Makindo Medical Notes"One small step for man, one large step for Makindo" |
|
|---|---|
| Download all this content in the Apps now Android App and Apple iPhone/Pad App | |
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: The contents are under continuing development and improvements and despite all efforts may contain errors of omission or fact. This is not to be used for the assessment, diagnosis, or management of patients. It should not be regarded as medical advice by healthcare workers or laypeople. It is for educational purposes only. Please adhere to your local protocols. Use the BNF for drug information. If you are unwell please seek urgent healthcare advice. If you do not accept this then please do not use the website. Makindo Ltd. |
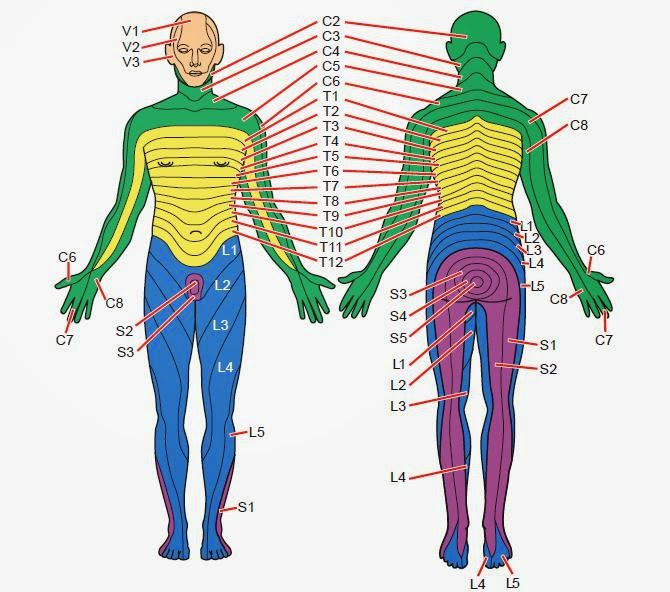
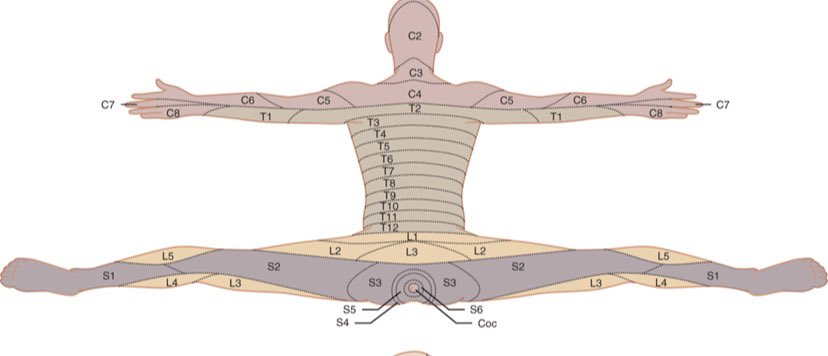
Dermatomes
Related Subjects: |Radial Nerve |Median Nerve |Ulnar Nerve |Musculocutaneous nerve |Axillary nerve |Brachial plexus |Dermatomes
Dermatomes of the Human Body: From Back of Head to Perianal
Definition: A dermatome is a region of skin innervated by sensory fibres from a single spinal nerve root. 💡 Key OSCE pearl: Each dermatome is a "segmental map" of spinal innervation, not the same as individual peripheral nerves.
📖 Cervical Dermatomes (C2–C8)
- C2: Back of head, occiput.
- C3: Neck.
- C4: Shoulder tip.
- C5: Lateral upper arm.
- C6: Lateral forearm & thumb 👍.
- C7: Middle finger ☝️.
- C8: Little finger & medial forearm.
🫀 Thoracic Dermatomes (T1–T12)
- T1: Medial forearm.
- T4: Nipple line landmark.
- T7–T9: Upper–mid abdomen.
- T10: Umbilicus 🎯.
- T12: Suprapubic region.
🦵 Lumbar Dermatomes (L1–L5)
- L1: Groin crease.
- L2: Upper anterior thigh.
- L3: Knee region.
- L4: Medial shin, medial malleolus.
- L5: Dorsum of foot, big toe.
🦶 Sacral Dermatomes (S1–S5)
- S1: Lateral foot, little toe.
- S2: Posterior thigh, calf.
- S3–S5: Perianal and perineal region ("saddle anaesthesia").
🧬 Embryological Origin
Dermatomes derive from somites, blocks of mesoderm alongside the neural tube. The dermatome component of each somite forms dermis → explaining the segmental skin innervation that persists into adult life.
