| Download the amazing global Makindo app: Android | Apple | |
|---|---|
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: Educational use only. Not for diagnosis or management. See below for full disclaimer. |
Anatomy and Physiology of the Eye
|Anatomy and Physiology of the Oesophagus |Anatomy and Physiology of the Diaphragm |Anatomy and Physiology of the Large Bowel (Colon, Rectum, Anal Canal) |Anatomy and Physiology of Small Bowel |Anatomy and Physiology of the Biliary system |Anatomy and Physiology of the Bone Marrow |Anatomy and Physiology of the Eye |Anatomy and Physiology of the Pharynx |Anatomy and Physiology of the Larynx |Anatomy and Physiology of the Ear |Anatomy and Physiology of the Nose |Anatomy and Physiology of Male Genitalia |Anatomy and Physiology of the Breast |Anatomy and Physiology of the Stomach |Anatomy and Physiology of the Rectum |Anatomy and Physiology of the SpleenThe eye is a precision optical instrument coupled to neural tissue. Vision depends on (1) clear media (cornea, aqueous, lens, vitreous), (2) accurate refraction and focus (cornea + lens), (3) healthy retinal phototransduction, and (4) intact optic nerve/visual pathways. Small changes in ocular anatomy (e.g., corneal shape, lens opacity, aqueous outflow resistance) can cause major changes in visual function (blur, glare, field loss, acute pain). This article covers high-yield anatomy, detailed physiology, and clinically important correlations.
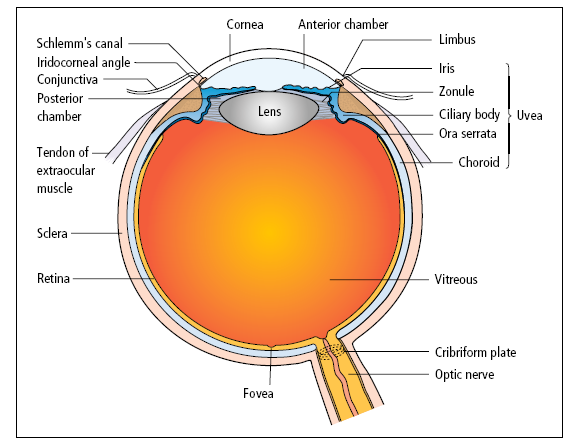
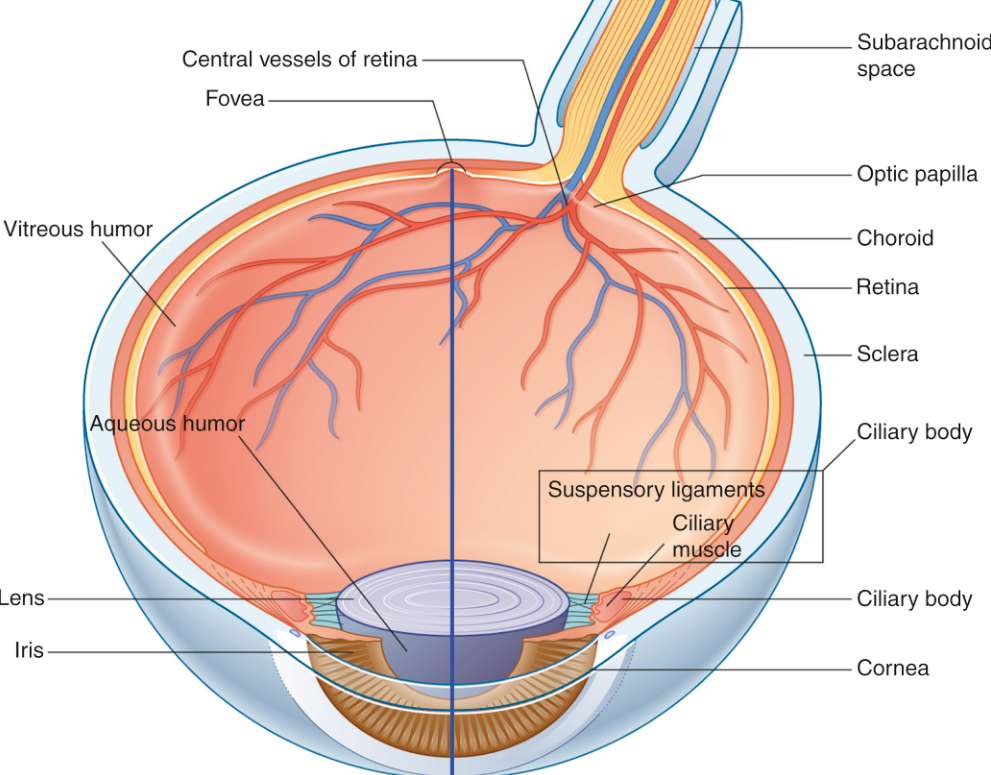
1) Gross Anatomy of the Globe
- Size & shape: approximately 24 mm (adult), nearly spherical; anterior surface more curved (cornea) than sclera.
