| Download the amazing global Makindo app: Android | Apple | |
|---|---|
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: Educational use only. Not for diagnosis or management. See below for full disclaimer. |
Anatomy and Physiology of the Biliary system
Related Subjects: |Anatomy and Physiology of the Oesophagus |Anatomy and Physiology of the Diaphragm |Anatomy and Physiology of the Large Bowel (Colon, Rectum, Anal Canal) |Anatomy and Physiology of Small Bowel |Anatomy and Physiology of the Biliary system |Anatomy and Physiology of the Bone Marrow |Anatomy and Physiology of the Eye |Anatomy and Physiology of the Pharynx |Anatomy and Physiology of the Larynx |Anatomy and Physiology of the Ear |Anatomy and Physiology of the Nose |Anatomy and Physiology of Male Genitalia |Anatomy and Physiology of the Breast |Anatomy and Physiology of the Stomach |Anatomy and Physiology of the Rectum |Anatomy and Physiology of the Spleen
The biliary system comprises the intrahepatic bile canaliculi and ducts, the extrahepatic bile ducts, and the gallbladder. Together, they produce, modify, store, and deliver bile into the duodenum. Bile is essential for fat digestion and absorption (micelle formation), provides the main route for bilirubin excretion, and is a key pathway for cholesterol elimination. The gallbladder is a pear-shaped sac beneath the liver in the right upper quadrant, acting as a reservoir that concentrates bile between meals and ejects it after feeding—especially after a fatty meal. 🥓
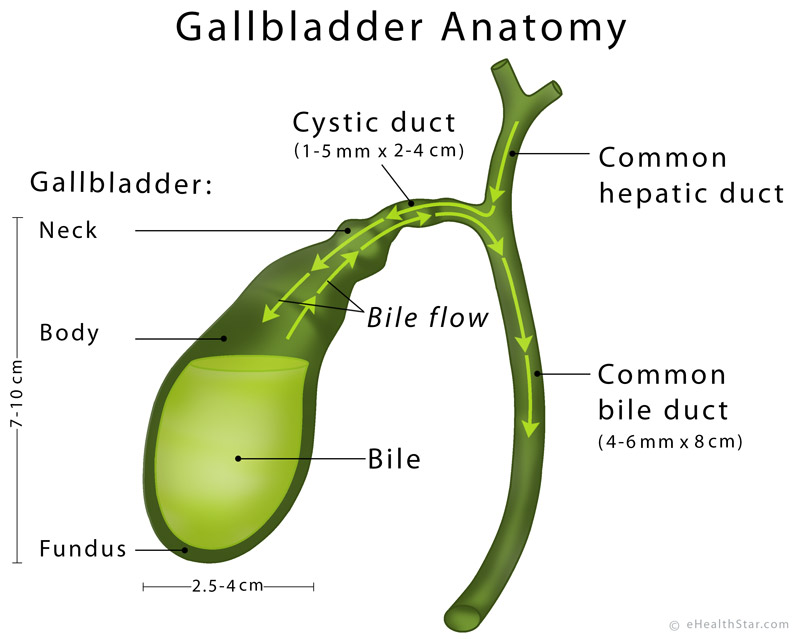
🧩 Gallbladder Anatomy
- Location: Lies in the gallbladder fossa on the inferior surface of the liver (between right and quadrate lobes), close to the hepatic flexure and duodenum.
- Size/Capacity: ~7–10 cm; typically holds ~30–60 mL.
- Parts:
- Fundus: rounded distal end; can contact the anterior abdominal wall (classically near the tip of the right 9th costal cartilage).
- Body: main storage segment, closely related to liver.
- Neck: tapers to the cystic duct; may form a dilatation (Hartmann’s pouch) where stones can lodge.
- Wall structure: mucosa with folds, smooth muscle layer for contraction, and an outer serosa/adventitia.
Note: gallbladder mucosa can actively absorb water and electrolytes—this is the basis of bile concentration.
