| Download the amazing global Makindo app: Android | Apple | |
|---|---|
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: Educational use only. Not for diagnosis or management. See below for full disclaimer. |
Acid maltase deficiency (Pompe disease)
🧬 Pompe disease is a rare lysosomal storage disorder where glycogen builds up inside lysosomes, damaging the 💓 heart, 🧠 muscles, and 🫁 other organs.
📖 About
- ⚖️ Autosomal recessive inheritance.
- 🦴 Classified as both a metabolic myopathy and a lysosomal storage disorder.
- 👶 Often presents in infancy, but 🧑🦳 late-onset forms may manifest in adults.
🔬 Mechanism
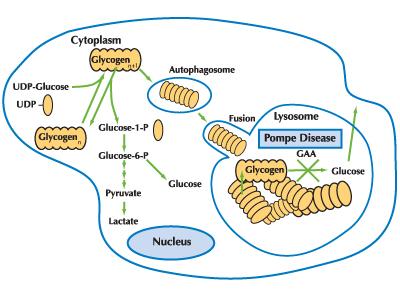
A deficiency in acid alpha-glucosidase (acid maltase) prevents the breakdown of glycogen into glucose. As glycogen accumulates inside lysosomes, cells become swollen and damaged, particularly in skeletal muscle, cardiac tissue, and the liver.
🧾 Aetiology
- 🔑 Caused by mutations in the GAA gene.
- ❌ Deficient acid alpha-1,4-glucosidase → glycogen trapped in lysosomes.
- 🔄 Normally, this enzyme converts glycogen → glucose; without it, toxic build-up occurs.
🩺 Clinical Features
- Infantile-onset: 🍼 Hypotonia (“floppy baby”), bulky muscles, and 👅 macroglossia.
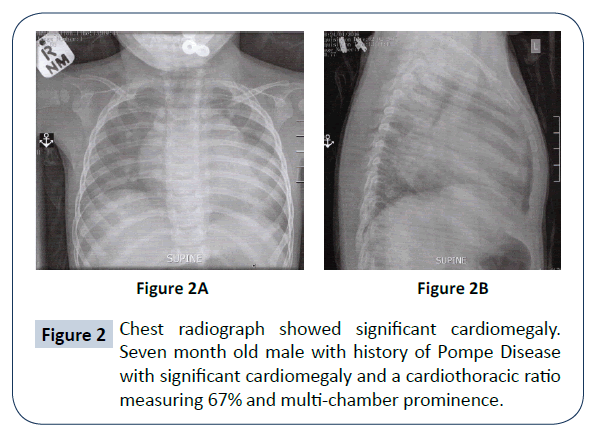
- 💓 Massive cardiomegaly → early congestive heart failure.
- 🫀 Hepatomegaly but notably ❌ no ketosis or hypoglycaemia (unlike other metabolic disorders).
- Late-onset: Progressive muscle weakness and respiratory difficulties, often without cardiomegaly.
🔍 Differential Diagnosis
- Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: Similar progressive weakness, but X-linked and due to dystrophin deficiency.
- Other glycogen storage diseases: e.g., Cori or McArdle disease, which present differently (hypoglycaemia, exercise intolerance).
🧪 Investigations
- 🧾 CK Levels: May be normal or mildly elevated.
- 🖥️ Abdominal Ultrasound: Hepatomegaly.
- 💓 Echocardiography: Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy/cardiomegaly.
- 🧪 LFTs: Raised AST and LDH.
- 🧬 Muscle Biopsy: Glycogen-filled lysosomes, vacuolisation.
- 🔬 Electron Microscopy: Confirms glycogen accumulation.
- 💉 Enzyme assay: Low acid alpha-glucosidase confirms diagnosis.
- 🧬 Genetic testing: Identifies GAA gene mutations, useful for family counselling.
💊 Management
- 🚨 Severe infantile forms → often fatal by 6–24 months if untreated.
- ⏳ Late-onset forms → slower progression, survival into adulthood possible.
- 💉 Enzyme replacement therapy (ERT): Recombinant human alpha-glucosidase improves survival, motor function, and cardiac outcomes.
- 🤝 Supportive care: physiotherapy, respiratory support, and cardiac management remain essential.
Categories
- A Level
- About
- Acute Medicine
- Anaesthetics and Critical Care
- Anatomy
- Anatomy and Physiology
- Biochemistry
- Book
- Cardiology
- Collections
- CompSci
- Crib Sheets
- Crib sheets
- Dental
- Dermatology
- Differentials
- Drugs
- ENT
- Education
- Electrocardiogram
- Embryology
- Emergency Medicine
- Endocrinology
- Ethics
- Foundation Doctors
- GCSE
- Gastroenterology
- General Practice
- Genetics
- Geriatric Medicine
- Guidelines
- Gynaecology
- Haematology
- Hepatology
- Immunology
- Infectious Diseases
- Infographic
- Investigations
- Lists
- Mandatory Training
- Medical Students
- Microbiology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Nutrition
- OSCE
- OSCEs
- Obstetrics
- Obstetrics Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Medicine and Dentistry
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatrics
- Palliative
- Pathology
- Pharmacology
- Physiology
- Procedures
- Psychiatry
- Public Health
- Radiology
- Renal
- Respiratory
- Resuscitation
- Revision
- Rheumatology
- Statistics and Research
- Stroke
- Surgery
- Toxicology
- Trauma and Orthopaedics
- USMLE
- Urology
- Vascular Surgery