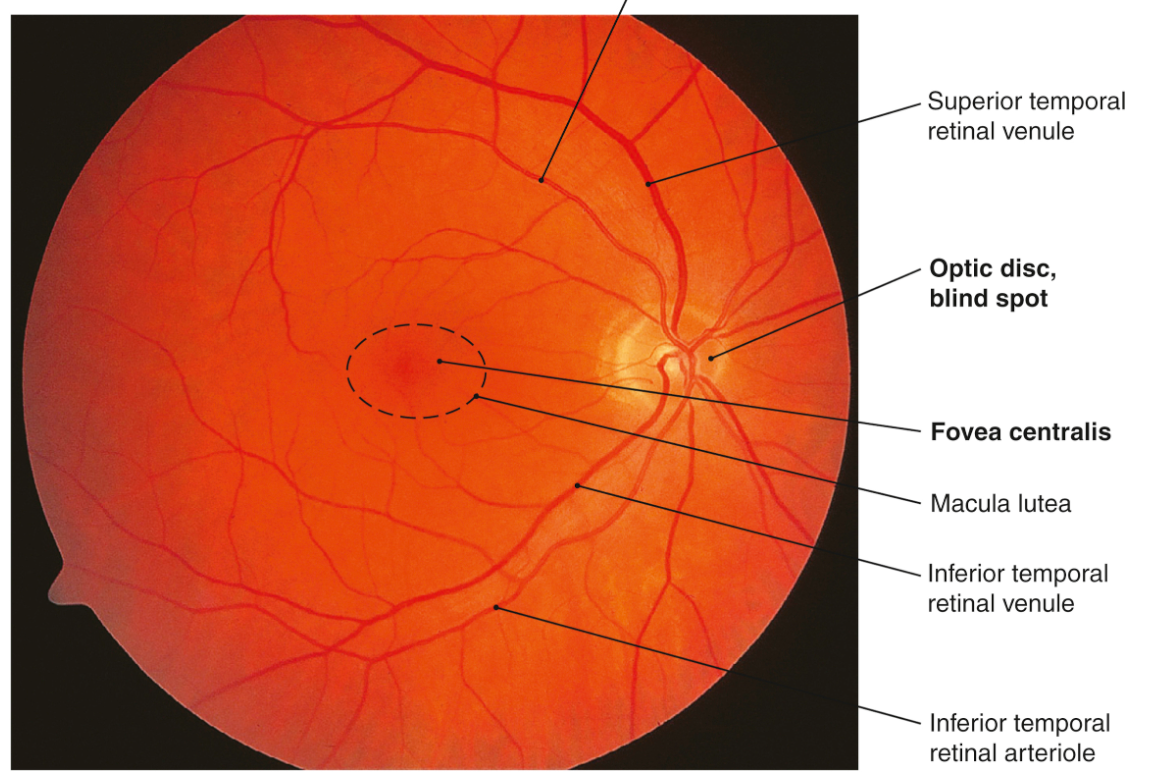
- Optical axis vs visual axis: not identical; slight nasal displacement of fovea explains optic disc position and physiologic blind spot.
- Three coats (“tunics”):
- 🟤 Fibrous tunic: sclera + cornea
- 🩸 Vascular tunic (uvea): iris + ciliary body + choroid
- 📸 Neural tunic: retina
2) Fibrous Tunic: Cornea and Sclera
The cornea provides ~70% of the eye’s refractive power because the air–cornea interface has a large refractive index change. The sclera provides strength and muscle attachment and helps maintain the globe’s shape against intraocular pressure.
- Cornea: transparent and avascular; nourished by tears, aqueous humour, and limbal vessels.
