| Download the amazing global Makindo app: Android | Apple | |
|---|---|
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: Educational use only. Not for diagnosis or management. See below for full disclaimer. |
Chondrocalcinosis
Related Subjects: |Tennis Elbow |Golfer's Elbow |Painful Shoulder syndromes |Plantar fasciitis |Carpal tunnel syndrome |Chondrocalcinosis |Monoarticular arthritis |Polyarticular arthritis |Seronegative Spondyloarthropathies |Ankylosing spondylitis |Enteropathic Spondyloarthritis |Reactive Arthritis |Psoriatic Arthritis |Adult Onset Still's Disease |Alkaptonuria |Behcet's Syndrome
🦴 About
- Arthritis caused by calcium pyrophosphate deposition (CPPD) in cartilage and periarticular tissues.
- Predominantly affects those over 50 years (younger cases usually suggest an underlying metabolic disorder).
- Most common joint: knee (can also affect wrists, shoulders, hips, and ankles).
- Can mimic gout, rheumatoid arthritis, or osteoarthritis.
- Termed “pseudogout” when it presents with acute monoarthritis.
🧬 Aetiology
- Deposition of calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate crystals within articular cartilage → inflammatory response.
- Chondrocalcinosis on imaging reflects crystal deposition in cartilage.
🩺 Clinical Presentation
- Acute, red, hot, swollen joint – often the knee.
- May present with fever and raised inflammatory markers, mimicking septic arthritis.
- Can cause recurrent acute flares or chronic arthropathy resembling osteoarthritis (esp. in wrists/shoulders).
🔗 Key Associations (classic exam list)
CPPD is frequently linked to metabolic/systemic disease, often tested in MRCP & PACES:
- 🧪 Hyperparathyroidism
- 🩸 Haemochromatosis
- ⚡ Hypomagnesaemia
- 🦋 Hypothyroidism (myxoedematous)
- 🟤 Ochronosis (alkaptonuria)
- 🧬 Wilson's disease
- 💉 Dialysis-dependent renal failure
- 📏 Acromegaly
🔬 Investigations
- Synovial fluid analysis (polarized light microscopy):
- Rhomboid-shaped crystals
- Positively birefringent under polarized light
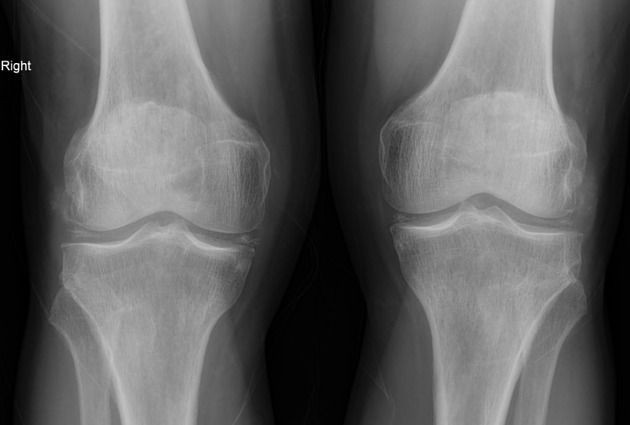
- 🔎 X-ray: Chondrocalcinosis (linear calcification in cartilage, especially knee meniscus and wrist TFCC).
- Blood tests: screen for metabolic associations (calcium, magnesium, iron studies, thyroid function, renal function).
💊 Management
- 🔹 Acute flare: joint aspiration + intra-articular corticosteroid injection; NSAIDs or colchicine if tolerated.
- 🔹 Supportive: rest, ice, analgesia.
- 🔹 Chronic/recurrent: low-dose colchicine prophylaxis; address underlying metabolic disorder.
- 🔹 Rehabilitation: physiotherapy to maintain joint function and mobility.
Cases — Chondrocalcinosis (Calcium Pyrophosphate Deposition Disease)
- Case 1 — Acute pseudogout flare 💥: A 71-year-old woman presents with acute, painful swelling of her right knee after a minor illness. Joint is hot, red, and tender. Aspirated synovial fluid: positively birefringent, rhomboid-shaped crystals. X-ray: calcification in menisci. Diagnosis: pseudogout attack due to chondrocalcinosis. Treated with NSAIDs and intra-articular steroid injection.
- Case 2 — Chronic arthropathy 🦴: A 66-year-old man with a history of haemochromatosis complains of progressive stiffness and pain in both wrists. Exam: reduced range of motion, no acute synovitis. X-ray: calcification in triangular fibrocartilage and joint space narrowing. Diagnosis: chronic CPPD arthropathy. Managed with analgesia and physiotherapy.
- Case 3 — Secondary cause 🔬: A 58-year-old woman with long-standing hypothyroidism develops recurrent swollen ankles and knees. Synovial fluid shows CPPD crystals. Investigations reveal associated hypomagnesaemia. Diagnosis: secondary chondrocalcinosis. Treated with magnesium replacement and joint-directed therapy.
Teaching Point 🩺: Chondrocalcinosis is due to calcium pyrophosphate deposition in cartilage. It can mimic gout, OA, or RA. Always check for secondary causes (haemochromatosis, hyperparathyroidism, hypomagnesaemia, hypothyroidism). Diagnosis: crystal analysis +
Categories
- A Level
- About
- Acute Medicine
- Anaesthetics and Critical Care
- Anatomy
- Anatomy and Physiology
- Biochemistry
- Book
- Cardiology
- Collections
- CompSci
- Crib Sheets
- Crib sheets
- Dental
- Dermatology
- Differentials
- Drugs
- ENT
- Education
- Electrocardiogram
- Embryology
- Emergency Medicine
- Endocrinology
- Ethics
- Foundation Doctors
- GCSE
- Gastroenterology
- General Practice
- Genetics
- Geriatric Medicine
- Guidelines
- Gynaecology
- Haematology
- Hepatology
- Immunology
- Infectious Diseases
- Infographic
- Investigations
- Lists
- Mandatory Training
- Medical Students
- Microbiology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Nutrition
- OSCE
- OSCEs
- Obstetrics
- Obstetrics Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Medicine and Dentistry
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatrics
- Palliative
- Pathology
- Pharmacology
- Physiology
- Procedures
- Psychiatry
- Public Health
- Radiology
- Renal
- Respiratory
- Resuscitation
- Revision
- Rheumatology
- Statistics and Research
- Stroke
- Surgery
- Toxicology
- Trauma and Orthopaedics
- USMLE
- Urology
- Vascular Surgery
