| Download the amazing global Makindo app: Android | Apple | |
|---|---|
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: Educational use only. Not for diagnosis or management. See below for full disclaimer. |
Anatomy and Physiology of Small Bowel
Related Subjects: |Anatomy and Physiology of the Oesophagus |Anatomy and Physiology of the Diaphragm |Anatomy and Physiology of the Large Bowel (Colon, Rectum, Anal Canal) |Anatomy and Physiology of Small Bowel |Anatomy and Physiology of the Biliary system |Anatomy and Physiology of the Bone Marrow |Anatomy and Physiology of the Eye |Anatomy and Physiology of the Pharynx |Anatomy and Physiology of the Larynx |Anatomy and Physiology of the Ear |Anatomy and Physiology of the Nose |Anatomy and Physiology of Male Genitalia |Anatomy and Physiology of the Breast |Anatomy and Physiology of the Stomach |Anatomy and Physiology of the Rectum |Anatomy and Physiology of the Spleen
The small intestine is a long, coiled tube (~6–7 m) extending from the pylorus to the ileocaecal valve. It is the major site of digestion and absorption, designed to maximise surface area, mix chyme with bile/pancreatic enzymes, and move nutrients into blood (portal) and lymph (lacteals). It is divided into duodenum, jejunum, and ileum, each with characteristic anatomy, blood supply, and absorptive specialisation.
📍 Sections of the Small Intestine (Anatomy + What each part does)
- Duodenum (25–30 cm): C-shaped and wrapped around the pancreatic head; mostly retroperitoneal.
- 4 parts: D1 (superior), D2 (descending), D3 (horizontal), D4 (ascending to DJ flexure).
- Receives secretions: bile + pancreatic enzymes enter at the major duodenal papilla via the hepatopancreatic ampulla (of Vater) (regulated by the sphincter of Oddi).
- Key role: neutralises gastric acid and initiates intensive chemical digestion.
- 📌 Clinical: duodenal ulcers; D2 is close to the bile duct/pancreas; D3 crosses anterior to the aorta/IVC (relevant to SMA syndrome anatomy).
- Jejunum (~2–2.5 m): usually upper-left abdomen; thicker wall, larger lumen, prominent folds.
- Macroscopically: “redder” (more vascular), thick mucosa, many plicae circulares.
- Key role: absorbs the majority of macronutrients (carbohydrate, protein, fat) and many micronutrients.
- 🧠 Mnemonic: “J is Juicy” (lots of folds/villi).
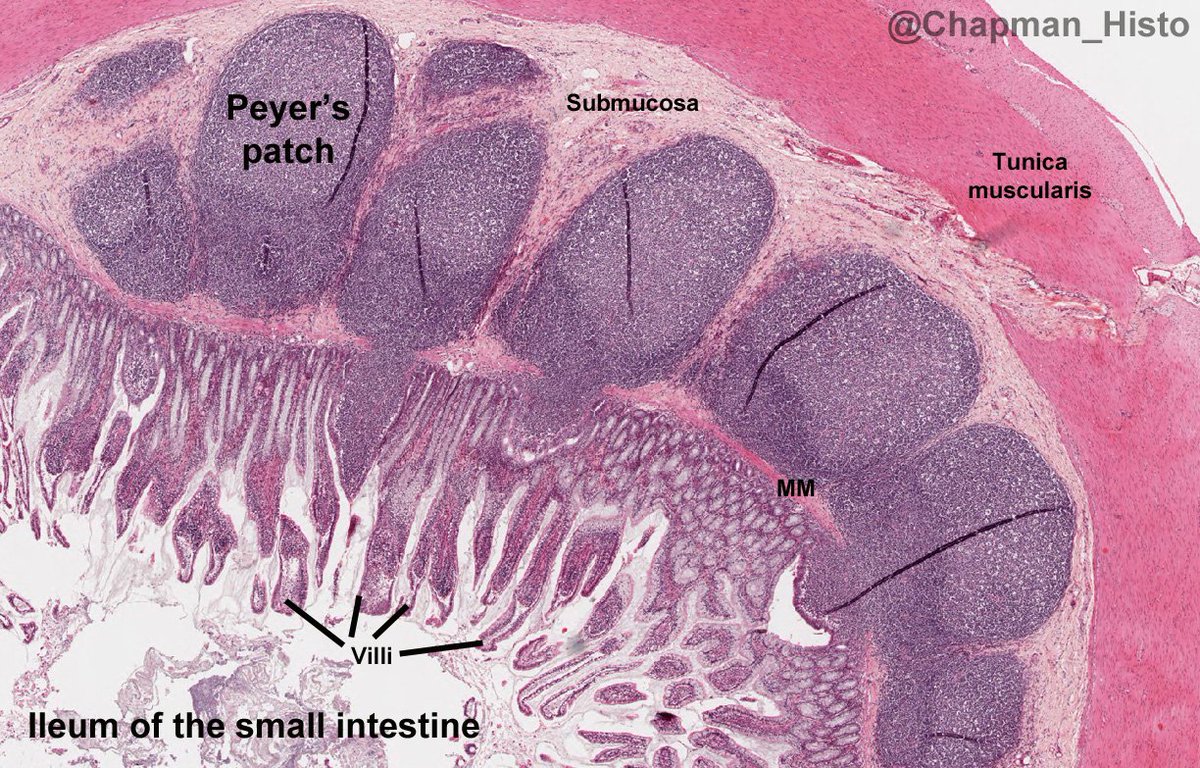
- Ileum (3–4 m): usually lower-right abdomen/pelvis; thinner wall, fewer folds, more immune tissue.