- Layers (high-yield): epithelium → Bowman’s layer → stroma → (Dua’s layer, described in some texts) → Descemet’s membrane → endothelium.
- Endothelium: pumps fluid out of cornea (maintains clarity); endothelial failure → corneal oedema and blurred vision.
- Innervation: very sensitive (CN V1 via long ciliary nerves) → pain with corneal abrasion.
- Sclera: opaque collagen; continuous with cornea at the limbus.
3) Vascular Tunic (Uvea): Iris, Ciliary Body, Choroid
🌈 Iris and Pupil
- Iris function: regulates light entry via pupil size and depth of field (small pupil → better depth of focus but less light).
- Muscles:
- Sphincter pupillae (parasympathetic) → constriction (miosis).
- Dilator pupillae (sympathetic) → dilation (mydriasis).
- Clinical: relative afferent pupillary defect (RAPD) indicates optic nerve/retinal pathology; acute angle closure can present with mid-dilated fixed pupil.
🔄 Ciliary Body and Accommodation
Accommodation is the ability to focus on near objects by increasing lens curvature. The ciliary muscle reduces zonular tension so the elastic lens becomes more convex, increasing refractive power.
- Ciliary processes: produce aqueous humour.
- Ciliary muscle: controls zonules (suspensory ligaments) and lens shape.
- Near vision: ciliary muscle contracts → zonules relax → lens rounds up.
- Distance vision: ciliary muscle relaxes → zonules tighten → lens flattens.
- Clinical: presbyopia = age-related loss of accommodation due to lens stiffening.
❤️ Choroid
- Function: highly vascular layer supplying oxygen/nutrients to outer retina (photoreceptors).
- Clinical: choroidal circulation compromise can affect photoreceptors; posterior ciliary artery disease is linked to AION.
4) The Retina: Neural Architecture and Key Regions
The retina is layered neural tissue that converts light into signals. Photoreceptors synapse onto bipolar cells, which synapse onto ganglion cells whose axons form the optic nerve. The inner retina is supplied by the central retinal artery; the outer retina relies largely on choroidal supply.
- Photoreceptors:
- Rods: high sensitivity (night/scotopic), motion detection, peripheral vision; no colour.
- Cones: high acuity (day/photopic), colour vision, concentrated in fovea.
- Macula & fovea: central vision; fovea has maximal cone density and minimal overlying layers to reduce light scatter.
- Optic disc: exit of optic nerve; no photoreceptors → physiologic blind spot.
Normal Fundus
5) Chambers, Fluids, and Intraocular Pressure (IOP)
Aqueous humour maintains intraocular pressure and provides nutrients to avascular structures (cornea, lens). IOP reflects the balance between aqueous production and outflow; disruption leads to glaucoma and optic nerve damage.
- Anterior chamber: between cornea and iris.
- Posterior chamber: between iris and lens (aqueous is produced here and flows forward through pupil).
- Vitreous chamber: behind lens, filled with vitreous gel (supports retinal apposition).
➡️ Aqueous humour flow
- Production: ciliary processes (active secretion and ultrafiltration).
- Pathway: posterior chamber → through pupil → anterior chamber.
- Outflow (main): trabecular meshwork → Schlemm’s canal → episcleral veins.
- Outflow (secondary): uveoscleral pathway.
- Clinical: increased outflow resistance (often trabecular) → raised IOP; acute angle closure = rapid IOP rise due to angle obstruction.
6) Lens and Refraction
Refraction focuses light onto the retina. The cornea provides most refractive power; the lens fine-tunes focus and accommodation. Refractive errors arise when the eye’s axial length and refractive power are mismatched.
- Lens: biconvex, transparent, avascular; enclosed in capsule; suspended by zonules.
- Transparency: depends on ordered crystallin proteins, low water content, and intact metabolism.
- Cataract: lens opacity → painless progressive visual loss, glare, reduced contrast.
- Refractive errors:
- Myopia: focus in front of retina (long eye/strong optics) → distance blur; corrected with minus lenses.
- Hyperopia: focus behind retina (short eye/weak optics) → near strain; corrected with plus lenses.
- Astigmatism: uneven corneal curvature → distorted focus; corrected with cylindrical lenses.
