| Download the amazing global Makindo app: Android | Apple | |
|---|---|
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: Educational use only. Not for diagnosis or management. See below for full disclaimer. |
Neurological Sensory Examination (OSCE)
Related Subjects: |Neurological History taking |Cortical functions |Motor System |Sensory System |Mental State Examination |Speech and Language Exam |Cranial nerves and examination |Assessing Cognition
🧠 Anatomy
- Conscious sensation travels from the receptor → spinal cord → thalamus → contralateral parietal lobe.
- Entry: via the dorsal root of the spinal cord.
- Two key ascending pathways:
- 🌟 Dorsal Columns: Proprioception, vibration, fine touch. Fibres ascend ipsilaterally → decussate in medulla → contralateral cortex.
- 🔥 Spinothalamic Tracts: Pain, temperature, crude touch. Fibres decussate almost immediately → ascend contralaterally → thalamus → cortex.
- Basic exam: Compare both sides with pinprick & cotton wool, test proprioception & temperature.
🔎 Sensory Modalities
- Proprioception (Dorsal Column): Move distal joints (finger/toe up/down) with eyes closed. 🌐 Romberg Test: Feet together, eyes closed. Instability = dorsal column dysfunction.
- Vibration (Dorsal Column): 128 Hz tuning fork on bony prominences (e.g. hallux, malleolus).
- Temperature (Spinothalamic): Use warm/cold tubes or tuning fork. Loss = spinothalamic lesion (e.g. Brown-Séquard, lateral medullary syndrome).
- Fine Touch (Dorsal Column): Cotton wool over dermatomes, moving from abnormal → normal.
- Pinprick (Spinothalamic): Disposable neurotip/pin for pain perception.
🩺 Interpretation
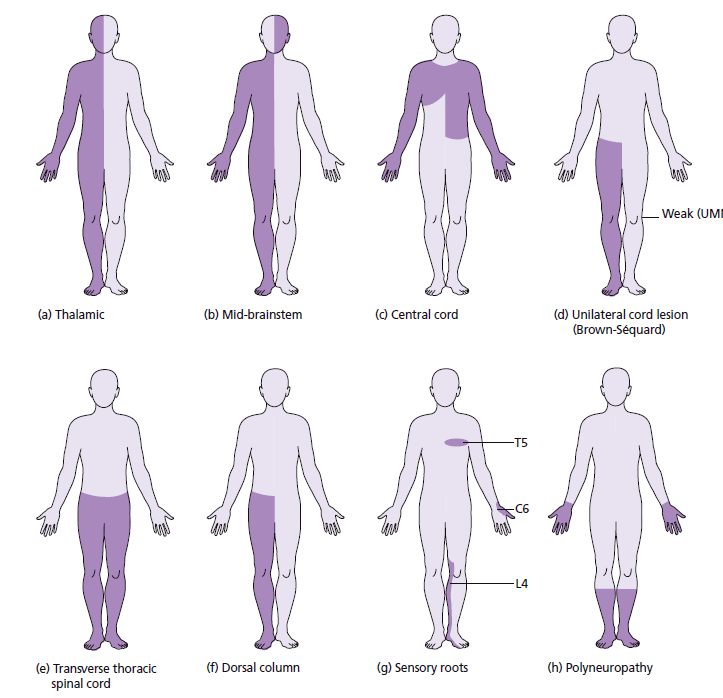
- 🧩 Patterns of sensory loss:
- Hemibody (face/arm/leg) → contralateral brain lesion.
- Cape-like loss over shoulders/arms → syringomyelia.
- Loss of vibration/proprioception → B12 deficiency (SACD, tabes dorsalis).
- Glove & stocking → peripheral neuropathy (e.g. diabetes).
- Sensory level → spinal cord lesion.
- Reduced perineal sensation → cauda equina syndrome.
- 🩺 Perineal exam: Essential if cauda equina suspected → check saddle sensation, anal tone, continence history.
