| Download the amazing global Makindo app: Android | Apple | |
|---|---|
| MEDICAL DISCLAIMER: Educational use only. Not for diagnosis or management. See below for full disclaimer. |
Acromegaly and Giantism
Related Subjects: |Male Infertility |Prolactin |Prolactinoma |Sheehan's syndrome |Acromegaly and Giantism
🧬 It is important to measure serum IGF-1 to rule out acromegaly ✅ and not rely on random GH levels (which fluctuate and are unreliable).
📖 About
- 👨⚕️ Pituitary tumour (somatotroph adenoma) → usually requires surgery
- 📏 Gigantism: GH excess before epiphyseal fusion (adolescents)
- 🧑 Acromegaly: GH excess in adults, usually 20–40 yrs
🧪 Aetiology
- ⛏️ Pituitary somatotroph adenomas (often ‘acidophil’ macroadenomas)
- 🧬 Sometimes due to G-protein mutations
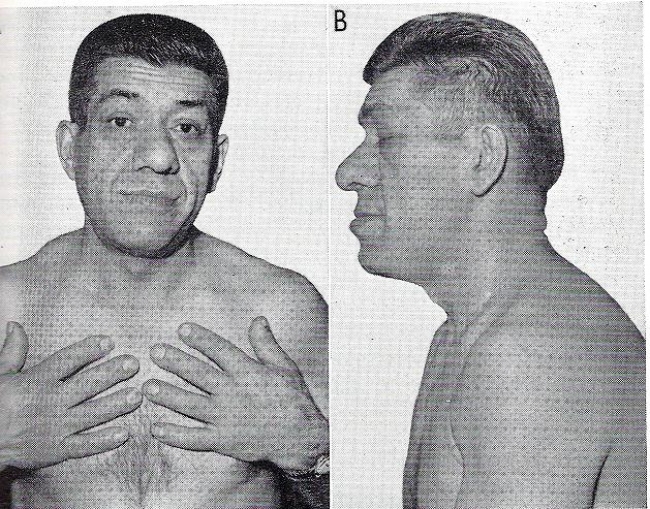
🩺 Clinical Features
- 📈 Hypertension, 💦 sweating, offensive odour
- 👃 Enlarged nose, 🦷 interdental spacing
- 🖐 Spade-like hands, ⛓️ thickened skin, hats/rings don’t fit
- 🦴 Prominent supraorbital ridges, frontal sinus enlargement
- 😬 Prognathism (enlarged jaw)
- 🫀 Organomegaly: liver, heart, tongue, lips, hands/feet (↑ heel pad)
- 🧠 Pituitary tumour mass effect (headache, visual field loss)
- 💉 Hyperglycaemia, T2DM, myopathy
- 💫 Carpal tunnel syndrome
- 📊 Colonic cancer risk ~5% if >50 yrs, >10 yrs disease, ≥3 skin tags
🤝 Associated Conditions
- 😴 Sleep apnoea
- 💉 Type 2 diabetes
- 🦴 Debilitating arthritis
- ✋ Carpal tunnel syndrome
- 💦 Hyperhidrosis
- 📈 Hypertension
🔍 Investigations
- 🧪 Basic bloods: FBC, U&E, LFTs, glucose, HbA1c
- 📈 Screening: ↑ Serum IGF-1 (3–10×) → first test, stable levels, monitor therapy
- ✅ Diagnostic: GH suppression test – 75 g glucose should ↓ GH < 0.4 mcg/L within 1–2h (failure = acromegaly)
- 🧠 Pituitary MRI + gadolinium → macroadenoma in 90%, bony changes (enlarged sella, thickened skull)
- 👁️ Formal perimetry if tumour abuts optic chiasm
- 🔄 Hormone screen: PRL, TFTs, FSH/LH, cortisol, testosterone/estradiol
- 📺 CT brain if MRI contraindicated
- 🔎 Colonoscopy (↑ risk of colonic neoplasia)
- ❤️ BNP, ECG, echocardiogram (exclude cardiomyopathy/heart failure)
🧾 Differential Diagnosis
- GH-secreting pituitary tumour
- Mixed GH/PRL pituitary adenoma
- GH/GHRH-secreting neuroendocrine tumour (e.g., pancreatic islet)
- “Acromegaloidism” in severe insulin resistance
💊 Management
- 🎯 Target: age-normalised IGF-1 + random GH < 1.0 mcg/L
- 🔪 Surgery: Trans-sphenoidal resection = 1st-line (repeatable). Transfrontal only for massive tumours
- ☢️ Radiotherapy: used post-surgery; risks = hypopituitarism, cranial nerve damage, secondary tumours
- 💉 Medical therapy:
- Somatostatin receptor ligands (octreotide, lanreotide) → ↓ GH, shrink tumour (50% cases)
- Dopamine agonist (cabergoline)
- GH receptor antagonist (pegvisomant) → ↓ IGF-1, adjunctive
- Often combined for efficacy + ↓ side effects
- 🧩 Pituitary hormone replacement as needed (thyroxine, hydrocortisone, sex hormones)
- 🔄 Repeat MRI every 3–6 months post-treatment
📚 References
Categories
- A Level
- About
- Acute Medicine
- Anaesthetics and Critical Care
- Anatomy
- Anatomy and Physiology
- Biochemistry
- Book
- Cardiology
- Collections
- CompSci
- Crib Sheets
- Dental
- Dermatology
- Differentials
- Drugs
- ENT
- Education
- Electrocardiogram
- Embryology
- Emergency Medicine
- Endocrinology
- Ethics
- Foundation Doctors
- GCSE
- Gastroenterology
- General Practice
- Genetics
- Geriatric Medicine
- Guidelines
- Gynaecology
- Haematology
- Hepatology
- Immunology
- Infectious Diseases
- Infographic
- Investigations
- Lists
- Mandatory Training
- Medical Students
- Microbiology
- Nephrology
- Neurology
- Neurosurgery
- Nutrition
- OSCE
- OSCEs
- Obstetrics
- Obstetrics Gynaecology
- Oncology
- Ophthalmology
- Oral Medicine and Dentistry
- Orthopaedics
- Paediatrics
- Palliative
- Pathology
- Pharmacology
- Physiology
- Procedures
- Psychiatry
- Public Health
- Radiology
- Renal
- Respiratory
- Resuscitation
- Revision
- Rheumatology
- Statistics and Research
- Stroke
- Surgery
- Toxicology
- Trauma and Orthopaedics
- USMLE
- Urology
- Vascular Surgery
