| Download the amazing global Makindo app: Android | Apple | |
|---|---|
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: Educational use only. Not for diagnosis or management. See below for full disclaimer. |
Language and Dysphasia
Aphasia is the most common early cognitive deficit after stroke, affecting 20–38% of patients. 🗣️ Language is central to identity, relationships, and independence, so loss of speech can be devastating. Almost one-third of stroke patients experience language difficulties, which may persist and affect mood, employment, and quality of life. ✅ Early recognition and referral for Speech & Language Therapy (SLT) are vital. Family/carer education improves patient outcomes.
🧠 Background
Language disturbance is highly localising to the dominant cerebral cortex (usually the left hemisphere). Key areas: Broca’s area (frontal lobe → expression) and Wernicke’s area (temporal/parietal → comprehension). ➡️ Aphasia is most often seen in left MCA strokes. By contrast, dysarthria (motor speech disorder) is less localising and often nonspecific. Language can be impaired in speaking, comprehension, reading, and writing. For further insight, see Stephen Pinker’s 📚 The Language Instinct.
📝 Key Terminology
| Terms |
|---|
|
🧬 Aetiology
Traditional models emphasise Broca’s area, Wernicke’s area, and the arcuate fasciculus. More recent studies show:
- 🎧 Speech sound recognition → superior temporal lobe bilaterally.
- 🌀 Frontal/motor regions modulate but do not generate comprehension.
- 🔀 Dual-stream model: dorsal stream (sensory-motor integration) vs ventral stream (comprehension).
📍 Key Anatomical Structures
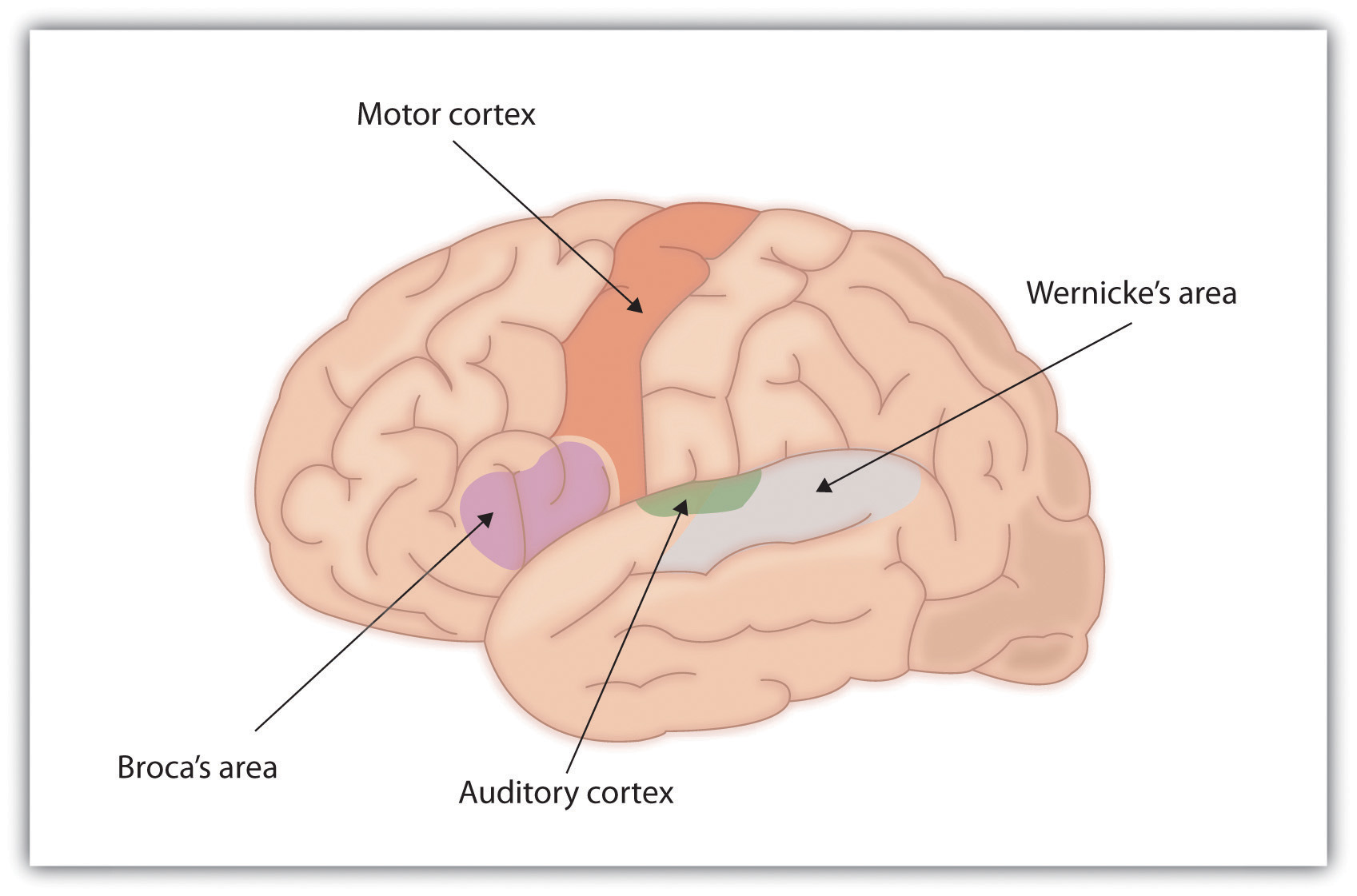
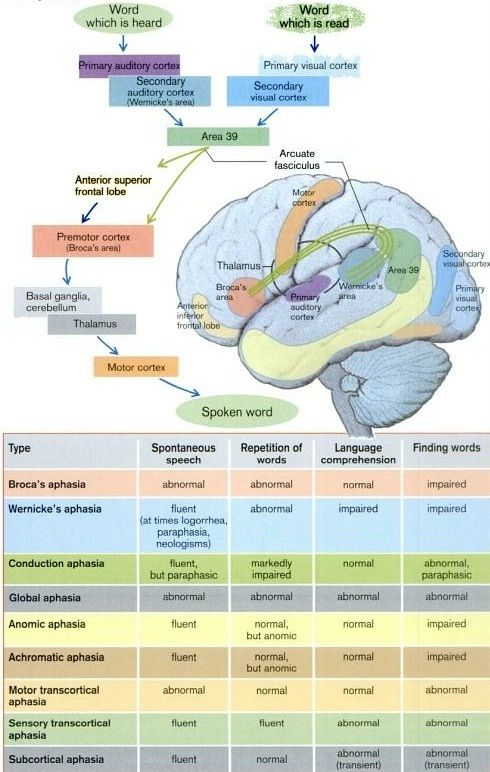
📊 Pathways for Repeating Words
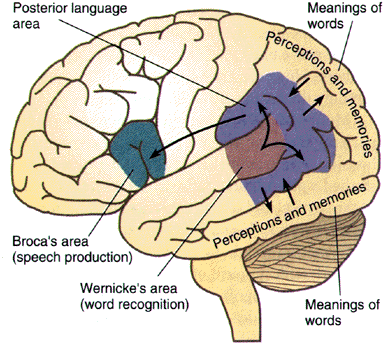
🔍 Key Exam Questions
- Differentiate from motor speech disorders.
- Differentiate from cognitive-communication disorders.
📖 Definition
Aphasia = disturbance of language due to brain damage, affecting:
- 👂 Comprehension → auditory & reading.
- 🗣️ Expression → speech, writing, signing.
📌 Important Distinctions
- Language: Grammar, vocabulary.
- Speech: Tongue/lip movements.
- Cognition: Attention, memory, problem-solving.
🧩 Language Input (Comprehension)
- 👂 Hearing → auditory cortex → Wernicke’s area.
- 👀 Reading → visual cortex → Wernicke’s area.
- 🧠 Meaning + context analysis.
🗣️ Language Output (Speech)
