Related Subjects:
|Hodgkin Lymphoma
|Non Hodgkin Lymphoma
|Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
|Intravascular large B-cell lymphoma
|Mantle cell lymphoma
|Marginal Zone Lymphoma
|Gastric (MALT) Lymphoma
|Primary CNS Lymphoma (PCNSL)
|Burkitt's lymphoma
|Follicular Lymphoma
🧠 Primary CNS Lymphoma (PCNSL) is a late complication of HIV (esp. CD4 < 50) and strongly associated with EBV infection. It is a rare, aggressive extranodal lymphoma, usually confined to the brain, CSF, and eyes.
📌 About
- Accounts for ~3% of all brain tumours; ~90% are B-cell lymphomas.
- Distinct from systemic lymphoma – typically no extracranial spread at diagnosis.
- Common sites: cerebrum, basal ganglia, thalamus, periventricular regions; can infiltrate optic nerves and eyes 👁️.
- Often presents as solitary but may be multifocal with angiocentric growth (around blood vessels).
🧬 Aetiology & Risk Factors
- High-grade diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) in most cases.
- EBV-driven in immunosuppressed patients (HIV/AIDS, transplant, chronic immunosuppression).
- Risk ↑ in:
- Advanced HIV/AIDS (CD4 < 50).
- Post-transplant patients (immunosuppressive drugs).
- Inherited immunodeficiency (Wiskott-Aldrich, Ataxia-telangiectasia).
🩺 Clinical Features
- Subacute focal deficits (hemiparesis, aphasia, sensory loss).
- Neuropsychiatric changes: confusion, memory decline, personality change.
- Raised ICP: headache, nausea, papilloedema.
- Seizures in some cases.
- Eye involvement common – slit-lamp exam crucial 👁️.
⚖️ Key Differentials
- Cerebral Toxoplasmosis (esp. HIV, multiple ring-enhancing lesions).
- High-grade glioma (glioblastoma, “butterfly” tumour).