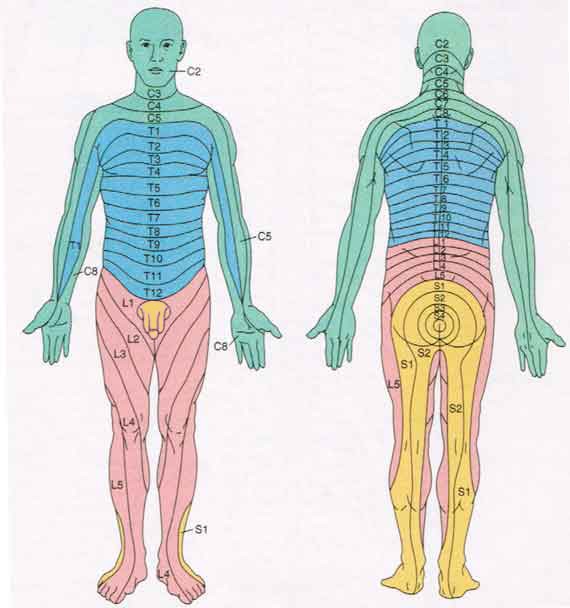
📍 Dermatomes
- 👍 Thumb: C6
- ☝️ Middle finger: C7
- 🤏 Little finger: C8
- 👕 Nipple line: T4
- 🪙 Umbilicus: T10
- 🦶 Big toe: L5
- 🦵 Little toe: S1
- 👖 Inner thigh: S2
- 🪑 Saddle area: S3–S5
🧾 Examination Steps (OSCE Style)
1. Introduction & Consent
- Introduce yourself, confirm patient identity & role.
- Explain procedure: “I’ll be testing different types of sensation.”
- Gain verbal consent, check comfort.
2. General Principles
- Position: patient seated or supine, relaxed.
- Exposure: only necessary areas, maintain dignity.
- Equipment: cotton wool, pin/neurotip, tuning fork (128 Hz), warm/cold tubes.
3. Light Touch
- Use cotton wool. Patient closes eyes, responds “yes” when touched.
- Compare both sides; map abnormalities.
4. Pain (Sharp/Dull)
- Use pin/neurotip alternating sharp vs blunt.
- Patient identifies “sharp” vs “dull.”
- Loss → spinothalamic dysfunction.
5. Temperature
- Use warm vs cold test tubes.
- Patient distinguishes warm vs cold → spinothalamic tract.
6. Vibration
- Strike tuning fork, place on bony prominence (toe, ankle, sternum).
- Ask patient when vibration starts/stops.
- Loss → peripheral neuropathy or dorsal column lesion.
7. Proprioception
- Hold digit by sides, move up/down with eyes closed.
- Patient identifies movement direction.
- Loss → dorsal column dysfunction.
8. Higher Discriminative Sensation
- Two-point discrimination: Paperclip/calipers.
- Graphesthesia: Draw number on palm.
- Stereognosis: Identify familiar object (coin, key) in hand.
Categories
- A Level
- About
- Acute Medicine
- Anaesthetics and Critical Care
- Anatomy
- Anatomy and Physiology
- Biochemistry
- Book
- Cardiology
- Collections
- CompSci
- Crib Sheets
- Crib sheets
- Dental
- Dermatology
- Differentials
- Drugs
- ENT
- Education
- Electrocardiogram
- Embryology
- Emergency Medicine
- Endocrinology
- Ethics
- Foundation Doctors
- GCSE
- Gastroenterology
- General Practice
- Genetics
- Geriatric Medicine
- Guidelines
- Gynaecology
- Haematology
- Hepatology
- Immunology
- Infectious Diseases
- Infographic
- Investigations
- Lists
- Mandatory Training
- Medical Students
- Microbiology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Nutrition
- OSCE
- OSCEs
- Obstetrics
- Obstetrics Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Medicine and Dentistry
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatrics
- Palliative
- Pathology
- Pharmacology
- Physiology
- Procedures
- Psychiatry
- Public Health
- Radiology
- Renal
- Respiratory
- Resuscitation
- Revision
- Rheumatology
- Statistics and Research
- Stroke
- Surgery
- Toxicology
- Trauma and Orthopaedics
- USMLE
- Urology
- Vascular Surgery
