| Download the amazing global Makindo app: Android | Apple | |
|---|---|
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: Educational use only. Not for diagnosis or management. See below for full disclaimer. |
Posterior circulation
Related Subjects: |Neurological History taking |Causes of Stroke |Ischaemic Stroke |Subarachnoid Haemorrhage |Small Vessel Disease |Vascular Dementia |Capsular and Pontine Warning Syndromes |Dementias |CADASIL |CARASIL |Cerebral Arterial Perfusion and Clinical Correlates |Anterior circulation Brain |Posterior circulation Brain |Acute Stroke Assessment (ROSIER&NIHSS) |Carotid Artery dissection |Vertebral artery dissection |Acute Stroke Assessment (ROSIER&NIHSS) |Atrial Fibrillation |Atrial Myxoma |Causes of Stroke |Ischaemic Stroke |Cancer and Stroke |Cerebral Venous thrombosis |Cardioembolic stroke |CT Basics for Stroke |Endocarditis and Stroke |Haemorrhagic Stroke |Stroke Thrombolysis |Hyperacute Stroke Care |Anatomy and Physiology of the Brain |Cryptogenic stroke |Carotid Web |Anterior / Medial Medullary Infarct (Dejerine Syndrome)
🩸 The vertebral arteries provide about one-third of the cerebral blood supply, forming the vital posterior circulation. Their branches supply the medulla, pons, cerebellum, and occipital lobes - regions critical for life-sustaining functions.
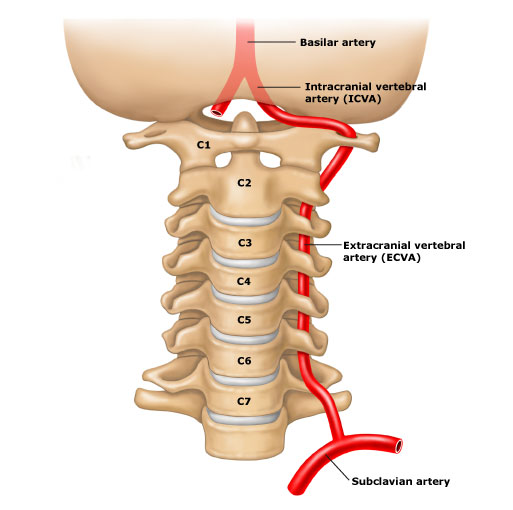
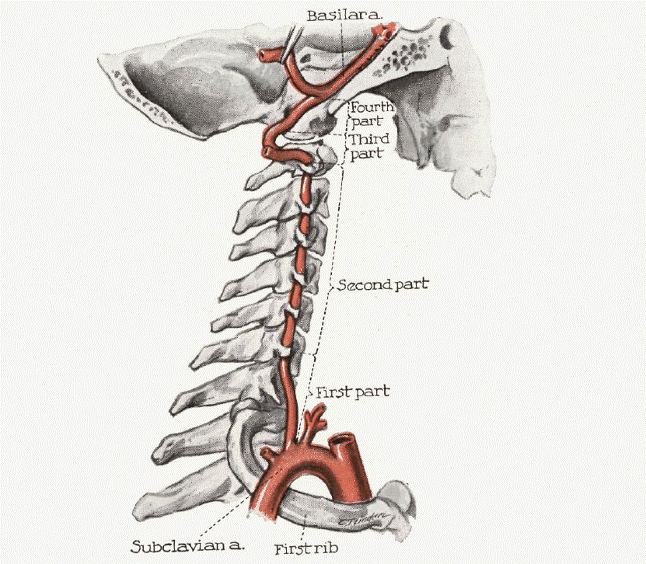
🧭 Vertebral Artery Course
- Arises as the first branch of the subclavian artery on each side.
- Enters the transverse foramen at C6, ascends through the foramina up to C1.
- Curves posteriorly around the atlas and enters the skull via the foramen magnum.
- At the lower border of the pons, the two vertebral arteries unite to form the basilar artery.
🌿 Major Branches
- Posterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery (PICA) 🧠
- Largest branch of the vertebral artery.
- Supplies the lateral medulla and inferior cerebellum.
- Occlusion → Wallenberg’s syndrome (lateral medullary syndrome).
- Anterior Spinal Artery 🟠
- Formed by contributions from both vertebral arteries; supplies ventral medulla and anterior spinal cord.
- Posterior Spinal Artery 🔵
- Supplies dorsal medulla and dorsal columns of spinal cord.
- Basilar Artery 🏗️
- Formed by vertebral fusion; supplies pons, cerebellum, and inner ear.
- Anterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery (AICA) ⚖️
- Supplies lateral pons and anterior inferior cerebellum.
- Superior Cerebellar Artery ⛰️
- Supplies superior cerebellum and lateral pons.
- Pontine Arteries ➕
- About 12 small perforators branching at right angles from the basilar artery to supply the medial pons.
- Internal Auditory (Labyrinthine) Artery 🎧
- Travels with CN VIII to supply the inner ear; infarction can cause sudden hearing loss and vertigo.
- Posterior Cerebral Artery (PCA) 👁️
- Embryologically linked to the internal carotid; later supplied by the basilar.
- Wraps around the cerebral peduncle to supply the occipital lobe and inferior temporal cortex.
🌐 Posterior Cerebral Artery (PCA) Branches
- Postero-medial Ganglionic Branches → thalami + walls of 3rd ventricle.
- Posterior Choroidal Branches → choroid plexus of 3rd ventricle.
- Postero-lateral Ganglionic Branches → lateral thalamus.
- Anterior Temporal Branch → uncus + anterior fusiform gyrus.
- Posterior Temporal Branch → inferior temporal gyri, lingual gyrus, cuneus, occipital cortex.
- Parieto-occipital Branch → parieto-occipital region, calcarine cortex.
🧑⚕️ Clinical Relevance
- 🔸 PICA stroke → Wallenberg’s syndrome (vertigo, ataxia, ipsilateral facial sensory loss, contralateral body sensory loss).
- 🔸 AICA stroke → lateral pontine syndrome (facial weakness, vertigo, hearing loss).
- 🔸 Basilar occlusion → catastrophic brainstem infarction, “locked-in syndrome.”
- 🔸 PCA stroke → contralateral homonymous hemianopia ± alexia without agraphia (if dominant hemisphere, splenium involvement).
Categories
- A Level
- About
- Acute Medicine
- Anaesthetics and Critical Care
- Anatomy
- Anatomy and Physiology
- Biochemistry
- Book
- Cardiology
- Collections
- CompSci
- Crib Sheets
- Crib sheets
- Dental
- Dermatology
- Differentials
- Drugs
- ENT
- Education
- Electrocardiogram
- Embryology
- Emergency Medicine
- Endocrinology
- Ethics
- Foundation Doctors
- GCSE
- Gastroenterology
- General Practice
- Genetics
- Geriatric Medicine
- Guidelines
- Gynaecology
- Haematology
- Hepatology
- Immunology
- Infectious Diseases
- Infographic
- Investigations
- Lists
- Mandatory Training
- Medical Students
- Microbiology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Nutrition
- OSCE
- OSCEs
- Obstetrics
- Obstetrics Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Medicine and Dentistry
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatrics
- Palliative
- Pathology
- Pharmacology
- Physiology
- Procedures
- Psychiatry
- Public Health
- Radiology
- Renal
- Respiratory
- Resuscitation
- Revision
- Rheumatology
- Statistics and Research
- Stroke
- Surgery
- Toxicology
- Trauma and Orthopaedics
- USMLE
- Urology
- Vascular Surgery