- Metastatic deposits.
🔍 Investigations
- Bloods: FBC, U&E, HIV screen, CD4 count, viral load.
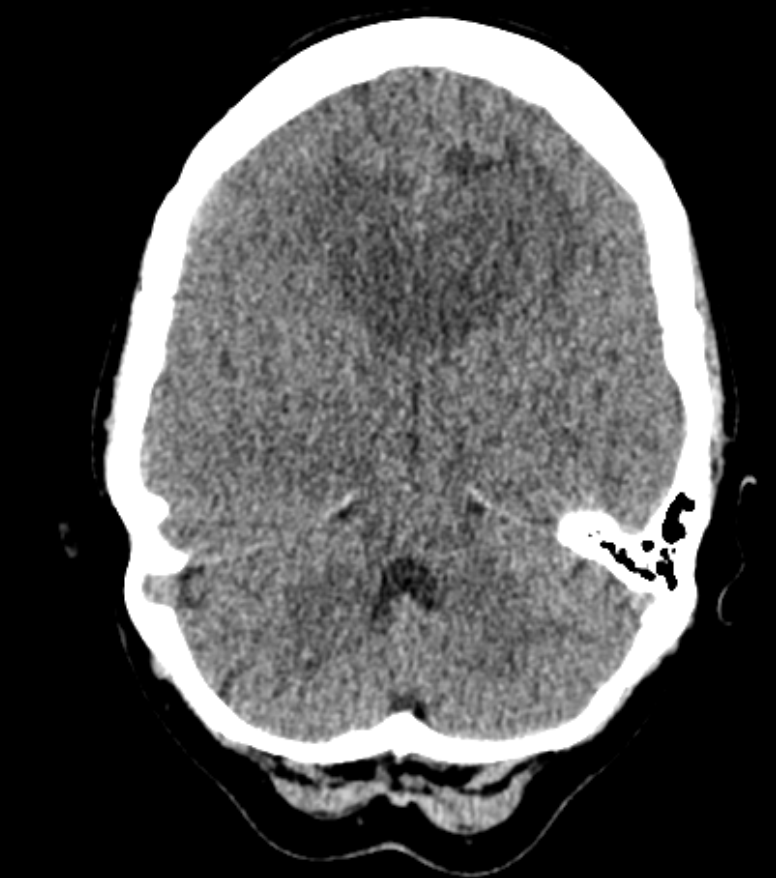
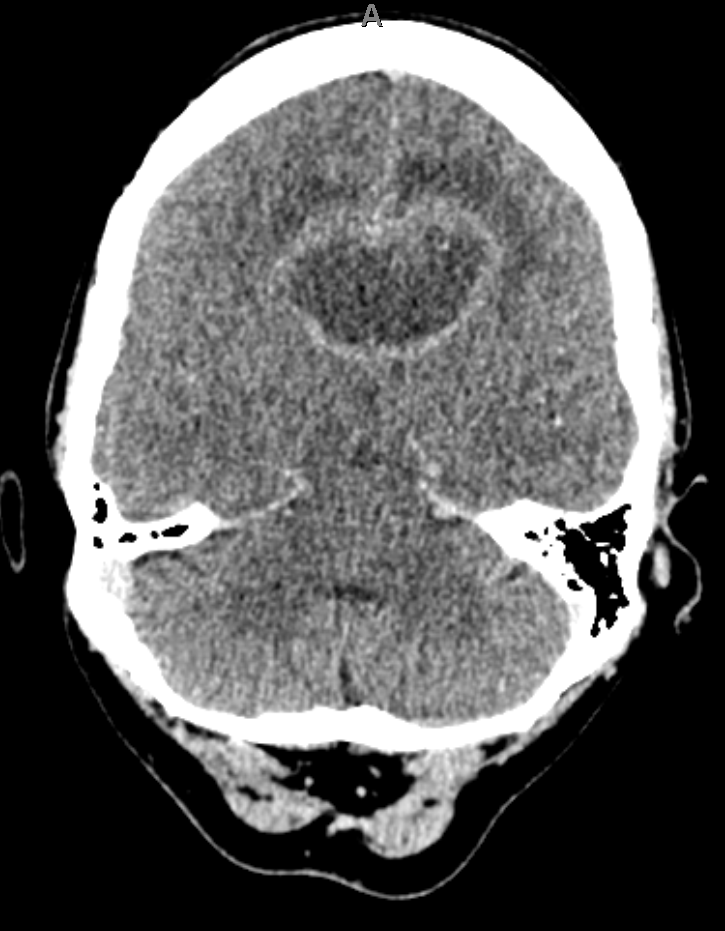
- MRI: Dense periventricular enhancing lesions, often homogeneously enhancing. May cross corpus callosum (“butterfly”). Dramatic but transient response to steroids 🎯.
- CT: Enhancing deep lesions with surrounding oedema.
- CSF: ↑WCC, ↑β2 microglobulin, monoclonal lymphocytes. EBV PCR highly suggestive in AIDS patients. (⚠️ LP contraindicated if mass effect).
- Stereotactic biopsy: Diagnostic gold standard.
- PET-CT & bone marrow: To exclude systemic lymphoma.
🧾 Imaging Differential: Butterfly Lesion
- Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM).
- Primary CNS lymphoma (consider HIV/EBV).
- Toxoplasmosis (HIV, multiple enhancing lesions).
 |
 > > |
💊 Management
- High-dose methotrexate (HD-MTX): cornerstone therapy, often with other agents.
- Steroids: Reduce oedema and may transiently shrink lesion, but complicate histology → biopsy ideally before steroids.
- Rituximab: Anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody, often added.
- Intrathecal chemotherapy: For leptomeningeal involvement.
- Radiotherapy: Whole-brain RT used less now due to neurotoxicity but still palliative in refractory cases.
- Surgery: Rare; only biopsy or debulking for mass effect.
- If AIDS patient: Empiric toxoplasmosis treatment + HAART before diagnosing lymphoma.
📈 Prognosis
- Poorer than systemic lymphoma; median survival 12–18 months with treatment.
- Best outcomes in younger, immunocompetent patients treated with HD-MTX.
- In HIV: prognosis improves significantly with HAART + chemo.
📚 References

 >
>