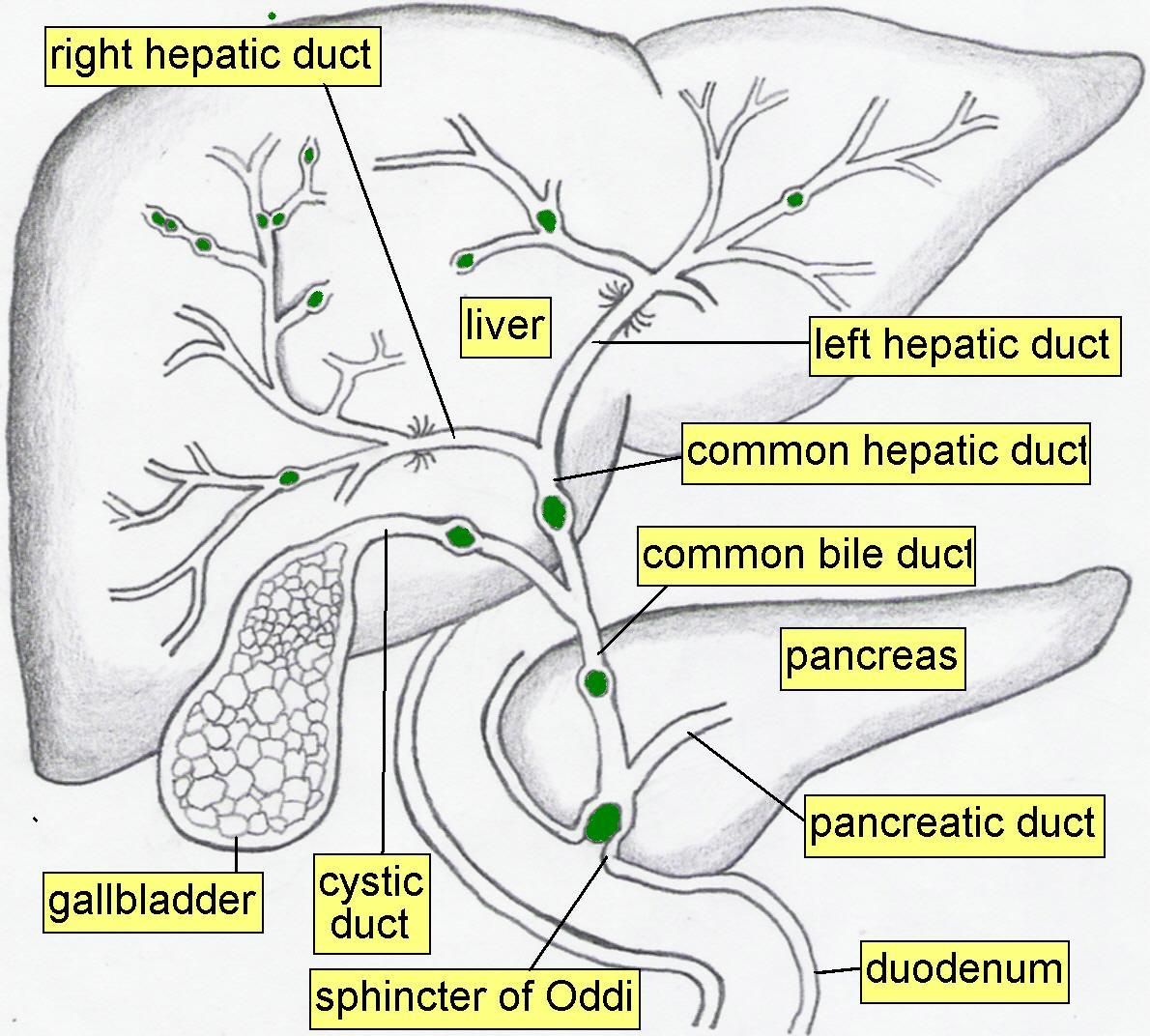
📍 Biliary Anatomy (Ducts and Junctions)
Bile formed in hepatocytes drains through a branching duct network. The extrahepatic ducts then provide a conduit to the duodenum and a pathway into/out of the gallbladder. Functionally, sphincter tone determines whether bile flows into the bowel or is diverted into the gallbladder for storage.