- Peyer’s patches (aggregated lymphoid follicles) are prominent.
- Key role: absorption of vitamin B12 (with intrinsic factor) and bile salts (enterohepatic circulation).
- 📌 Clinical: Crohn’s commonly affects terminal ileum → B12 deficiency, bile salt malabsorption (diarrhoea), gallstones (less bile salt pool).
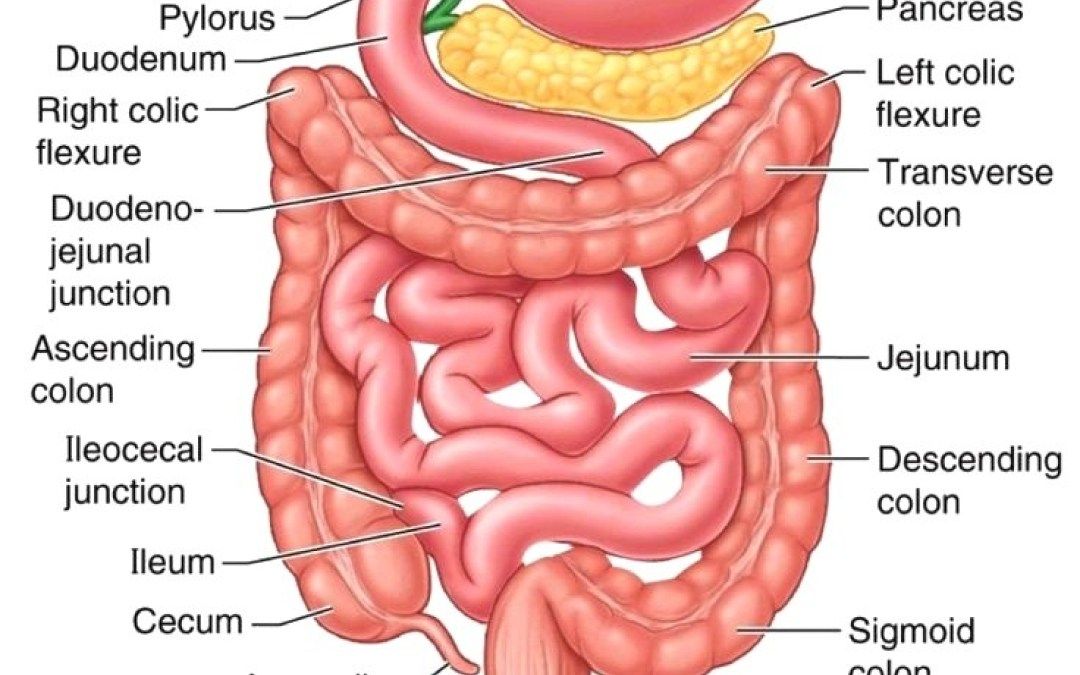
🧭 Jejunum vs Ileum (Quick anatomy clues)
- Jejunum: thicker wall, larger diameter, more plicae, fewer arterial arcades, longer vasa recta.
- Ileum: thinner wall, smaller diameter, fewer plicae, more arcades, shorter vasa recta, Peyer’s patches.
🧱 Layers of the Small Bowel Wall
The small bowel wall is built for absorption and coordinated motility. The mucosa provides massive surface area and specialised transporters; the submucosa houses vessels/plexuses; and the muscular layers generate segmentation and peristalsis under enteric control.
