| Download the amazing global Makindo app: Android | Apple | |
|---|---|
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: Educational use only. Not for diagnosis or management. See below for full disclaimer. |
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
Related Subjects: |Urothelial tumour s |Haematuria |Acute Urinary Retention |Anuria and Oliguria |Bladder cancer |Renal cell carcinoma |Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia |IgA nephropathy |Prostate Cancer |Henoch-Schonlein purpura |Glomerulonephritis
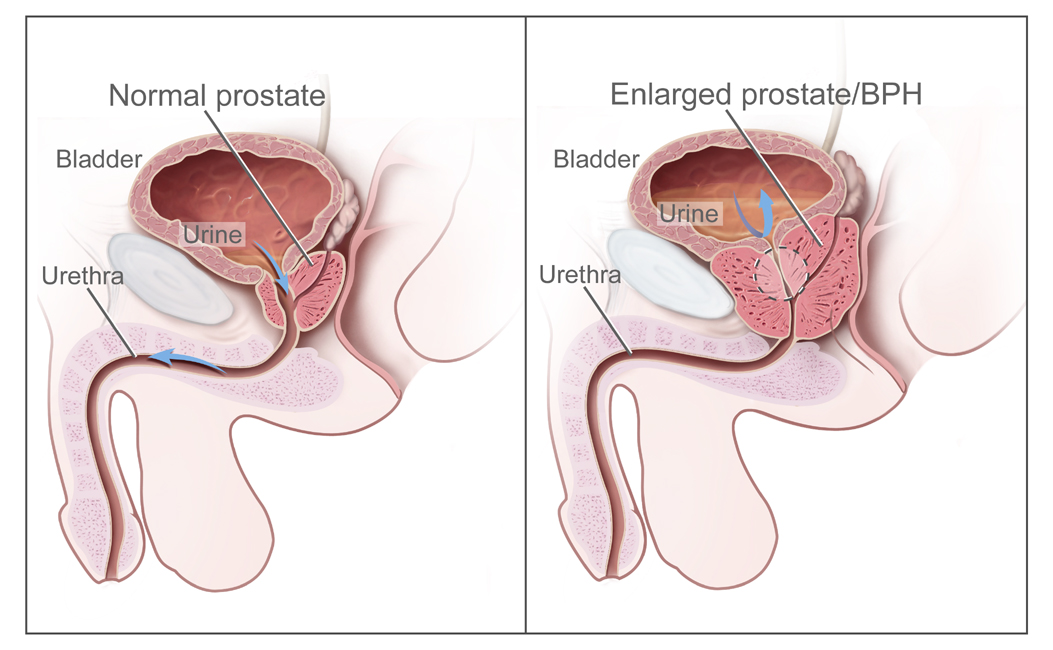
🔵 Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) is usually confined to the peri-urethral glands in the centre of the prostate. 📏 Importantly, prostate size does not always correlate with the degree of urinary obstruction.
📌 About
- Prostate size alone is not a reliable predictor of urinary outlet obstruction 🚫.
🧬 Pathology
- Represents hyperplasia (increase in cell number) rather than hypertrophy.
- Confined mainly to the peri-urethral (transition) zone.
- Prostate size ≠ severity of symptoms.
👨 Clinical
- Common in men >50 yrs; prevalence: Black > White > Asian.
- Voiding symptoms: weak stream, hesitancy, terminal dribbling 🚽.
- Storage symptoms: frequency, urgency, nocturia ⏰.
- Incomplete emptying → chronic retention with large bladder.
- Exam: smooth enlarged prostate, palpable bladder.
⚠️ Complications
- Acute urinary retention (can be worsened by drugs ❗ e.g. anticholinergics, antihistamines, antidepressants).
- Recurrent UTIs 🦠.
- Hydroureter, hydronephrosis, renal failure 🩸.
- Bladder calculi & infection.
🔍 Investigations
- Urinalysis (MSU if positive); haematuria → investigate for malignancy 🔎.
- Bloods: U&E, FBC, PSA (interpret carefully: ↑ with BPH, infection, cancer, recent catheterisation).
- KUB X-ray: consider if stone suspected.
- Post-void residual bladder volume (USS or catheter).
- 24-hr voiding diary: frequency & volume.
- Abdominal USS: kidney size, hydronephrosis, bladder wall.
- Flexible cystoscopy: if haematuria, obstruction, or diagnostic uncertainty.