- Wernicke’s → word selection.
- Arcuate fasciculus → relay.
- Broca’s → motor plan.
- Primary Motor Cortex → speech muscles.
🔄 Repetition (Tests Whole Circuit)
- Auditory cortex → Wernicke’s → arcuate fasciculus → Broca’s → motor cortex → cranial nerves.
🛏️ Bedside Assessment
- 👋 Observe greetings → fluency clues.
- 📢 Fluency & volume assessment.
- 🧾 Comprehension → multi-step commands (“Touch chin, nose, ear”).
- 🔁 Repetition tasks: “No ifs, ands, or buts”, “British constitution”.
| Always assess hearing in suspected speech disorders. |
🗨️ Dyspraxic Speech
Apraxia of speech = difficulty planning/coordinating speech, not due to weakness. 🎵 Features: slow, effortful, abnormal rhythm (prosody). Common with left inferior frontal gyrus/anterior insula lesions. ➡️ Best managed with intensive 1:1 SLT.
📈 Prognosis
- ⏱️ Spontaneous recovery most within 2 weeks → 3 months.
- ♀️ Women often recover speech better than men.
- 🎓 Higher IQ/education, left-handedness → better outcomes.
- 💪 Early, intensive therapy = best chance of recovery.
🛠️ Management
- 🩺 Early Recognition: Involve SLT promptly.
- 👨👩👧 Family Education: Use gestures, patience, visual cues.
- 📆 Therapy Timeline: Most effective in first 4 months.
🔗 Links & References
Categories
- A Level
- About
- Acute Medicine
- Anaesthetics and Critical Care
- Anatomy
- Anatomy and Physiology
- Biochemistry
- Book
- Cardiology
- Collections
- CompSci
- Crib Sheets
- Crib sheets
- Dental
- Dermatology
- Differentials
- Drugs
- ENT
- Education
- Electrocardiogram
- Embryology
- Emergency Medicine
- Endocrinology
- Ethics
- Foundation Doctors
- GCSE
- Gastroenterology
- General Practice
- Genetics
- Geriatric Medicine
- Guidelines
- Gynaecology
- Haematology
- Hepatology
- Immunology
- Infectious Diseases
- Infographic
- Investigations
- Lists
- Mandatory Training
- Medical Students
- Microbiology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Nutrition
- OSCE
- OSCEs
- Obstetrics
- Obstetrics Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Medicine and Dentistry
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatrics
- Palliative
- Pathology
- Pharmacology
- Physiology
- Procedures
- Psychiatry
- Public Health
- Radiology
- Renal
- Respiratory
- Resuscitation
- Revision
- Rheumatology
- Statistics and Research
- Stroke
- Surgery
- Toxicology
- Trauma and Orthopaedics
- USMLE
- Urology
- Vascular Surgery