- Mucosa: villi + microvilli (“brush border”) massively increase surface area.
- Enterocytes: absorb nutrients via transporters/enzymes on microvilli.
- Goblet cells: mucus for lubrication and barrier function.
- Enteroendocrine cells: secrete hormones (CCK, secretin, GIP/GLP-1, motilin, etc.).
- Paneth cells (crypts): antimicrobial peptides (innate defence).
- Submucosa: blood vessels, lymphatics, and submucosal (Meissner) plexus.
- Duodenum: contains Brunner’s glands secreting alkaline mucus (protects mucosa and helps neutralise acid).
- Muscularis externa: inner circular + outer longitudinal smooth muscle regulated by myenteric (Auerbach) plexus.
- Serosa: peritoneal covering (except retroperitoneal segments such as most of duodenum).
🔬 Microanatomy & Surface Area (How absorption is maximised)
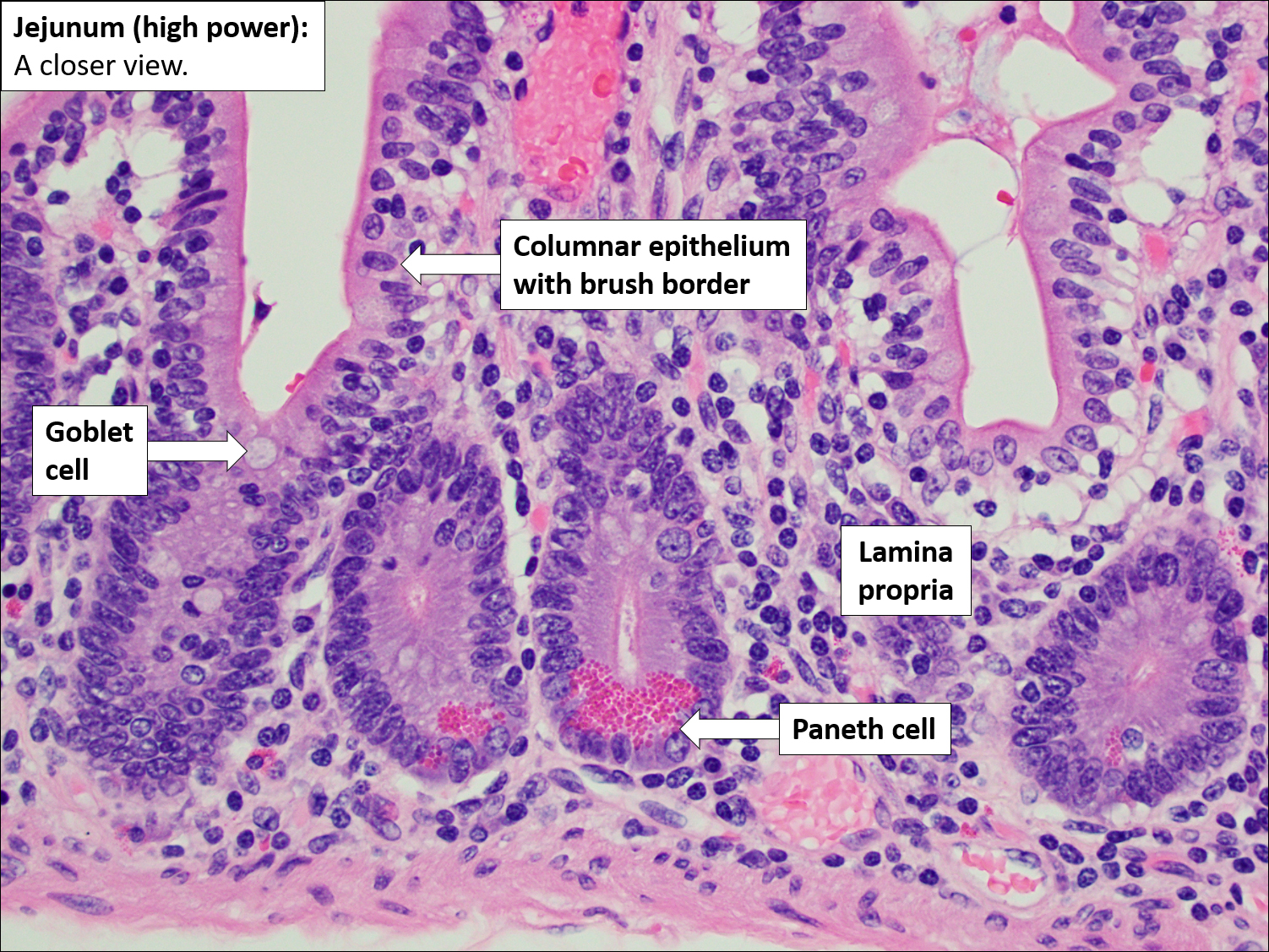
- Plicae circulares: permanent circular folds; most prominent in jejunum → slow transit and increase contact time.