7) Orbit Anatomy: Walls, Contents, and Extraocular Muscles
The orbit protects the globe and houses the muscles, nerves, vessels, and lacrimal system. Understanding orbital anatomy is crucial in trauma (blow-out fractures), infection spread, and cranial neuropathies.
🏰 Bony orbit (7 bones)
- Roof: frontal
- Floor: maxilla (plus contributions from zygomatic/palatine)
- Lateral wall: zygomatic + sphenoid
- Medial wall: ethmoid + lacrimal + maxilla + sphenoid
- Optic canal: in sphenoid; transmits optic nerve and ophthalmic artery
🎯 Extraocular muscles (EOM) and innervation
- Mnemonic: LR6 SO4 AO3
- Lateral rectus → abduction (CN VI)
- Superior oblique → intorsion + depression (esp in adduction) (CN IV)
- All others (SR, IR, MR, IO) → CN III
- Clinical: CN VI palsy → failure to abduct → horizontal diplopia worse on gaze to affected side.
💧 Lacrimal apparatus
- Lacrimal gland: superolateral orbit → tears.
- Drainage: puncta → canaliculi → lacrimal sac → nasolacrimal duct → inferior meatus (nose).
- Clinical: nasolacrimal obstruction in infants → epiphora; dacryocystitis causes painful swelling at medial canthus.
8) Blood Supply and Venous Drainage 🩸
The eye has a dual circulation: central retinal artery for inner retina and posterior ciliary arteries for choroid/outer retina. Venous drainage communicates with the cavernous sinus, explaining the danger of orbital/facial infections.
🩸 Arterial blood supply
- Main artery: ophthalmic artery (branch of ICA) enters via optic canal.
- Key branches:
- Central retinal artery → inner retina (occlusion → sudden painless visual loss; classically cherry-red spot).
- Posterior ciliary arteries:
- Short posterior ciliary → choroid and optic nerve head contribution.
- Long posterior ciliary → iris/ciliary body region.
- Lacrimal artery → lacrimal gland and orbital structures.
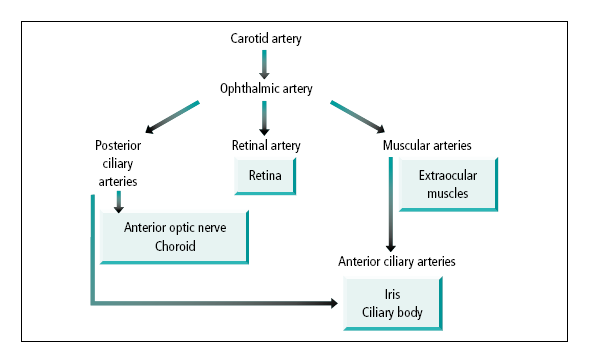
🩸 Venous drainage
- Superior ophthalmic vein → cavernous sinus (communicates with facial vein).
- Inferior ophthalmic vein → cavernous sinus or pterygoid venous plexus.
- Clinical: cavernous sinus thrombosis can present with ophthalmoplegia, chemosis, proptosis, and cranial nerve deficits.
9) Visual Physiology: From Light to Perception
👁️ Introduction
Vision begins when light enters the eye and interacts with specialized cells called photoreceptors in the retina. - 🌙 Rods: ~120 million/eye, highly sensitive to low light, essential for night vision. - 🌞 Cones: ~8 million/eye, function in bright light, responsible for colour vision and high acuity. - 🎯 Cones are densely concentrated in the fovea for sharp central vision.
When light strikes photoreceptors, visual pigments react: rhodopsin in rods, opsins in cones. This triggers 11-cis retinal → all-trans retinal conversion ➡️ activates G-protein cascade ➡️ electrical signal → brain. Slow reconversion (all-trans → 11-cis) explains delayed dark adaptation after bright light exposure.
🔬 Photoreceptor Function & Visual Pigments
- 🌙 Rods:
- Scattered throughout retina, sparse in fovea.
- Night vision; highly light-sensitive but monochrome.
- Pigment: Rhodopsin.
- Lower acuity, slower adaptation vs cones.
- 🌞 Cones:
- Dense in fovea → high-acuity, colour vision.
- Work best in bright light.
- 3 subtypes: red, green, blue opsins.
- Rapid light adaptation compared to rods.