- Urodynamics: in neurogenic bladder suspicion or failed prior prostate surgery.
💡 General Lifestyle Advice
- Limit alcohol 🍺, caffeine ☕, and evening fluids.
- Avoid decongestants/antihistamines as they worsen retention.
- Bladder training: urinate regularly (every 4–6 hrs). Double voiding can help.
- Maintain healthy weight & stay active 🏃 - reduces risk of retention.
- Keep warm 🧥 - cold triggers retention.
💊 Medical Management
- Alpha-blockers (Tamsulosin, Alfuzosin): relax smooth muscle → symptom relief. SE: postural hypotension, dizziness.
- 5-α reductase inhibitors (Finasteride, Dutasteride): shrink prostate (↓DHT). Takes 3–6 months; SE: retrograde ejaculation, ↓ libido.
- Combination therapy: in large prostates or severe symptoms.
- Anticholinergics (e.g. Oxybutynin): for storage symptoms; caution in frail elderly (delirium risk).
- Mirabegron: β3 agonist alternative for OAB; SE: hypertension.
🧴 Catheterisation & TWOC
- Acute retention: catheterise + start Tamsulosin → trial without catheter (TWOC) after 1–2 days.
- If fails: intermittent self-catheterisation or long-term catheter (urethral/suprapubic).
- Severe chronic retention (>1 L) → often requires long-term catheterisation.
📤 Indications for Urology Referral
- Suspicion of malignancy (hard nodular prostate, raised PSA).
- Obstructive uropathy: AKI, ↑ urea/creatinine.
- Large bladder, recurrent retention, or hydronephrosis.
- Rapidly worsening LUTS or failure of medical therapy.
🔪 Surgery: TURP
- Transurethral Resection of the Prostate (TURP): removes obstructive tissue via resectoscope.
- Benefits: strong urine flow & rapid relief.
- Complications: bleeding, TURP syndrome (dilutional hyponatraemia), clot retention, stricture, retrograde ejaculation, incontinence.
- Very large prostates → may need open prostatectomy.
Case 1 – Mild symptoms
58-year-old with daytime frequency and nocturia ×2. DRE normal, PSA ok, Post void residual 40 mL. Try lifestyle changes (less evening fluids, cut caffeine/alcohol). If still troublesome, start an alpha-blocker and review in 4–6 weeks.
Case 2 – Moderate symptoms, enlarged prostate
66-year-old with mixed LUTS (IPSS 18), smooth enlarged prostate, PSA 2.4 µg/L, volume ~45 mL, PVR 120 mL. Start tamsulosin and add a 5-alpha-reductase inhibitor (works over months). Consider bladder drug (e.g., mirabegron) only if PVR is low and storage symptoms persist.
Case 3 – Acute urinary retention
74-year-old unable to pass urine after a heavy night. Catheterise (record volume), start an alpha-blocker, check for UTI/culprit meds. Plan a trial without catheter in 2–7 days. If it fails or there are complications, refer for surgery (e.g., TURP/HoLEP) based on prostate size and fitness.
Categories
- A Level
- About
- Acute Medicine
- Anaesthetics and Critical Care
- Anatomy
- Anatomy and Physiology
- Biochemistry
- Book
- Cardiology
- Collections
- CompSci
- Crib Sheets
- Crib sheets
- Dental
- Dermatology
- Differentials
- Drugs
- ENT
- Education
- Electrocardiogram
- Embryology
- Emergency Medicine
- Endocrinology
- Ethics
- Foundation Doctors
- GCSE
- Gastroenterology
- General Practice
- Genetics
- Geriatric Medicine
- Guidelines
- Gynaecology
- Haematology
- Hepatology
- Immunology
- Infectious Diseases
- Infographic
- Investigations
- Lists
- Mandatory Training
- Medical Students
- Microbiology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Nutrition
- OSCE
- OSCEs
- Obstetrics
- Obstetrics Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Medicine and Dentistry
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatrics
- Palliative
- Pathology
- Pharmacology
- Physiology
- Procedures
- Psychiatry
- Public Health
- Radiology
- Renal
- Respiratory
- Resuscitation
- Revision
- Rheumatology
- Statistics and Research
- Stroke
- Surgery
- Toxicology
- Trauma and Orthopaedics
- USMLE
- Urology
- Vascular Surgery
