Related Subjects:
|Acute Severe Colitis
|Ulcerative Colitis
|Microscopic colitis
|Irritable bowel syndrome
|Lower Gastrointestinal (Rectal) Bleeding
🔥 Ulcerative colitis (UC) = a relapsing-remitting inflammatory disease of the colon, with continuous mucosal inflammation starting in the rectum.
⚠️ Risks: acute severe colitis (medical emergency) + ↑ risk of colorectal cancer.
📖 About
- Chronic, relapsing-remitting inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) affecting colon & rectum only.
- More common than Crohn’s disease. Incidence ~10–20/100,000; prevalence 50–100/100,000.
- Classically in Caucasians & Jewish populations; peak onset 20–40 years.
🧬 Aetiology
- Dysregulated immune response to gut flora + environment in genetically predisposed individuals.
- ⚡ Protective: smoking & prior appendicectomy.
- 🔎 Autoantibodies: pANCA often positive.
- Common association: Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC).
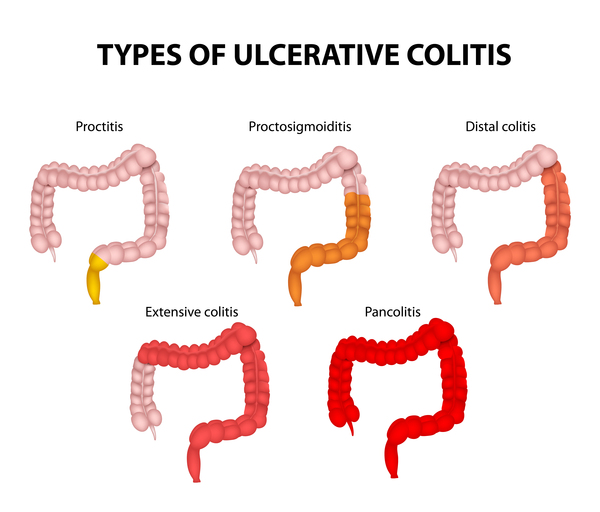
🗺️ Extent of Disease
Always starts in the rectum (proctitis) and extends proximally in a continuous manner.
🩺 Clinical Presentation
- 💩 Bloody diarrhoea with mucus (may be 10–20/day in severe cases).
- 🚽 Urgency, tenesmus, incontinence.
- 🤒 Systemic features in severe disease: fever, tachycardia, weight loss.
- ⚡ Flares triggered by infections, NSAIDs, antibiotics, stress.
🌍 Extra-intestinal Features
- 🖐️ Skin: erythema nodosum, pyoderma gangrenosum.
- 👁️ Eyes: iritis, episcleritis.
- 🦴 Joints: arthritis, sacroiliitis.
- 🩺 Liver: PSC (strong link).
- Other: mouth ulcers, clubbing, ↑ VTE risk, amyloidosis.
🧪 Pathology
- Confined to colon & rectum; continuous pattern.
- Mucosal-only inflammation (no transmural involvement).
- Histology: goblet cell depletion, crypt abscesses, pseudopolyps.
- Chronic disease: loss of haustra → “lead-pipe colon”, ↑ cancer risk.
📊 Assessing Severity (Modified Truelove & Witts’ Criteria)
| Severity | Features |
|---|
| 🙂 Mild | <4 bloody stools/day; no systemic upset; Hb >115; CRP <5 |
| 😐 Moderate | 4–6 stools/day; mild systemic disturbance; Hb >105; CRP <30 |
| 😟 Severe | >6 bloody stools/day + systemic features (T >37.8, HR >90, Hb <105, CRP >30) |
| 🚨 Fulminant | ≥10 stools/day, continuous bleeding, severe toxicity, colonic dilatation on AXR |
🔎 Investigations
- 🩸 Bloods: FBC (anaemia), CRP/ESR, U&E, LFTs, pANCA.
- 💩 Faecal calprotectin: raised in active inflammation.
- 📷 Imaging:
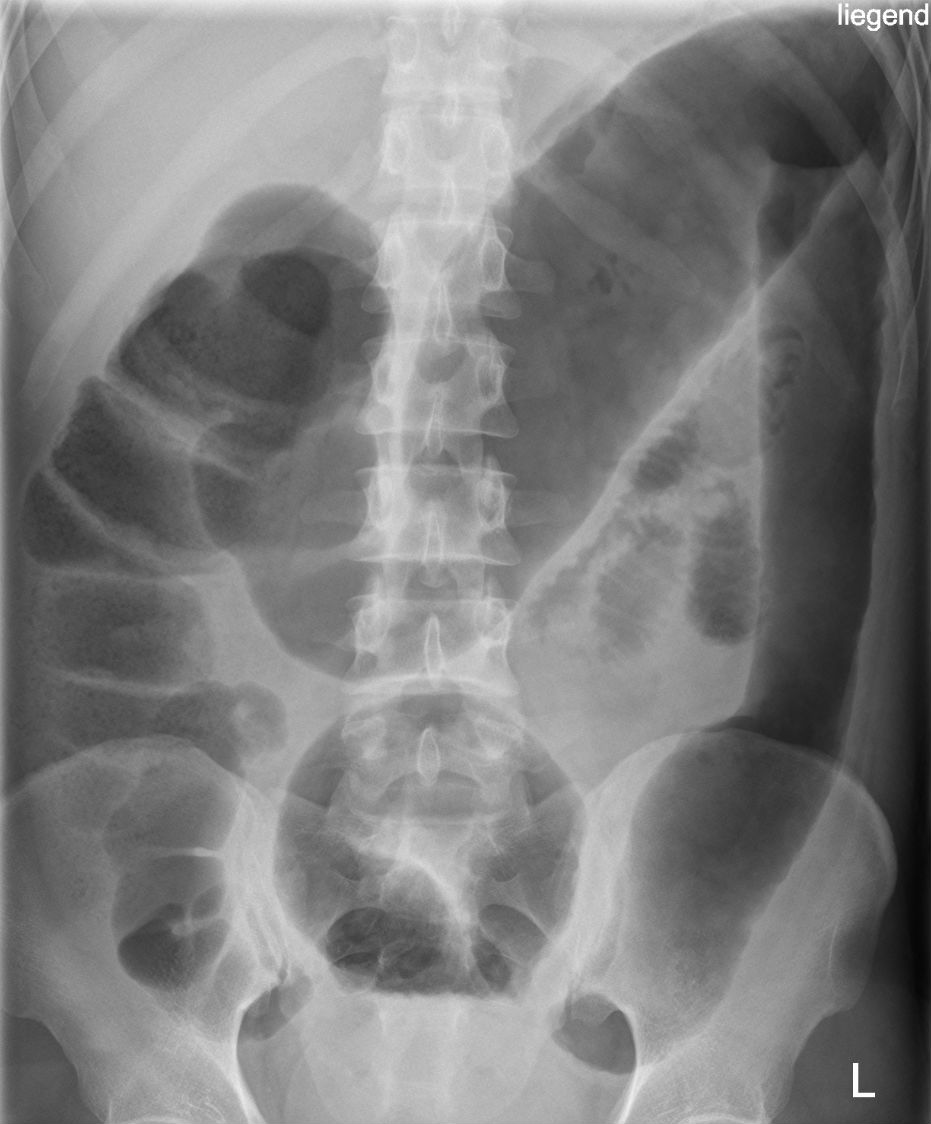
– AXR: toxic megacolon (>6 cm), thumbprinting.
– Sigmoidoscopy (preferred in flare): friable, erythematous mucosa.
– Colonoscopy: for extent & surveillance (avoid in acute flare).
– Barium enema (historical): lead-pipe colon, avoid in acute flare.
🔍 Comparison: Crohn’s Disease vs Ulcerative Colitis
| Feature |
🌱 Crohn’s Disease |
🔥 Ulcerative Colitis |
| Distribution |
Anywhere mouth → anus, most often terminal ileum; skip lesions |