- Villi: finger-like mucosal projections containing capillaries + a central lymphatic lacteal.
- Microvilli: brush border on enterocytes; contain enzymes and transporters for final digestion/uptake.
- Crypts of Lieberkühn: glands between villi; include stem cells for rapid epithelial turnover (important in chemo/radiation injury).
⚙️ Physiology: Digestion, Absorption, Secretion, Hormones, Immunity
Small bowel function is an integrated system: luminal digestion (pancreatic enzymes + bile), brush border “final processing”, transporter-mediated uptake, and coordinated motility to optimise mixing and contact with mucosa. Hormones tune this process to meal composition, while immune structures maintain barrier integrity against pathogens.
🍽️ 1) Digestion (Luminal + Brush Border)
- Neutralisation: gastric acid entering duodenum is buffered by bicarbonate-rich pancreatic secretions and alkaline mucus.
- Carbohydrates: pancreatic amylase → oligosaccharides; brush border disaccharidases (lactase, sucrase, maltase) → monosaccharides.
- Proteins: pancreatic proteases (trypsin, chymotrypsin, elastase) + brush border peptidases → amino acids/dipeptides.
- Fats: bile salts emulsify; pancreatic lipase produces fatty acids + monoglycerides → micelles → enterocytes.
💧 2) Absorption (What is absorbed where?)
Absorption uses specific transporters: some are sodium-coupled, some are facilitated diffusion, and lipids largely use micelle delivery and lymphatic transport. Large volumes of fluid are absorbed daily—most ingested + secreted fluid is reclaimed before reaching colon.
- Carbohydrates:
- Glucose & galactose: absorbed via SGLT1 (Na⁺-dependent cotransport).
- Fructose: absorbed via GLUT5 (facilitated diffusion).
- All exit basolaterally via GLUT2 to portal blood.
- Proteins:
- Amino acids via Na⁺-coupled transporters; di-/tripeptides via PEPT1 (H⁺-coupled) → hydrolysed intracellularly.
- Lipids:
- Micelles deliver fatty acids/monoglycerides to brush border → diffuse into enterocytes.
- Re-esterified to triglycerides → packaged as chylomicrons → enter lacteals → lymph → systemic circulation (thoracic duct).
- Clinical link: lymphatic obstruction or mucosal disease can cause steatorrhoea.
- Vitamins & minerals (classic sites):
- Iron: duodenum/proximal jejunum (heme/non-heme pathways).
- Calcium: duodenum/jejunum (vitamin D dependent).
- Folate: jejunum.
- Vitamin B12: terminal ileum (requires intrinsic factor).
- Bile salts: terminal ileum (reabsorbed to maintain bile salt pool).
- Fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K): absorbed with lipids (affected by cholestasis/pancreatic insufficiency).
- Water: absorbed throughout small bowel by osmosis following solute absorption (Na⁺ is the major driver).
🧴 3) Secretion (Fluid, Mucus, and Electrolytes)
- Crypt secretion: chloride secretion draws water into lumen (helps flush and mix contents).
- Mucus: lubricates and protects epithelium (goblet cells; Brunner’s glands in duodenum).
- Clinical link: secretory diarrhoea can result from increased Cl⁻ secretion (e.g., enterotoxins) overwhelming absorptive capacity.
🧠 4) Enteroendocrine Hormones (Meal → coordinated response)
- CCK: released in response to fats/proteins → stimulates pancreatic enzyme secretion, gallbladder contraction, relaxes sphincter of Oddi; slows gastric emptying.
- Secretin: released in response to acid → stimulates pancreatic bicarbonate and bile duct bicarbonate; protects duodenum.
- GIP/GLP-1: incretins → enhance glucose-dependent insulin secretion; slow gastric emptying (GLP-1).
- Motilin: promotes migrating motor complex (MMC) between meals.
🛡️ 5) Immune Function
- Peyer’s patches in ileum sample antigens via M cells → IgA responses.