- Intrahepatic bile flow: hepatocytes secrete bile into bile canaliculi → canals of Hering → interlobular ducts → segmental ducts.
- Right + left hepatic ducts: drain bile from each lobe → unite to form the common hepatic duct.
- Cystic duct: connects gallbladder neck to the common hepatic duct; contains spiral folds (valves of Heister) that help keep the lumen patent.
- Common bile duct (CBD): formed by union of common hepatic duct + cystic duct; passes toward the duodenum (clinically important for obstructive jaundice).
- Ampulla of Vater (hepatopancreatic ampulla): junction of CBD and main pancreatic duct before opening into the 2nd part of duodenum.
- Sphincter of Oddi: smooth muscle complex controlling entry of bile and pancreatic juice into duodenum and preventing duodenal reflux.
🧪 Bile: Composition and Why it Matters
Bile is not just “digestive juice”—it is a detergent-like mixture that enables fat absorption, a vehicle for waste excretion, and a regulator of gut microbiota and motility. Its composition determines gallstone risk: when cholesterol exceeds the solubilising capacity of bile salts and phospholipids, crystals can form.
- Bile salts (bile acids): synthesised from cholesterol in the liver (primary bile acids) then modified by gut bacteria (secondary bile acids).
👉 Key role: emulsify fats and form micelles enabling absorption of lipids and fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K). - Phospholipids (e.g., lecithin): stabilise micelles with bile salts and help keep cholesterol soluble.
- Cholesterol: excreted in bile; excess or altered bile salt pool increases gallstone risk.
- Bilirubin: waste product of haem metabolism; conjugated in liver and excreted via bile (gives bile its colour).
- Water & electrolytes: provide fluid medium; duct cells can add bicarbonate-rich fluid (especially with secretin).
⚙️ Physiology: Production, Modification, Storage, Release
1) 🏭 Hepatic bile production (continuous)
- Hepatocytes continuously produce bile: bile acids/bilirubin/cholesterol are secreted into canaliculi.
- Bile acid–dependent flow: the greater the bile acid secretion, the greater the bile flow.
- Enterohepatic circulation: most bile salts are reabsorbed in the terminal ileum and returned via portal blood, providing a “recycling loop” that maintains the bile salt pool.
2) 🧯 Ductal modification (cholangiocytes)
- Cholangiocytes (bile duct epithelial cells) modify bile by secreting bicarbonate-rich fluid and water.
- Secretin strongly stimulates ductal bicarbonate secretion → helps neutralise duodenal acid and optimises pancreatic enzyme function.
3) 🧺 Gallbladder storage and concentration
- Between meals, the sphincter of Oddi is relatively contracted → bile is diverted into the gallbladder.
- The gallbladder mucosa absorbs water and electrolytes → bile becomes concentrated (bile salts and pigments increase relative to water).
- Mucus secretion helps protect the epithelium and lubricate bile flow.
4) ➡️ Bile release (post-prandial)
A fatty meal triggers hormonal and neural signals that coordinate gallbladder contraction with sphincter relaxation—this ensures bile reaches the duodenum precisely when lipids arrive, enabling micelle formation and absorption.
- CCK (cholecystokinin): released from duodenal/jejunal I cells in response to fat and protein.
- ✅ Gallbladder contraction (smooth muscle).
- ✅ Sphincter of Oddi relaxation (facilitates bile entry).
- ✅ Stimulates pancreatic enzyme secretion (paired digestion response).
- Vagus nerve: cephalic and gastric phases provide mild contraction and priming even before nutrients reach duodenum.
- Secretin: enhances biliary bicarbonate-rich secretion, especially with acid in duodenum.
➡️ Summary of Bile Flow
- Production: continuous in liver → intrahepatic ducts → hepatic ducts → common hepatic duct.
- Storage: diverted to gallbladder via cystic duct between meals.
- Release: meal (fat) → CCK + vagal tone → gallbladder contraction + Oddi relaxation → bile into duodenum.