🌗 Light & Dark Adaptation
🔆 Light adaptation: Dark → bright → cones activate, pupils constrict, stabilises within ~3 mins. 🌙 Dark adaptation: Bright → dim → rods need time to regenerate rhodopsin → sensitivity builds over ~30 mins.
➡️ Cones adapt quickly (~10 mins), rods slowly (~30 mins). This is why sudden darkness leaves you “blind” for a while until rods recover.
⚡ Photoreceptor Response at Membrane Level
- In darkness: photoreceptors are depolarised (~ -40 mV) via cGMP-gated Na+/Ca2+ channels → “dark current.” - In light: cGMP ↓, channels close → hyperpolarisation → reduced neurotransmitter release → visual signal sent to brain.
🎨 Bleaching & Regeneration of Pigments
- Bleaching: Light converts 11-cis → all-trans retinal → pigment inactive until regenerated. - Regeneration: All-trans → 11-cis retinal. 🌞 Cones regenerate faster (quick bright-light adaptation). 🌙 Rods regenerate slowly (explains slow dark adaptation).
📝 Clinical Pearls
- Vitamin A deficiency → impaired rhodopsin cycle → night blindness.
- Retinitis pigmentosa → progressive rod loss → tunnel vision, night blindness.
- Age-related macular degeneration → cone dysfunction → central vision loss.
- Exam favourite: Dark adaptation = rods, Light adaptation = cones.
✅ Conclusion
The interplay between rods and cones allows us to function in both dim and bright conditions. - 🌙 Rods = night, low acuity, slow. - 🌞 Cones = day, colour, sharp. Together, they give humans a remarkable visual range across environments.
🧠 Visual pathway (overview)
- Retina → optic nerve → optic chiasm (nasal fibres cross) → optic tract → lateral geniculate nucleus → optic radiations → visual cortex (occipital lobe).
- Clinical: chiasmal lesions (e.g., pituitary mass) → bitemporal hemianopia.
10) Clinical Correlations (High Yield)
- 🔴 CRAO: sudden painless monocular vision loss; emergency; associated with embolic disease.
- ⚡ AION: optic nerve head ischaemia (often posterior ciliary circulation); consider giant cell arteritis in older adults with systemic symptoms.
- 👁️ Glaucoma: optic neuropathy often linked to IOP; open-angle (chronic) vs angle-closure (acute painful red eye).
- 🌫️ Cataract: progressive painless blur + glare; treated surgically with lens replacement.
- 🌀 Retinal detachment: flashes/floaters + curtain of vision loss; urgent ophthalmology.
- 🧩 Blow-out fracture: orbital floor (maxilla) fracture → diplopia (inferior rectus entrapment) and infraorbital numbness.
✅ Summary
The eye’s anatomy is organised into three tunics: fibrous (cornea/sclera), uveal (iris/ciliary body/choroid), and retina. Physiology depends on refraction (cornea + lens), aqueous humour dynamics (IOP balance), and phototransduction (rods/cones → optic nerve → brain). A dual blood supply (central retinal vs posterior ciliary systems) explains classic vascular emergencies such as CRAO and AION.
Categories
- A Level
- About
- Acute Medicine
- Anaesthetics and Critical Care
- Anatomy
- Anatomy and Physiology
- Biochemistry
- Book
- Cardiology
- Collections
- CompSci
- Crib Sheets
- Crib sheets
- Dental
- Dermatology
- Differentials
- Drugs
- ENT
- Education
- Electrocardiogram
- Embryology
- Emergency Medicine
- Endocrinology
- Ethics
- Foundation Doctors
- GCSE
- Gastroenterology
- General Practice
- Genetics
- Geriatric Medicine
- Guidelines
- Gynaecology
- Haematology
- Hepatology
- Immunology
- Infectious Diseases
- Infographic
- Investigations
- Lists
- Mandatory Training
- Medical Students
- Microbiology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Nutrition
- OSCE
- OSCEs
- Obstetrics
- Obstetrics Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Medicine and Dentistry
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatrics
- Palliative
- Pathology
- Pharmacology
- Physiology
- Procedures
- Psychiatry
- Public Health
- Radiology
- Renal
- Respiratory
- Resuscitation
- Revision
- Rheumatology
- Statistics and Research
- Stroke
- Surgery
- Toxicology
- Trauma and Orthopaedics
- USMLE
- Urology
- Vascular Surgery
