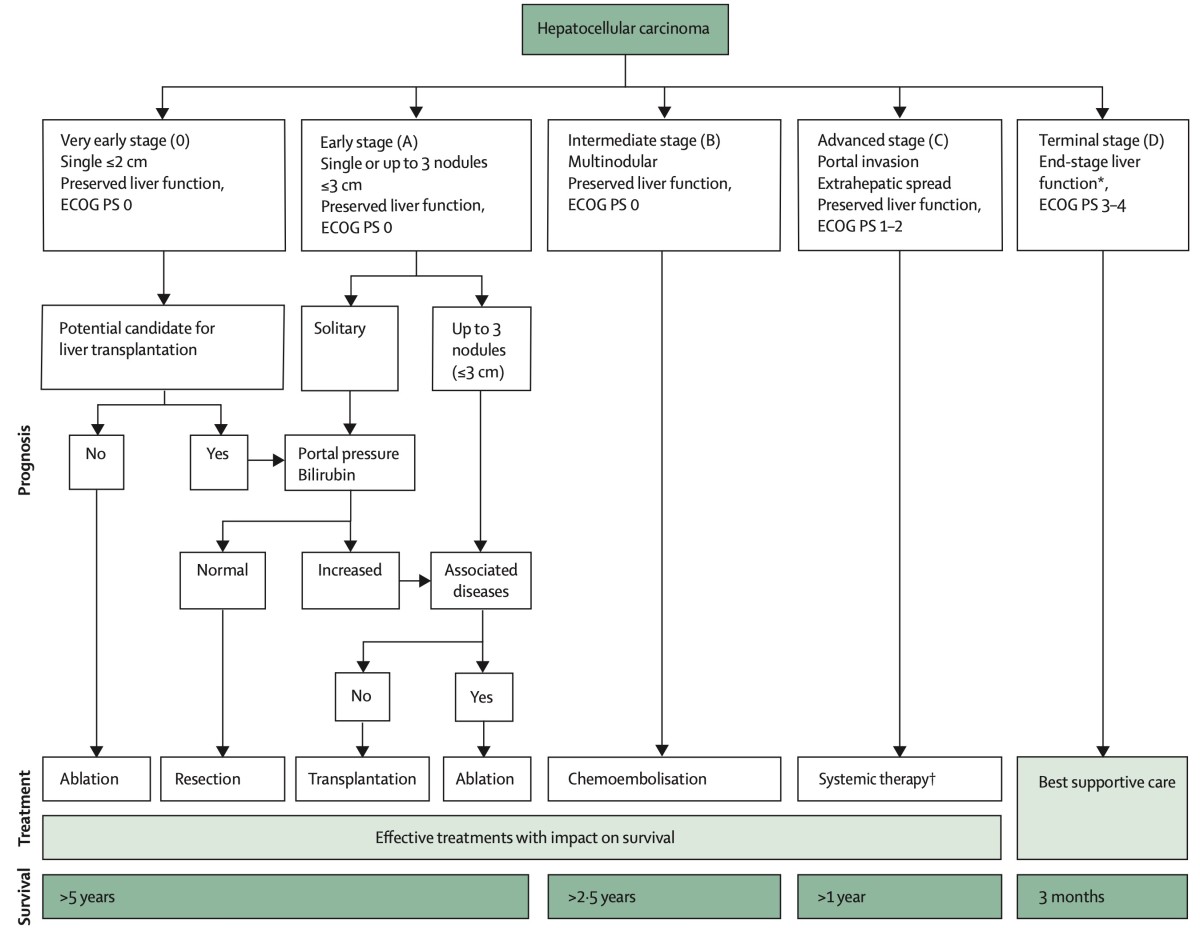
🛠️ Management
- Resection: Best for solitary tumours with preserved liver function (Child-Pugh A, no portal hypertension).
- Liver Transplantation: For unresectable cases meeting Milan criteria (single tumour ≤5 cm or ≤3 tumours ≤3 cm, no vascular invasion/metastases).
- Ablation (RFA/Microwave): Effective for small lesions; less so for large or deep tumours.
- Transarterial chemoembolisation (TACE): Used for multifocal disease without vascular invasion/extrahepatic spread.
- Systemic therapy: Sorafenib (tyrosine kinase inhibitor), Lenvatinib (non-inferior alternative), Regorafenib for progression. Newer immunotherapies (atezolizumab + bevacizumab) showing survival benefit 🌟.
📚 References
Categories
- A Level
- About
- Acute Medicine
- Anaesthetics and Critical Care
- Anatomy
- Anatomy and Physiology
- Biochemistry
- Book
- Cardiology
- Collections
- CompSci
- Crib Sheets
- Crib sheets
- Dental
- Dermatology
- Differentials
- Drugs
- ENT
- Education
- Electrocardiogram
- Embryology
- Emergency Medicine
- Endocrinology
- Ethics
- Foundation Doctors
- GCSE
- Gastroenterology
- General Practice
- Genetics
- Geriatric Medicine
- Guidelines
- Gynaecology
- Haematology
- Hepatology
- Immunology
- Infectious Diseases
- Infographic
- Investigations
- Lists
- Mandatory Training
- Medical Students
- Microbiology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Nutrition
- OSCE
- OSCEs
- Obstetrics
- Obstetrics Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Medicine and Dentistry
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatrics
- Palliative
- Pathology
- Pharmacology
- Physiology
- Procedures
- Psychiatry
- Public Health
- Radiology
- Renal
- Respiratory
- Resuscitation
- Revision
- Rheumatology
- Statistics and Research
- Stroke
- Surgery
- Toxicology
- Trauma and Orthopaedics
- USMLE
- Urology
- Vascular Surgery