🩸 Blood Supply and Lymphatics
- Arterial: cystic artery (usually from right hepatic artery).
- Venous: cystic veins drain to portal venous system/hepatic sinusoids.
- Lymph: cystic node (of Lund) → hepatic nodes → coeliac nodes (relevant in malignancy spread).
🧠 Nerve Supply (Autonomic)
- Parasympathetic (vagus): promotes gallbladder contraction and bile flow (supports digestive phase).
- Sympathetic: reduces gallbladder contraction and can reduce GI motility; contributes to pain pathways.
- Visceral pain referral: biliary pain often felt in RUQ/epigastrium and may refer to right shoulder/scapula (diaphragmatic irritation via phrenic nerve).
⚠️ Clinical Relevance (High yield)
- 🪨 Cholelithiasis (gallstones): cholesterol or pigment stones form when bile becomes supersaturated, stasis occurs, or nucleation factors increase.
📌 Risk factors: “5 Fs” (classical teaching) + haemolysis (pigment) + rapid weight loss/TPN. - ⏳ Biliary colic: transient cystic duct obstruction → episodic RUQ/epigastric pain often after fatty meal; no systemic inflammation.
- 🔥 Acute cholecystitis: persistent cystic duct obstruction → gallbladder inflammation; Murphy’s sign; fever/leukocytosis; risk of empyema, gangrene, perforation.
- 🚧 Choledocholithiasis: stone in CBD → obstructive jaundice (dark urine, pale stools, pruritus) ± pancreatitis.
- 🦠 Cholangitis: infected obstructed bile duct → Charcot’s triad (fever, jaundice, RUQ pain) ± hypotension/confusion (Reynolds’ pentad) → emergency requiring antibiotics and urgent biliary decompression.
- ⚡ Gallstone pancreatitis: transient obstruction at ampulla triggers pancreatic inflammation; suspect with epigastric pain radiating to back + raised lipase.
- 🎗️ Gallbladder carcinoma: uncommon; associated with chronic inflammation and gallstones in some contexts; often late presentation.
📊 Quick Revision Table
| Structure | Main Function | High-yield Clinical Note |
|---|---|---|
| Gallbladder | Stores & concentrates bile | Stones → biliary colic/cholecystitis |
| Cystic duct | Connects gallbladder to biliary tree | Obstruction → biliary colic; Hartmann’s pouch stones |
| Common hepatic duct | Conveys bile from liver | Obstruction causes jaundice proximal to cystic duct |
| Common bile duct | Delivers bile to duodenum | Choledocholithiasis → jaundice ± pancreatitis |
| Sphincter of Oddi | Controls bile/pancreatic flow; prevents reflux | Obstruction/spasm → biliary pain; infection risk if obstructed |
| Ampulla of Vater | Common entry point to duodenum | Stone here → gallstone pancreatitis |
Categories
- A Level
- About
- Acute Medicine
- Anaesthetics and Critical Care
- Anatomy
- Anatomy and Physiology
- Biochemistry
- Book
- Cardiology
- Collections
- CompSci
- Crib Sheets
- Crib sheets
- Dental
- Dermatology
- Differentials
- Drugs
- ENT
- Education
- Electrocardiogram
- Embryology
- Emergency Medicine
- Endocrinology
- Ethics
- Foundation Doctors
- GCSE
- Gastroenterology
- General Practice
- Genetics
- Geriatric Medicine
- Guidelines
- Gynaecology
- Haematology
- Hepatology
- Immunology
- Infectious Diseases
- Infographic
- Investigations
- Lists
- Mandatory Training
- Medical Students
- Microbiology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Nutrition
- OSCE
- OSCEs
- Obstetrics
- Obstetrics Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Medicine and Dentistry
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatrics
- Palliative
- Pathology
- Pharmacology
- Physiology
- Procedures
- Psychiatry
- Public Health
- Radiology
- Renal
- Respiratory
- Resuscitation
- Revision
- Rheumatology
- Statistics and Research
- Stroke
- Surgery
- Toxicology
- Trauma and Orthopaedics
- USMLE
- Urology
- Vascular Surgery