- Paneth cells secrete defensins/lysozyme; tight junctions maintain barrier.
- Clinical link: immune dysregulation contributes to IBD; impaired barrier can predispose to infection and inflammation.
🌊 Motility (How chyme is mixed and propelled)
Motility optimises digestion and absorption by mixing chyme with enzymes and repeatedly exposing it to the mucosal surface. The enteric nervous system coordinates local reflexes, while the autonomic nervous system modulates tone and speed.
- Segmentation: rhythmic, non-propulsive contractions → mixing + increased mucosal contact → enhanced absorption.
- Peristalsis: propulsive wave moving chyme distally (“law of the intestine”).
- Migrating motor complex (MMC): fasting “housekeeper” waves sweeping residual material/bacteria distally; reduced by feeding.
🩸 Blood Supply & Lymphatic Drainage
- Arterial supply:
- Duodenum: proximal via celiac trunk (gastroduodenal/superior pancreaticoduodenal); distal via SMA (inferior pancreaticoduodenal).
- Jejunum & ileum: superior mesenteric artery via jejunal/ileal branches forming arterial arcades.
- Venous drainage: SMV → portal vein → liver (first-pass metabolism of absorbed substances).
- Lymphatics: lacteals → mesenteric lymph nodes → cisterna chyli → thoracic duct (key for lipid transport).
🧠 Nerve Supply
- Parasympathetic (vagus): ↑ motility and secretion; enhances coordinated digestion.
- Sympathetic (via mesenteric plexuses): ↓ motility and secretion; vasoconstriction; contracts sphincters (stress slows gut).
- Enteric nervous system: myenteric (Auerbach) plexus drives motility; submucosal (Meissner) regulates secretion and blood flow.
⚠️ Clinical Relevance
- 🌾 Coeliac disease: immune-mediated villous atrophy → malabsorption, diarrhoea, weight loss, anaemia (iron/folate), osteoporosis (Ca/Vit D).
- 🔥 Crohn’s disease: transmural inflammation (often terminal ileum) → strictures, fistulae, malabsorption (B12/bile salts).
- 🦠 SIBO: excess bacteria → bloating, diarrhoea, B12 deficiency; often after surgery, strictures, or motility disorders.
- 🩸 Duodenal ulcers: H. pylori/NSAIDs; can bleed or perforate; duodenum is the commonest small bowel ulcer site.
- ⛔ Ileus: functional obstruction with absent peristalsis (post-op, sepsis, electrolyte disturbance) → distension and vomiting.
- 🚧 Mechanical obstruction: adhesions, hernias, tumours → colicky pain, vomiting, distension; high-pitched tinkling early.
📊 Quick Revision Table
| Section | Typical Length | Key Specialisation | High-yield Clinical Note |
|---|---|---|---|
| Duodenum | 25–30 cm | Neutralisation + enzyme/bile mixing | Ulcers; close to pancreas/bile duct |
| Jejunum | ~2–2.5 m | Maximal absorption (plicae/villi prominent) | Folate absorption; malabsorption if extensive disease |
| Ileum | 3–4 m | Peyer’s patches; B12 + bile salts | Crohn’s; B12 deficiency/bile salt diarrhoea post-resection |
Categories
- A Level
- About
- Acute Medicine
- Anaesthetics and Critical Care
- Anatomy
- Anatomy and Physiology
- Biochemistry
- Book
- Cardiology
- Collections
- CompSci
- Crib Sheets
- Crib sheets
- Dental
- Dermatology
- Differentials
- Drugs
- ENT
- Education
- Electrocardiogram
- Embryology
- Emergency Medicine
- Endocrinology
- Ethics
- Foundation Doctors
- GCSE
- Gastroenterology
- General Practice
- Genetics
- Geriatric Medicine
- Guidelines
- Gynaecology
- Haematology
- Hepatology
- Immunology
- Infectious Diseases
- Infographic
- Investigations
- Lists
- Mandatory Training
- Medical Students
- Microbiology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Nutrition
- OSCE
- OSCEs
- Obstetrics
- Obstetrics Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Medicine and Dentistry
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatrics
- Palliative
- Pathology
- Pharmacology
- Physiology
- Procedures
- Psychiatry
- Public Health
- Radiology
- Renal
- Respiratory
- Resuscitation
- Revision
- Rheumatology
- Statistics and Research
- Stroke
- Surgery
- Toxicology
- Trauma and Orthopaedics
- USMLE
- Urology
- Vascular Surgery