Starts in rectum, continuous spread proximally through colon |
| Depth of Inflammation |
Transmural (full thickness) |
Mucosa + submucosa only |
| Histology |
Non-caseating granulomas, fissures |
Crypt abscesses, mucosal ulceration, no granulomas |
| Appearance |
“Cobblestone” mucosa, thick bowel wall, strictures, fistulas |
Red, raw, friable mucosa, pseudopolyps |
| Symptoms |
RLQ pain, weight loss, diarrhoea (± blood), perianal disease |
Bloody diarrhoea, urgency, tenesmus, LLQ pain |
| Smoking |
🚬 Risk factor (worsens disease) |
🚭 Protective (symptoms often worse in ex-smokers) |
| Extra-intestinal |
More renal stones (oxalate), gallstones, B12 deficiency |
PSC (primary sclerosing cholangitis), ↑ colorectal cancer risk |
| Fistula/Stricture |
✅ Common (entero-enteric, perianal, entero-vesical) |
❌ Rare |
| Surgery |
Not curative (recurs in new bowel segments) |
Curative (colectomy removes disease) |
| Cancer risk |
Increased with colonic involvement |
High with long-standing pancolitis or PSC |
💡 Teaching Tip: In exams, remember the mnemonic:
- Crohn’s → Cobblestone, Complete wall (transmural), Complications (fistulae/strictures)
- UC → starts in Ulcerated rectum, continuous, mucosal only, curable with colectomy.
💊 Management (Step-Up)
| Step | Treatment |
|---|
| 1 | 5-ASA (Mesalazine, Sulfasalazine) ± rectal 5-ASA for distal disease |
| 2 | Rectal steroids |
| 3 | Oral steroids (Prednisolone 40–60 mg, tapered) |
| 4 | IV steroids (Hydrocortisone, Methylprednisolone) |
| 5 | Immunomodulators (Azathioprine, 6-Mercaptopurine) |
| 6 | Biologics (Infliximab, Vedolizumab) or IV Ciclosporin |
| 7 | Surgery (panproctocolectomy + ileoanal pouch) |
⚠️ Acute Severe UC
- Admit + IV fluids, IV hydrocortisone, nutritional support, VTE prophylaxis.
- Monitor stool frequency, vitals, bloods, AXR daily.
- If no response in 3–5 days → Rescue therapy (Ciclosporin / Infliximab) or Surgery.
- 🚨 Toxic megacolon: urgent surgical input (colectomy if deterioration).
🔪 Surgical Options
- Panproctocolectomy + ileal pouch-anal anastomosis → curative, ↓ cancer risk, but ↑ stool frequency, pouchitis risk.
📦 Other Treatment Options
- 🛡️ Immunosuppressants: Azathioprine, Mercaptopurine (monitor FBC closely).
- 💉 Biologics: Infliximab, Vedolizumab for refractory disease.
- 💊 Ciclosporin: Acute rescue therapy if steroids fail.
🌱 Supportive Care
- Dietitian input → nutritional optimisation.
- IBD nurse specialist → flare-up support, medication counselling.
💡 Teaching Pearls:
– UC = continuous, mucosal-only inflammation starting at rectum (vs Crohn’s = skip lesions, transmural).
– Acute severe colitis = emergency: IV steroids first, colectomy if no response.
– Long-term risk: colorectal cancer → surveillance colonoscopy.
– Extra-intestinal features (skin, eyes, joints, liver) often parallel disease activity.
📚 References