🧠 Dermatomes, Myotomes & Reflexes by Nerve Root
| Nerve Root | Dermatome (Sensation) | Myotome (Motor) | Reflex |
|---|---|---|---|
| C5 | Lateral shoulder (regimental badge area) | Shoulder abduction (deltoid) | Biceps (with C6) |
| C6 | Lateral forearm, thumb & index finger | Elbow flexion, wrist extension | Biceps / brachioradialis |
| C7 | Middle finger | Elbow extension (triceps), wrist flexion | Triceps |
| C8 | Little finger, medial forearm | Finger flexion & thumb extension | — |
| T1 | Medial arm & elbow | Finger abduction/adduction (interossei) | — |
| L2 | Anterior thigh | Hip flexion | — |
| L3 | Medial thigh/knee | Knee extension (quadriceps) | — |
| L4 | Medial leg & ankle | Ankle dorsiflexion | Patellar (knee jerk) |
| L5 | Dorsum of foot, great toe | Great toe extension (EHL) | — |
| S1 | Lateral foot & heel | Ankle plantarflexion | Ankle (Achilles) |
| S2 | Posterior thigh | Knee flexion (hamstrings) | — |
| S3–S5 | Perianal region ("saddle anaesthesia") | Anal sphincter | Anal wink / bulbocavernosus |
⚕️ Clinical Relevance
- Spinal cord injury: Sensory level defines lesion level.
- Disc herniation: Radiculopathy follows dermatomal distribution (e.g. L5 → dorsum of foot pain).
- Shingles: Varicella zoster virus reactivation → painful vesicles in single dermatome.
- Saddle anaesthesia (S3–S5): Red flag for cauda equina syndrome 🚨.
🌟 Summary
Dermatomes are segmental skin maps of spinal nerve sensory innervation. They are crucial for localisation of neurological lesions, diagnosing radiculopathies, and recognising conditions such as shingles or spinal cord injury.
📋 Dermatomes vs Peripheral Nerve Territories
Dermatomes (spinal root level) and peripheral nerve territories (terminal branches of the brachial/lumbosacral plexus) do not always overlap. ⚠️ This distinction is essential in neurology and orthopaedics for localising lesions (radiculopathy vs peripheral neuropathy).
| Landmark | Dermatome | Peripheral Nerve Supply |
|---|---|---|
| Thumb | C6 | Median (palmar), Radial (dorsal) |
| Middle finger | C7 | Median nerve |
| Little finger | C8 | Ulnar nerve |
| Lateral forearm | C6 | Musculocutaneous (lateral cutaneous nerve of forearm) |
| Medial forearm | T1 | Medial cutaneous nerve of forearm |
| Dorsum of foot, big toe | L5 | Deep peroneal nerve (webspace between 1st–2nd toe) |
| Lateral foot & little toe | S1 | Sural nerve |
| Perianal region | S3–S5 | Pudendal & perianal branches |
💡 Exam tip: - Radiculopathy (root lesion): Sensory loss follows a dermatome (e.g. L5 → dorsum of foot). - Peripheral neuropathy: Sensory loss follows a nerve territory (e.g. common peroneal nerve palsy → lateral shin, dorsum of foot). Recognising this distinction helps localise the lesion accurately.
📷 Images
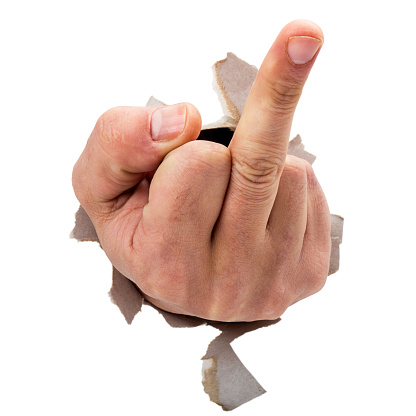
Middle Finger = C7

Dermatome Maps
Categories
-
| About | Anaesthetics and Critical Care | Anatomy | Biochemistry | Cardiology | Clinical Cases | CompSci | Crib | Dermatology | Differentials | Drugs | ENT | Electrocardiogram | Embryology | Emergency Medicine | Endocrinology | Ethics | Foundation Doctors | Gastroenterology | General Information | General Practice | Genetics | Geriatric Medicine | Guidelines | Haematology | Hepatology | Immunology | Infectious Diseases | Infographic | Investigations | Lists | Microbiology | Miscellaneous | Nephrology | Neuroanatomy | Neurology | Nutrition | OSCE | Obstetrics Gynaecology | Oncology | Ophthalmology | Oral Medicine and Dentistry | Paediatrics | Palliative | Pathology | Pharmacology | Physiology | Procedures | Psychiatry | Radiology | Respiratory | Resuscitation | Rheumatology | Statistics and Research | Stroke | Surgery | Toxicology | Trauma and Orthopaedics | Twitter | Urology